hypsometric curve → hipsometrijska krivulja
Hypsometric curve (or hypsographic curve) shows the distribution of height of a given area (on land) and depth (at sea). The term originates from the Greek word hypsos meaning height. The part of the curve that reflects the cross section of the ocean bottom is called the bathygraphic curve.
Horizontal dashed lines indicate average height of the continents at 840 meters above sea level, and average depth of the oceans at 3 682.2 meters below sea level. If all the land above sea level (green) was moved into the sea (blue), the oceans would still be 3 km deep.
reverse osmosis → reverzna osmoza
Reverse osmosis is the method used for obtaining freshwater from saltwater. The process uses a semi-permeable membrane through which pure water and not the salts will pass. The saltwater must be pressurised to approximately 25 bar, which makes it operationally expensive to produce large quantities of fresh water by this method.
iodine → jod
Iodine was discovered by Bernard Courtois (France) in 1811. The origin of the name comes from the Greek word iodes meaning violet. It is shiny, black, non-metallic solid with characteristic odour. Sublimes easily and as a gas it is violet and intensely irritating to the eyes, nose and throat. Iodine occurs on land and in the sea in sodium and potassium compounds. Required in small amounts by humans. Once used as an antiseptic, but no longer due to its poisonous nature.
Knudsen’s pipette → Knudsenova pipeta
Kudsen's automatic pipette, developed by the Danish physicist Martin Knudsen (1871-1949), allows quick and accurate transfer of a constant volume of liquid (sea water), usually around 15 mL. On the top of pipette is a double sided C vent that can establish flow between the body of the pipette and one of the branches (A or B), or isolate the body of the pipette from both of the branches. Sucking through the B branch the pipette is filled with liquid, it is closed with a twist of the C valve and the liquid is released by rotating the valve towards the A branch (so atmospheric air can enter the pipette). Emptying the pipette takes around 30 seconds. Before it's first use, the pipette must be calibrated with distilled water.
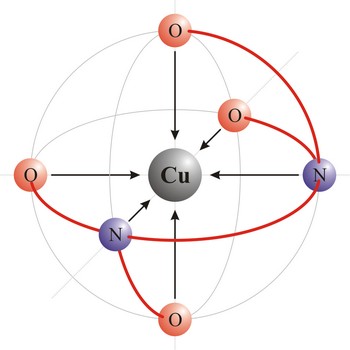
ligand → ligand
Ligand is an ion (F-, Cl-, Br-, I-, S2-, CN-, NCS-, OH-, NH2-) or molecule (NH3, H2O, NO, CO) that donates a pair of electrons to a metal atom or ion in forming a coordination complex. The main way of classifying ligands is by the number of points at which they are attached to, or bound to, the metal center. This is the denticity. Ligands with one potential donor atom are monodentate. Polydentate ligand is a ligand that is attached to a central metal ion by bonds from two or more donor atoms. Ligands with more than one potential donor atom are known as ambidentate, such as the thiocyanate ion, NCS-, which can bind to the metal center with either the nitrogen or sulphur atoms. Chelating ligands are those polydentate ligands which can form a ring including the metal atom.
limestone → vapnenac
Limestone is a sedimentary rock composed primarily of calcium carbonate in the form of the mineral calcite.. Some 10 % to 15 % of all sedimentary rocks are limestones. Limestone is usually organic, but it may also be inorganic. Calcium carbonate may have been directly precipitated from the sea-water or by the lithification of coral reefs, marine organism shells, or marine organism skeletons.
magnesium → magnezij
Magnesium was discovered by Sir Humphry Davy (England) in 1808. The origin of the name comes from the Greek word Magnesia, a district of Thessaly. It is lightweight, malleable, silvery-white metal. Burns in air with a brilliant white flame and reacts with water as temperature elevates. Can ignite in air. React violently with oxidants. Magnesium is found in large deposits in the form of magnesite, dolomite and other minerals. It is usually obtained by electrolysis of melted magnesium chloride (MgCl2) derived from brines, wells and sea water. Used in alloys to make airplanes, missiles and other uses for light metals. Have structural properties similar to aluminium.
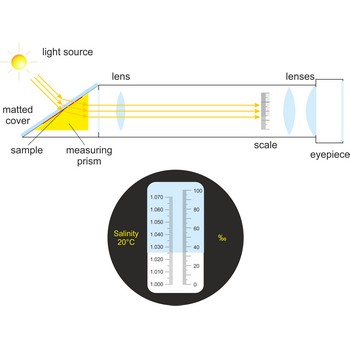
refractometer → refraktometar
Refractometer is an optical device used from measurement of refractive index. A refractometer takes advantage of the fact that light bends as it passes through different materials. It can be used to measure the salinity of water or the amount of sugar in fresh grapes. Refractometers are available with or without automatic temperature compensation (ATC).
When using a conventional saltwater refractometer, a sample is placed on an optical prism in the sample window. As light shines through the sample, it is bent according to the salinity of the water, and casts a shadow on the scale that is visible through the eyepiece. Salinity is read directly through the eyepiece.
salinity → salinitet
Salinity (S) is a measure of the quantity of dissolved salts in seawater. It is formally defined as the total amount of dissolved solids in seawater in parts per thousand (‰) by weight when all the carbonate has been converted to oxide, the bromide and iodide to chloride, and all organic matter is completely oxidized.
Chlorinity is the oldest of the salinity measures considered and is still a corner-stone in the study of dissolved material in seawater. Based on the principle of constant relative proportions it provides a measure of the total amount of dissolved material in seawater in terms of the concentration of halides. The relationship between chlorinity (Cl) and salinity as set forth in Knudsen’s tables is
In 1962, however, a better expression for the relationship between total dissolved salts and chlorinity was found to be
Practical Salinity (SP) was introduced as a replacement for Chlorinity. Practical Salinity is is relatively easy to measure using standard conductometers, measurements are more precise and less time consuming than measurements of Chlorinity and accurate measurements can even be made in situ. Practical salinity SP is defined on the Practical Salinity Scale of 1978 (PSS-78) in terms of the conductivity ratio K15 which is the electrical conductivity of the sample at temperature t68 = 15 °C and pressure equal to one standard atmosphere, divided by the conductivity of a standard potassium chloride (KCl) solution at the same temperature and pressure. The mass fraction of KCl in the standard solution is 0.0324356 (32.4356 g of KCl in 1 kg of solution).
Note that Practical Salinity is a unit-less quantity. Though sometimes convenient, it is technically incorrect to quote Practical Salinity in "psu". For most purposes one can assume that the psu and the ‰, are synonymous.
The global average salinity of ocean waters is about 35 ‰, that is, about 35 g of solid substances are dissolved in 1 kg of seawater.
Citing this page:
Generalic, Eni. "Morska milja." Croatian-English Chemistry Dictionary & Glossary. 29 June 2022. KTF-Split. {Date of access}. <https://glossary.periodni.com>.
Glossary
Periodic Table