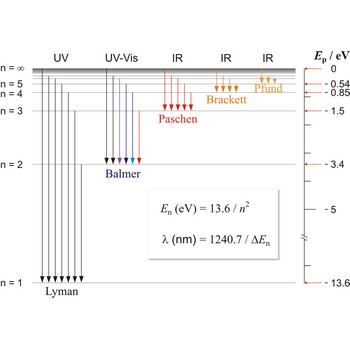
Paschen series → Paschenova serija
Paschen series are the series of lines in the spectrum of the hydrogen atom which corresponds to transitions between the state with principal quantum number n = 3 and successive higher states.
Petri dish → Petrijeva zdjelica
Petri dish is a shallow glass or plastic flat bottomed dish with a lid. Used primarily in laboratories for the culture of bacteria and other microorganisms on specially prepared media. It was named after the German bacteriologist Julius Richard Petri (1852-1921) who invented it in 1877.
photochemical reaction → fotokemijska reakcija
Photochemical reactions are those reactions which are conducted under the influence of light that is under the influence of ultraviolet, visible and infrared part of the light spectrum. Some systems can be influenced only by radiation that is absorbed by that system. Photochemical reactions are for example photosynthesis, creation of photography, generation of phosgene, creation of hydrochloride etc.
photomultiplier → fotomultiplikator
Photomultiplier (photomultiplier tube or PMT) is a very versatile and sensitive detector of radiant energy in the ultraviolet, visible, and near infrared regions of the electromagnetic spectrum. A typical photomultiplier tube consists of a photoemissive cathode (photocathode) followed by focusing electrodes, an electron multiplier (dynode) and an electron collector (anode) in a vacuum tube.
picnometer → piknometar
Picnometer is a special glass flask which is used for determining a relative density of liquids using the weight of a known volume. It usually has a glass faceted cork which is pierced in the centre like a thin capillary through which surplus of liquid runs out.
platinum → platina
Platinum was discovered by Antonio de Ulloa (South America) in 1735. The origin of the name comes from the Spanish word platina meaning silver. It is rare, very heavy, soft, silvery-white metal. Resists oxygen and water. Platinum is produced from deposits of native, or elemental. Used in jewellery, to make crucible and special containers and as a catalyst. Used with cobalt to produce very strong magnets. Also to make standard weights and measures. Resists corrosion and acid attacks except aqua regia.
potassium → kalij
Potassium was discovered by Sir Humphry Davy (England) in 1807. The origin of the name comes from the Arabic word qali meaning alkali (the origin of the symbol K comes from the Latin word kalium). It is soft, waxy, silver-white metal. Fresh surface has silvery sheen. Quickly forms dull oxide coating on exposure to air. Reacts strongly with water. Reacts with water to give off flammable gas. Reacts violently with oxidants. Occurs only in compounds. Potassium is found in minerals like carnallite [(KMgCl3)·6H2O] and sylvite (KCL). Pure metal is produced by the reaction of hot potassium chloride and sodium vapours in a special retort. Used as potash in making glass and soap. Also as saltpetre, potassium nitrate (KNO3) to make explosives and to colour fireworks in mauve. Vital to function of nerve and muscle tissues.
proton → proton
Proton is a stable elementary particle of unit positive charge and spin 1/2. Protons and neutrons, which are collectively called nucleons, are the constituents of the nucleus.
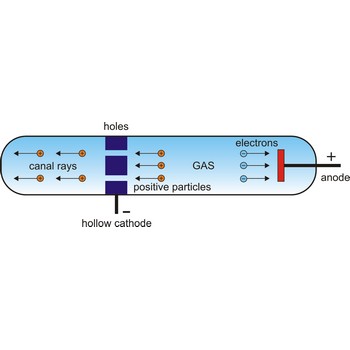
In 1886, German physicist Eugene Goldstein (1850-1930) discovered positive particles by using a modified Crookes tube with holes in the cathode in an evacuated tube. When cathode rays were given off in one direction toward the anode, other rays found their way through the holes in the cathode and sped off in the opposite direction. Since these other rays traveled in the direction opposite to the negatively charged cathode rays, it seemed that they must be composed of positively charged particles. Rutherford suggested that this fundamental positive particle be called the proton.
relative density → relativna gustoća
Relative density (d) is the ratio of the density of a substance to the density of some reference substance. For liquids or solids it is the ratio of the density (usually at 20 °C) to the density of water at 4 °C. Since one must specify the temperature of both the sample and the water to have a precisely defined quantity, the use of this term is now discouraged. This quantity was formerly called specific gravity.
resistivity → električna otpornost
Electrical resistivity, or specific resistance (ρ) is the electric field strength divided by the current density when there is no electromotive force in the conductor. Resistivity is an intrinsic property of a material. Materials with low resistivity are good conductors of electricity and materials with high resistivity are good insulators.
For a conductor of uniform cross section with area A and length L, and whose resistance is R, the resistivity is given by
The SI unit is Ω m.
Citing this page:
Generalic, Eni. "Mil-spec." Croatian-English Chemistry Dictionary & Glossary. 29 June 2022. KTF-Split. {Date of access}. <https://glossary.periodni.com>.
Glossary
Periodic Table