lanthanides → lantanoidi
Lanthanides (lanthanons, lanthanoids or rare-earth elements) are a series of fourteen elements in the periodic table, generally considered to range in proton number from cerium to lutetium inclusive. It was convenient to divide these elements into the cerium group or light earth: cerium (Ce), praseodymium (Pr), neodymium (Nd), promethium (Pm), samarium (Sm), europium (Eu); and the yttrium group or heavy earths: gadolinium (Gd), terbium (Tb), dysprosium (Dy), holmium (Ho), erbium (Er), thulium (Tm), ytterbium (Yb) i lutetium (Lu). The position of lanthanum is somewhat equivocal and, although not itself a lanthanide, it is often included with them for comparative purpose. The lanthanides are sometimes simply called the rare earths. Apart from unstable Pm, the lanthanides are actually not rare. Cerium is the 26. most abundant of all elements, 5 times as abundant as Pb. All are silvery very reactive metals.
niobium → niobij
Niobium was discovered by Charles Hatchett (England) in 1801. The origin of the name comes from the Greek word Niobe meaning daughter of Tantalus in Greek mythology (tantalum is closely related to niobium in the periodic table). It is shiny white, soft, ductile metal. Exposed surfaces form oxide film. Niobium occurs in a mineral columbite. It is used in stainless steel alloys for nuclear reactors, jets and missiles. Used as an alloy with iron and nickel. It can be used in nuclear reactors and is known to be superconductive when alloyed with tin, aluminium or zirconium.
noble gas → plemeniti plin
Noble gas refers to any element of the group of six elements in group 18 of the periodic table. They are helium (He), neon (Ne), argon (Ar), krypton (Kr), xenon (Xe), and radon (Rn). Unlike most elements, the noble gases are monoatomic. The atoms have stable configurations of electrons. Therefore, under normal conditions they do not form compounds with other elements.
They were generally called inert gases until about 1962 when xenon tetrafluoride, XeF4, was produced in the laboratory. This was the first report of a stable compound of a noble gas with another single element.
octet rule → pravilo okteta
Octet rule states that the chemical properties of the elements repeat on a regular basis with increasing atomic mass, and that the chemical properties of each eight element are similar. Since the inert gases, with the exception of helium have eight electrons in their outer shells, this stable electronic configuration is called the octet rule. In chemical reactions atoms of elements tend to react in such a way as to achieve the electronic configuration of the inert gas nearest to them in the periodic table. There are a number of exceptions to the octet rule.
period → perioda
Periods are horizontal rows in the periodic table, each period begin with an alkali metal (one electron in the outermost principal quantum level) and ending with a noble gas (each having eight electrons in the outermost principal quantum level, except for helium, which is limited to two).
tantalum → tantal
Tantalum was discovered by Anders Ekeberg (Sweden) in 1802. The origin of the name comes from the Greek word Tantalos meaning father of Niobe in Greek mythology, (tantalum is closely related to niobium in the periodic table). It is rare, grey, heavy, hard but ductile, metal with a high melting point. Exposed surfaces form corrosion resistant oxide film. Attacked by HF and fused alkalis. Metal ignites in air. Tantalum always found with niobium. Chiefly occurs in the mineral tantalite. Often used as an economical substitute for platinum. Tantalum pentoxide is used in capacitors and in camera lenses to increase refracting power. It and its alloys are corrosion and wear resistant so it is used to make surgical and dental tools.
atomic clock → atomski sat
Atomic clock is an apparatus for standardizing time based on periodic phenomena within atoms or molecules (ammonia clock; caesium clock).
Bravais lattice → Bravaisova rešetka
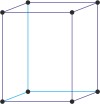
Bravais lattice is a set of points constructed by translating a single point in discrete steps by a set of basis vectors. The French crystallographer Auguste Bravais (1811-1863) established that in three-dimensional space only fourteen different lattices may be constructed. All crystalline materials recognised till now fit in one of these arrangements. The fourteen three-dimensional lattices, classified by crystal system, are shown to the bottom.
|
Crystal system
|
Bravais lattices
|
|||
|
cubic a=b=c α=β=γ=90° |
 |
 |
 |
|
|
|
simple cubic
|
body-centered cubic
|
face-centered cubic
|
|
|
tetragonal a=b≠c α=β=γ=90° |
 |
 |
||
|
|
simple tetragonal
|
body-centered tetragonal
|
||
|
orthorhombic a≠b≠c α=β=γ=90° |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
|
simple orthorhombic
|
base-centered orthorhombic
|
body-centered orthorhombic
|
face-centered orthorhombic
|
|
monoclinic a≠b≠c α=γ=90°≠β |
 |
 |
||
|
|
simple monoclinic
|
base-centered monoclinic
|
||
|
hexagonal a=b≠c α=β=90° γ=120° |
 |
|||
|
|
hexagonal
|
|||
|
rhombohedral a=b=c α=β=γ≠90° |
 |
|||
|
|
rhombohedral
|
|||
|
triclinic a≠b≠c α≠β≠γ≠90° |
 |
|||
|
triclinic
|
||||
frequency → frekvencija
Frequency (ν) is the number of cycles of a periodic phenomenon divided by time. Hertz (Hz) is the SI derived unit, with a special name, for frequency, equal to s-1. It was named after the German scientist Heinrich Hertza (1857-1894).
Citing this page:
Generalic, Eni. "La primer tabla periodica." Croatian-English Chemistry Dictionary & Glossary. 29 June 2022. KTF-Split. {Date of access}. <https://glossary.periodni.com>.
Glossary
Periodic Table


