neon → neon
Neon was discovered by Sir William Ramsay and Morris W. Travers (England) in 1898. The origin of the name comes from the Greek word neon meaning new. It is colourless, odourless inert gas. Non-reactive even with fluorine. Fourth most abundant element in the universe. Neon is obtained by liquefaction of air and separated from the other gases by fractional distillation. Primarily for lighting.
equilibrium constant → konstanta ravnoteže
The equilibrium constant (K) was originally introduced in 1863 by Norwegian chemists C.M. Guldberg and P. Waage using the law of mass action. For a reversible chemical reaction represented by the equation
chemical equilibrium occurs when the rate of the forward reaction equals the rate of the back reaction, so that the concentrations of products and reactants reach steady-state values.
The equilibrium constant is the ratio of chemical activities of the species A, B, C, and D at equilibrium.
To a certain approximation, the activities can be replaced by concentrations.
For gas reactions, partial pressures are used rather than concentrations
The units of Kp and Kc depend on the numbers of molecules appearing in the stoichiometric equation (a, b, c, and d).
The value equilibrium constant depends on the temperature. If the forward reaction is exothermic, the equilibrium constant decreases as the temperature rises. The equilibrium constant shows the position of equilibrium. A low value of K indicates that [C] and [D] are small compared to [A] and [B]; i.e. that the back reaction predominates.
The equilibrium constant is related to ΔrG°, the standard Gibbs free energy change in the reaction, by
oxidation → oksidacija
The term oxidation originally meant a reaction in which oxygen combines chemically with another substance. More generally, oxidation is a part of a chemical reaction in which a reactant loses electrons (increases oxidation number). Simultaneous reduction of a different reactant must occur (redox reaction).
Pauli exclusion principle → Paulijev princip zabrane
Pauli exclusion principle is the statement that two electrons in an atom cannot have identical all four quantum numbers. It was first formulated in 1925 by the Austrian-born Swiss physicst Wolfgang Ernst Pauli (1900-1958).
Faraday’s laws of electrolysis → Faradayevi zakoni elektrolize
Faraday’s laws of electrolysis are two laws found by British chemist and physicist Michael Faraday (1791-1867) in his experiments on electrolysis:
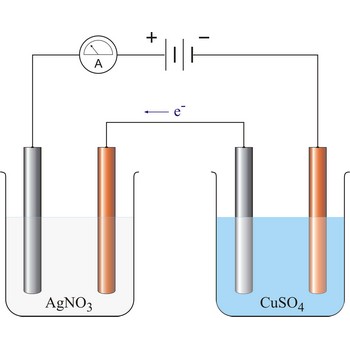
1. The quantity of matter extracted on the electrode is proportional to the quantity of charge (Q = I·t) which has flown in electrolysis time.
where z = number of electrons changed in reaction and F = Faraday’s constant which equals 96 487 C mol-1.
2. The masses of the elements liberated by the same quantity of electricity are directly proportional to their chemical equivalents.
96 487 C will discharge 1 mol Ag and 1/2 mol Cu. The relevant half reactions are:
fuel cell → gorivi članak
Fuel cell is a device that converts chemical energy into electrical energy. It is different from a battery in that the energy conversion continues as long as fuel and oxidising agent are fed to the fuel cell; that is, in principle indefinitely. (A battery is manufactured with a limited amount of chemicals, and it is exhausted when all the chemicals have reacted.) It is a galvanic cell where spontaneous chemical reactions occur at the electrodes. The fuel is oxidised at the anode, and the oxidising agent (almost always oxygen or air) is reduced at the cathode. Presently, the most commonly used fuel is hydrogen. More conventional fuels (e.g., petrol or natural gas) must be converted (reformed) into hydrogen before they can be utilised in a fuel cell.
Some fuel cells employ an aqueous solution as electrolyte, that can be either acidic or basic (alkaline), or an ion-exchange membrane soaked in aqueous solution can act as the electrolyte. These fuel cells operate at relatively low temperatures (from room temperature to not much above the boiling point of water). Some fuel cells employ molten salts (especially carbonates) as electrolytes and have to operate at temperatures of several hundred degrees centigrade (Celsius). Others employ ionically conductive solids as electrolyte and must operate close to 1 000 °C.
permeability → permeabilnost
Permeability (Latin permeare, to pass through) is a passage or diffusion of a gas, vapour, liquid, or solid through a material without physically or chemically affecting it.
fugacity → fugacitet
Fugacity (f) is a thermodynamic function used in place of partial pressure in reactions involving real gases and mixtures. For a component of a mixture, it is defined by
where μ is the chemical potential.
The fugacity of a gas is equal to the pressure if the gas is ideal. The fugacity of a liquid or solid is the fugacity of the vapour with which it is in equilibrium. The ratio of the fugacity to the fugacity in some standard state is the activity.
Citing this page:
Generalic, Eni. "Kvantna kemija." Croatian-English Chemistry Dictionary & Glossary. 29 June 2022. KTF-Split. {Date of access}. <https://glossary.periodni.com>.
Glossary
Periodic Table