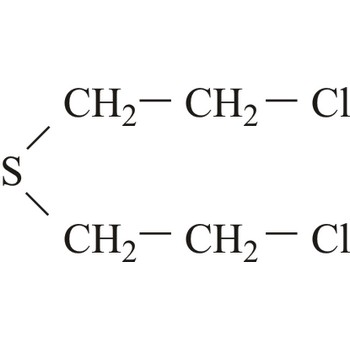methyl orange → metil oranž
Methyl orange is an acid-base indicator, in acid it turns red and in a base it turns yellow.
metre → metar
Metre (m) is the SI base unit of length.
The meter is the length of the path travelled by light in vacuum during a time interval of 1/299 792 458 s.
This definition, adopted by the General Conference on Weights and Measure in October 1983, replaced the 1967 definition based on the krypton lamp.
microscope → mikroskop
Microscope is an instrument that produces enlarged images of small objects. The optical microscopes (light microscope) use visible light and a system of lenses to magnify images. Typical magnification of a light microscope is up to 1500× ("1500 times")with a theoretical resolution limit of around 200 nm. Instead of using light, electron microscopes transmit a beam of electrons through, or onto the surface of, a specimen. An electron beam has a much shorter wavelength than does light, and can reveal structures as small as 2 nm.
mineral → mineral
Minerals are compounds in which metals can be found in nature. Metals in nature can appear as:
| autochthonous | Au, Cu, Pt, Ag, Pd, Hg, Ir |
| oxides | Fe, Al, Sn, Cr, Mn, W, Cu |
| sulphides | Cu, Pb, Zn, Ni, Ag, Co, Sb, Hg, Mo, Cd, Bi |
| carbonates | Fe, Zn, Cu, Mg, Mn, Pb |
| silicates | Ni, Cu, Zn, Mn |
| chlorides | Ag, Cu, Mg, Na, K |
| sulphates | Ca, Ba, Sr, Cu |
Moh’s scale → Mohsova skala
Mohs’ scale of mineral hardness characterises the scratch resistance of various minerals through the ability of a harder material to scratch a softer. It was created by the German mineralogist Friedrich Mohs (1773-1839). Mohs based the scale on the ten readily available minerals.
| Hardness | Mineral |
|---|---|
| 1 | talc (Mg3Si4O10(OH)2) |
| 2 | gypsum (CaSO4·2H2O) |
| 3 | calcite (CaCO3) |
| 4 | fluorite (CaF2) |
| 5 | apatite (Ca5(PO4)3(OH-,Cl-,F-)) |
| 6 | orthoclase feldspar (KAlSi3O8) |
| 7 | quartz (SiO2) |
| 8 | topaz (Al2SiO4(OH-,F-)2) |
| 9 | corundum (Al2O2) |
| 10 | diamond (C) |
mole → mol
Mole (mol) is the SI base unit of amount of substance.
The mole is the amount of substance of a system which contains as many elementary entities as there are atoms in 0.012 kg of carbon 12.
When the mole is used, the elementary entities must be specified and may be atoms, molecules, ions, electrons, other particles, or specified groups of such particles. In this definition, it is understood that the carbon 12 atoms are unbound, at rest and in their ground state.
molecular shape → oblik molekule
Molecular shape is the three dimensional arrangement of atoms in space around a central atom. The molecular formula of a substance does not give an indication of its shape. For example, CO2 is a linear molecule, but SO2 is angular.
The three-dimensional shapes of many small molecules can be predicted by applying the valence shell electron pair repulsion theory (VSEPR). When atoms combine to form molecules, pairs of valence electrons arrange themselves as far from each other as possible. Another way to characterize molecular shape is in terms of hybrid orbitals.
molybdenum → molibden
Molybdenum was discovered by Carl William Scheele (Sweden) in 1778. The origin of the name comes from the Greek word molybdos meaning lead. It is silvery white, very hard metal, but is softer and more ductile than tungsten. Molybdenum is found in the minerals molybdenite (MoS2) and wulfenite (MoO4Pb). Its alloys are used in aircraft, missiles and protective coatings in boiler plate.
mustard agent → plikavac
Mustard agents are usually classified as blistering agents owing to the similarity of the wounds caused by these substances resembling burns and blisters. However, since mustard agents also cause severe damage to the eyes, respiratory system and internal organs, they should preferably be described as blistering and tissue-injuring agents. Normal mustard agent (yperite), 1,1-thio-bis-[2-chloroethane], reacts with a large number of biological molecules. The effect of mustard agent is delayed and the first symptoms do not occur between 2-24 hours after exposure. At room temperature, mustard agent is a liquid with low volatility and is very stable during storage.
monosaccharide → monosaharid
Monosaccharides are carbohydrates, with the general formula Cn(H2O)n, that cannot be decomposed to a simpler carbohydrates by hydrolysis.
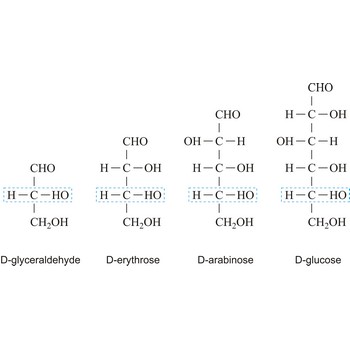
Depending on whether the molecule contains an aldehyde group (-CHO) or a ketone group (-CO-) monosaccharide can be a polyhydroxy aldehyde (aldose) or a polyhydroxy ketone (ketose). These aldehyde and ketone groups confer reduction properties on monosaccharides. They are also classified according to the number of carbon atoms they contain: trioses have three carbon atoms, tetroses four, pentoses five, hexoses six, heptoses seven, etc. These two systems of classification are often combined. For example, a six-carbon polyhydroxy aldehyde such as D-glucose is an aldohexose, whereas a six-carbon polyhydroxy ketone such as D-fructose is a ketohexose.
The notations D and L are used to describe the configurations of carbohydrates. In Fischer projections of monosaccharides, the carbonyl group is always placed on top (in the case of aldoses) or as close to the top as possible (in the case of ketoses). If the OH group attached to the bottom-most asymmetric carbon (the carbon that is second from the bottom) is on the right, then the compound is a D-sugar. If the OH group is on the left, then the compound is an L-sugar. Almost all sugars found in nature are D-sugars.
Monosaccharides can exist as either straight-chain or ring-shaped molecules. During the conversion from straight-chain form to cyclic form, the carbon atom containing the carbonyl oxygen, called the anomeric carbon, becomes a chiral center with two possible configurations (anomers), α and β. When the stereochemistry of the first carbon matches the stereochemistry of the last stereogenic center the sugar is the α-anomer when they are opposite the sugar is the β-anomer.
Citing this page:
Generalic, Eni. "Ledište." Croatian-English Chemistry Dictionary & Glossary. 29 June 2022. KTF-Split. {Date of access}. <https://glossary.periodni.com>.
Glossary
Periodic Table