radium → radij
Radium was discovered by Marie and Pierre Curie (France) in 1898. The origin of the name comes from the Latin word radius meaning ray. It is silvery-white radioactive metal. Reacts with oxygen and water. Highly radiotoxic. Carcinogen by inhalation, ingestion, or exposure. Radium is found in uranium ores at 1 part per 3 million parts uranium. Used in treating cancer because of the gamma rays it gives off.
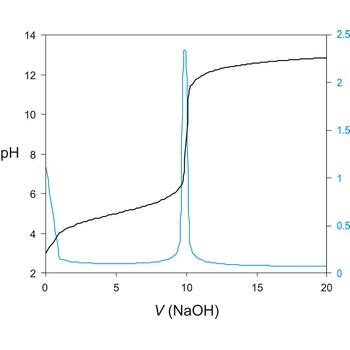
titration curve → titracijska krivulja
Titration curve is a graphic representation of the amount of a species present vs. volume of solution added during a titration. A titration curve has a characteristic sigmoid curve. The inflection point in the titration curve marks the end-point of the titration. Blue line is the first derivative of the titration curve.
uranium → uranij
Uranium was discovered by Martin Heinrich Klaproth (Germany) in 1789. Named after the planet Uranus. It is silvery-white, dense, ductile, malleable, radioactive metal. Resists alkalis; tarnishes in air; attacked by steam and acids. Radiotoxic. Uranium occurs in many rocks, but in large amounts only in such minerals as pitchblende and carnotite. For many centuries it was used as a pigment for glass. Now it is used as a fuel in nuclear reactors and in bombs.
solar cell → sunčeva ćelija
Solar cell, or photovoltaic cell, is a device that captures sunlight and transforms it directly to electricity. All solar cells make use of photovoltaic effect, so often they are called photovoltaic cells. Almost all solar cells are built from solid-state semiconducting materials, and in the vast majority of these the semiconductor is silicon.
The photovoltaic effect involves the generation of mobile charge carriers-electrons and positively charged holes-by the absorption of a photon of light. This pair of charge carriers is produced when an electron in the highest filled electronic band of a semiconductor (the valence band) absorbs a photon of sufficient energy to promote it into the empty energy band (the conduction band). The excitation process can be induced only by a photon with an energy corresponding to the width of the energy gap that separates the valence and the conduction band. The creation of an electron-hole pair can be converted into the generation of an electrical current in a semiconductor junction device, wherein a layer of semiconducting material lies back to back with a layer of either a different semiconductor or a metal. In most photovoltaic cells, the junction is p-n junction, in which p-doped and n-doped semiconductors are married together. At the interface of the two, the predominance of positively charged carriers (holes) in the p-doped material and of negatively charged carriers (electrons) in the n-doped material sets up an electric field, which falls off to either side of the junction across a space-charge region. When absorption of a photon in this region generates an electron-hole pair, these charge carriers are driven in opposite directions by the electric field, i.e. away from the interface and toward the top and bottom of the two-layer structure, where metal electrodes on these faces collect the current. The electrode on the top layer (through which light is absorbed) is divided into strips so as not to obscure the semiconducting layers below. In most widely used commercial solar cells, the p-doped and n-doped semiconductive layers are formed within a monolithic piece of crystalline silicon. Silicon is able to absorb sunlight at those wavelengths at which it is most intense-from the near-infrared region (wavelengths of around 1200 nm) to the violet (around 350 nm).
volumetric flask → odmjerna tikvica
Volumetric flasks are bottles made of glass, in a pear like in shape with long thin necks and flat bottoms. All come with a ground glass stopper for a tight seal. Volume marking is cut in glass with fluoride acid around the neck, so that parallax should be avoided (flask is put in front of the eyes so that one can see only a straight horizontal line). A volumetric flask is calibrated to contain (TC or In) the indicated volume of water at 20 °C when the bottom of the meniscus is adjusted to just rest on the center of the line marked on the neck of the flask. They are used for preparing the exactly known volume of sample solution and standard solutions of reagents. On each flask with volume designation a temperature on which the flask has been calibrated is designated.
volumetric pipette → prijenosna pipeta
Volumetric pipettes (transfer or belly pipette) are used in volumetric analysis, when there is a need for taking exact smaller volume of a sample solution or reagent. The upper tube of volumetric pipette has a ringlike marking (mark) which marks its calibrated volume. Pipettes calibrated to deliver (TD or Ex) the indicated volume. By sucking in (with mouth, propipette or a water pump) the liquid is pulled in a little bit above the mark and the opening of the pipet is closed with a forefingertip. Outer wall of pipet is wiped and, with a slight forefinger loosening, the liquid is released until it reaches the mark. Mark must figure as a tangent on a lower edge of the liquid meniscus. A pipette is emptied out by lifting the forefinger off and letting the liquid flow out of the pipette freely. After another 15 s and the tip of the pipette is pulled onto the inner wall of the vessel. It is absolutely forbidden to blow out the contents of the pipette.
ytterbium → iterbij
Ytterbium was discovered by Jean de Marignac (France) in 1878. Named after Ytterby, a village in Sweden. It is silvery, lustrous, malleable and ductile metal. Oxidizes slowly in air. Reacts with water. Flammable dust. Ytterbium is found in minerals such as yttria, monazite, gadolinite and xenotime. Used in metallurgical and chemical experiments.
zinc → cink
Zinc was discovered by Andreas Marggraf (Germany) in 1746. The origin of the name comes from the German word zink. It is bluish-silver, ductile metal. Reacts with alkalis and acids. Tarnishes in air. Zinc is found in the minerals zinc blende (sphalerite) (ZnS), calamine, franklinite, smithsonite (ZnCO3), willemite and zincite (ZnO). Used to coat other metal (galvanizing) to protect them from rusting. Although some 90 % of the zinc is used for galvanizing steel. Zinc metal is used in the common dry-cell battery. Also used in alloys such as brass, bronze. Zinc compounds are also used in the manufacture of paints, cosmetics, plastics, electronic devices, and other products.
zirconium → cirkonij
Zirconium was discovered by Martin Heinrich Klaproth (Germany) in 1789. The origin of the name comes from the Arabic word zargun meaning gold colour. It is grey-white, lustrous, corrosion-resistant metal. Exposed surfaces form oxide protective film. Zirconium is found in many minerals such as zircon and baddeleyite. Used in alloys such as zircaloy this is used in nuclear applications since it does not readily absorb neutrons. Also baddeleyite is used in lab crucibles. Used in high-performance pumps and valves. Clear zircon (ZrSiO4) is a popular gemstone.
Citing this page:
Generalic, Eni. "Marl." Croatian-English Chemistry Dictionary & Glossary. 29 June 2022. KTF-Split. {Date of access}. <https://glossary.periodni.com>.
Glossary
Periodic Table