photoelectric threshold → fotoelektrični prag
Photoelectric threshold is a maximum length of electromagnetic wave which can still cause the photoelectric effect.
threonine → treonin
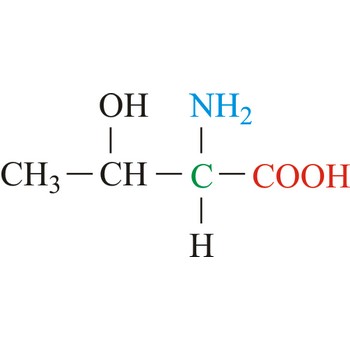
Threonine is neutral amino acids with polar side chains. It differs from serine by having a methyl substituent in place of one of the hydrogens on the β carbon. Threonine is a site of phosphorylation and glycosylation which is important for enzyme regulation and cell signaling. It is an essential amino acid, which means that humans cannot synthesize it, so it must be ingested.
- Abbreviations: Thr, T
- IUPAC name: 2-amino-3-hydroxybutanoic acid
- Molecular formula: C4H9NO3
- Molecular weight: 119.12 g/mol
aldehydes → aldehidi
Aldehydes are a broad class of organic compounds having the generic formula RCHO, and characterized by an unsaturated carbonyl group (C=O). They are formed from alcohols by either dehydrogenation or oxidation. Their chemical derivation is indicated by the name al(cohol) + dehyd(rogenation). An example of these distinct aromatic compounds is formaldehyde.
Arrhenius equation → Arheniusova jednadžba
In 1889, Svante Arrhenius explained the variation of rate constants with temperature for several elementary reactions using the relationship
where the rate constant k is the total frequency of collisions between reaction molecules A times the fraction of collisions exp(-Ea/RT) that have an energy that exceeds a threshold activation energy Ea at a temperature of T (in kelvin). R is the universal gas constant.
aspartic acid → asparaginska kiselina
Aspartic acid is an electrically charged amino acids with acidic side chains. As a group the charged amino acids are relatively abundant and are generally located on the surface of the protein. Aspartic acid and glutamic acid play important roles as general acids in enzyme active centers, as well as in maintaining the solubility and ionic character of proteins. Aspartic acid (sometimes referred to as asparate depending on pH) is non-essential in mammals, being produced from oxaloacetate by transamination.
- Abbreviations: Asp, D
- IUPAC name: 2-aminobutanedioic acid
- Molecular formula: C4H7NO4
- Molecular weight: 133.10 g/mol
atomic absorption spectroscopy → atomska apsorpcijska spektroskopija
Atomic absorption spectroscopy (AAS) An analytical technique in which a sample is vapourised and the nonexcited atoms absorb electromagnetic radiation at characteristic wavelengths.
atomic number → atomski broj
Atomic number (Z) is a characteristic property of an element, equal to the number of protons in the nucleus. The atomic number and the element symbol are two alternate ways to label an element. In nuclide symbols, the atomic number is a leading subscript; for example, in 2He.
atomic spectroscopy → atomska spektroskopija
Atomic spectroscopy is an expensive analytical method which uses absorption (AAS), emission (AES) and fluorescent (AFS) characteristics of the analyte.
carbon fibre → ugljično vlakno
Carbon fibres are threadlike strands of pure carbon that are strong and flexible. Carbon fibres can be bound in a plastic resin matrix to form a strong composite. It is light-weight and stronger than steel.
Citing this page:
Generalic, Eni. "Manhwa disciple of three kings characters." Croatian-English Chemistry Dictionary & Glossary. 29 June 2022. KTF-Split. {Date of access}. <https://glossary.periodni.com>.
Glossary
Periodic Table