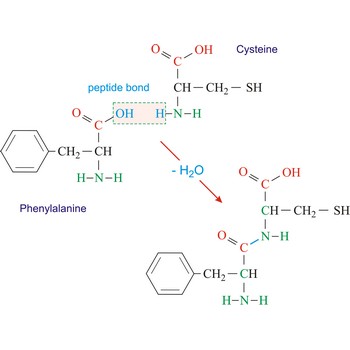
peptide bond → peptidna veza
Peptide bond emerges when two amino acid join in a way that the carbon atom from one connects with the nitrogen atom from the other (creating a C-N bond).
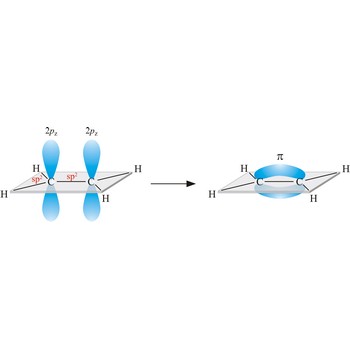
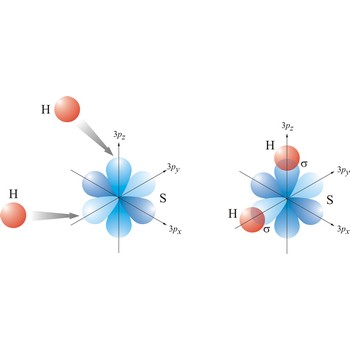
sigma bond → sigma veza
Most single bonds are sigma bonds (σ-bond). In the valence bond theory, a sigma bond is a valence bond that is symmetrical around the imaginary line between the bonded atoms.
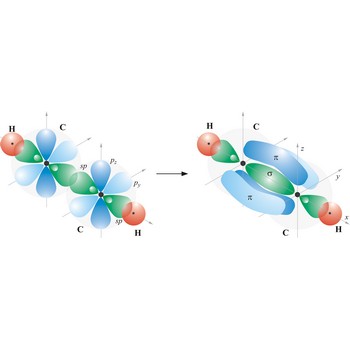
triple bond → trostruka veza
Triple bond. (≡) is a covalent bond that involves 3 bonding pairs. In the valence bond theory, one of the bonds in a triple bond is a sigma bond and the other two are pi bonds. For example, the central bond in acetylene is a triple bond: H-C≡C-H.
metal hydride → metalni hidrid
Metal hydrides are compounds formed of atoms of a metal combined with atoms of hydrogen in which hydrogen has an oxidation number -1.
valence bond theory → teorija valentne veze
Valence bond theory is a theory that explains the shapes of molecules in terms of overlaps between half-filled atomic orbitals, or half filled hybridised orbitals.
metallic glass → metalno staklo
Certain alloys can solidify by extremely rapid cooling out of melt without formation of a crystal lattice, that is in the amorphous form - such, amorphous alloys are so called metallic glasses. The alloy of zirconium, beryllium, titanium, copper, and nickel is one of the first metallic glasses that can be made in bulk and formed into strong, hard, useful objects.
Unlike pure metals and most metal alloys, metallic glasses have no regular crystalline structure. This lack of long range order or microstructure is related to such desirable features as strength and low damping which is one reason why the premier use for zirconium-based metallic glass is in the manufacture of expensive golf club heads. Metallic glasses can be quite strong yet highly elastic, and they can also be quite tough (resistant to fracture). Even more interesting are the thermal properties; for instance, just like an oxide glass, there is a temperature (called the glass transition temperature) above which a metallic glass becomes quite soft and flows easily. This means that there are lots of opportunities for easily forming metallic glasses into complex shapes.
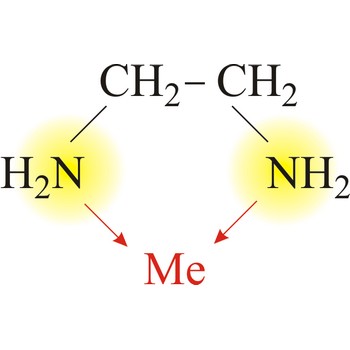
bidentate ligand → bidentatni ligand
Bidentate ligand is a ligand that has two "teeth" or atoms that coordinate directly to the central atom in a complex. An example of a bidentate ligand is ethylenediamine. A single molecule of ethylenediamine can form two bonds to a metal ion. The bonds form between the metal ion and the nitrogen atoms of ethylenediamine.
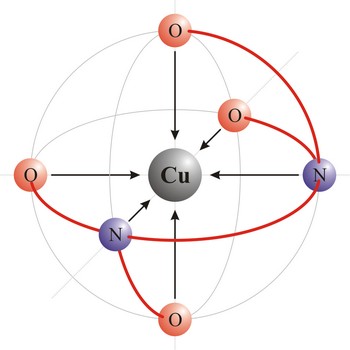
chelate → kelat
Chelate is a compound characterized by the presence of bonds from two or more bonding sites within the same ligand to a central metal atom. For example, copper complexes with EDTA to form a chelate. Chelate complexes are more stable than complexes with the corresponding monodentate ligands.
Citing this page:
Generalic, Eni. "Metalna veza." Croatian-English Chemistry Dictionary & Glossary. 29 June 2022. KTF-Split. {Date of access}. <https://glossary.periodni.com>.
Glossary
Periodic Table