superfluid helium → superfluidni helij
Superfluidity in helium-4 was discovered in 1938 by the Soviet physicist Pyotr Leonidovich Kapitsa. Helium-4 exhibits superfluidity when it is cooled below 2.18 K (-270.97 C), which is called the lambda (λ) point. At these temperatures, helium-4 exhibits the characteristics of two distinct fluids, one of which appears to flow without friction. An extensive series of experiments showed that in this state of helium, called helium II (He II), there is an apparent enormous rise in heat conductivity, at an increase rate of about three million. Another unusual property of He II is its mobile, rapid flow through capillaries or over the rim of its containment vessel as a thin film that exhibits no measurable viscosity and appears unaffected by the forces of gravity or evaporation and condensation.
thermosphere → termosfera
Thermosphere is the layer of the earth’s atmosphere extending from the top of the mesosphere (80 km - 90 km above the surface) to about 500 km. It is characterised by a rapid increase in temperature with increasing altitude up to about 200 km, followed by a levelling off in the 300 km - 500 km region.
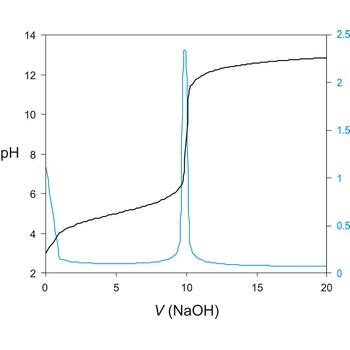
titration curve → titracijska krivulja
Titration curve is a graphic representation of the amount of a species present vs. volume of solution added during a titration. A titration curve has a characteristic sigmoid curve. The inflection point in the titration curve marks the end-point of the titration. Blue line is the first derivative of the titration curve.
transition metal → prijelazni element
This group of metals is distinguished from other metals not by their physical properties, but by their electronic structure. Transition metals are elements characterized by a partially filled d subshell. The First Transition Series comprises scandium (Sc), titanium (Ti), vanadium (V), chromium (Cr), manganese (Mn), iron (Fe), cobalt (Co), nickel (Ni) and copper (Cu). The Second and Third Transition Series include the lanthanides and actinides, respectively.
The transition metals are noted for their variability in oxidation state. Thus, manganese has two electrons in its outside shell and five electrons in the next shell down, and exhibits oxidation states of +1, +2, +3, +4, +5, +6, and +7.
They are also characterised by the fact that well into the series, going from left to right, the properties of the succeeding metals do not differ greatly from the preceding ones.
troposphere → troposfera
Troposphere is the lowest part of the earth’s atmosphere, extending to 10 km to 15 km above the surface. It is characterized by a decrease in temperature with increasing altitude. The exact height varies with latitude and season.
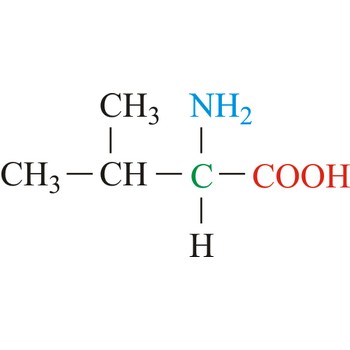
valine → valin
Valine is hydrophobic amino acids with aliphatic side chain. It is a member of the branched-chain amino acid family, along with leucine and isoleucine. Valine differs from threonine by replacement of the hydroxyl group with a methyl substituent, but they are of roughly the same shape and volume. The nonpolar hydrophobic amino acids tend to cluster together within proteins, stabilizing protein structure by means of hydrophobic interactions. Valine is an essential amino acid, which means that it cannot be synthesized in the body and must be obtained through dietary sources.
- Abbreviations: Val, V
- IUPAC name: 2-amino-3-methylbutanoic acid
- Molecular formula: C5H11NO2
- Molecular weight: 117.15 g/mol
van der Waals’ equation → van der Waalsova jednadžba
Van der Waals’ equation is an equation of state for real fluids which takes the form:
where p is pressure, Vm is molar volume, T is temperature, R is the molar gas constant, and a and b are characteristic parameters of the substance which describe the effect of attractive and repulsive intermolecular forces.
Citing this page:
Generalic, Eni. "Manhwa disciple of three kings characters." Croatian-English Chemistry Dictionary & Glossary. 29 June 2022. KTF-Split. {Date of access}. <https://glossary.periodni.com>.
Glossary
Periodic Table