lattice → kristalna rešetka
Crystal lattice is a three-dimensional array of points that embodies the pattern of repetition in a crystalline solid. Don’t mix up atoms with lattice points: lattice points are infinitesimal points in space - atoms are physical objects.
Bragg angle → Braggov kut
Bragg angle (Θ) is the angle between an incident X-ray beam and a set of crystal planes for which the secondary radiation displays maximum intensity as a result of constructive interference. British physicist Sir William Henry Bragg and his son Sir William Lawrence Bragg developed a simple relation for scattering angles, now call Bragg’s law.
which relates the angle θ between a crystal plane and the diffracted X-ray beam, the wavelength λ of the x-rays, the crystal plane spacing d, and the diffraction order n (any integer).
The diffraction experiment as presently considered is intended to provide quantitative information on the lattice constant and shape characteristics of the unit cell.
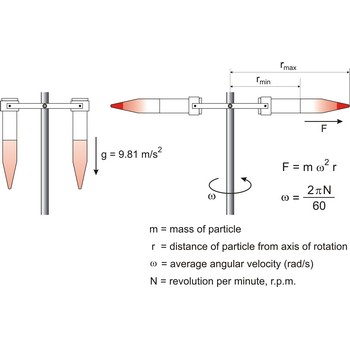
centrifugation → centrifugiranje
Centrifugation is sedimentation of particles under the influence of the centrifugal force and it is used for separation of superfine suspensions. At centrifuging forces up to 10 000 times greater than gravity force are used, and at ultracentrifuge up to 600 000 times as great.
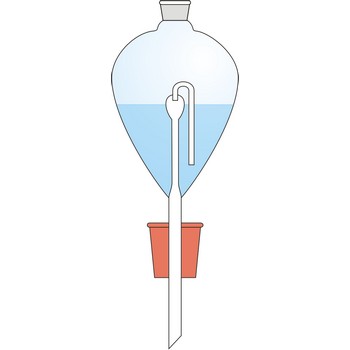
Contat-Gockel’s valve → Contat-Gockelov ventil
Contat-Göckel’s valve is used for maintenance of inert atmosphere in a flask. The valve is filled with a saturated solution of sodium bicarbonate (NaHCO3) so that the end of the tube is covered. Solution inside the valve keeps the flask contents away from the oxygen influence from air. If low pressure is created inside the flask (when the flask is cooled), the solution will penetrate inside it from funnel and in a reaction with acid CO2 is generated which fills up the flask.
Solution from the funnel will keep penetrating until CO2 pressure in the flask is equalised with the outer pressure.
pyrotechnics → pirotehnika
Pyrotechnics include the production of fireworks, devices and mixtures for illumination using easily inflammable and explosive chemicals.
superconductivity → supravodljivost
Superconductivity is the phenomenon in which certain metals, alloys, and compounds below a certain temperature, the transition point (Tc), lose electrical resistance and magnetic permeability, i.e. have infinite electrical conductivity (Meissner effect and Josephson effect).
deoxyribonucleic acid → dezoksiribonukleinska kiselina
Deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) is a nucleic acid with 2-deoxy-D-ribose as the sugar in its nucleotides. DNA contains encoded genetic information, specifically templates for the synthesis of all of an organism’s proteins and enzymes.
DNA was first identified in the 1869 by Swiss chemist Friedrich Miescher (1844-1895). In 1953, American biologist James Dewey Watson (1928-) and English physicist Francis Harry Compton Crick (1916–2004) had discovered that DNA occurs in the cell as a double helix, with two long strands of the molecule wound around each other, and further that the chemical structure of the molecule dictates that adenine (A) always aligns or pairs with thymine (T), and cytosine (C) always pairs with guanine (G). It is this base pairing that allows DNA in a cell to copy itself, and transfer its information to a new cell. The diameter of the helix is 2.0 nm and there is a residue on each chain every 0.34 nm in the z direction. The angle between each residue on the same strand is 36°, so that the structure repeats after 10 residues (3.4 nm) on each strand.
ecological footprint → ekološki otisak
The Ecological Footprint is defined as the area of productive land and water ecosystems required to produce the resources that the population consumes (food, fiber, timber, energy, and space for infrastructure) and assimilate the wastes that the population produces (CO2 is the only waste product currently included), wherever on Earth the land and water is located. It compares actual throughput of renewable resources relative to what is annually renewed. Non-renewable resources are not assessed, as by definition their use is not sustainable.
Ecological footprints and biocapacity are expressed in global hectares (gha). Each unit corresponds to one hectare of biologically productive space with world average productivity. In U.S. Footprint results are often presented in global acres (ga). One U.S. acre is equal to 0.405 hectares.
Humanity is currently consuming renewable resources at a faster rate than ecosystems can regenerate them and continuing to release more CO2 than ecosystems can absorb. In 2007, humanity's Footprint was 18 billion gha, or 2.7 gha per person. However, the Earth's biocapacity was only 11.9 billion gha, or 1.8 gha per person. This represents an ecological overshoot of 50 per cent. Put another way, people used the equivalent of 1.5 planets to support their activities (more developed countries generally make higher demands on the Earth's ecosystems than poorer, less developed countries).
Citing this page:
Generalic, Eni. "Luoli.info." Croatian-English Chemistry Dictionary & Glossary. 29 June 2022. KTF-Split. 3 Apr. 2025. <https://glossary.periodni.com>.
Glossary
Periodic Table