electron spin → elektronski spin
Electron spin (s) is the quantum number, equal to 1/2, that specifies the intrinsic angular momentum of the electron.
Einstein, Albert → Einstein, Albert
Albert Einstein (1879-1955) is a German born American physicist, who took Swiss nationality in 1901. A year later he went to work in the Bern patent office. In 1905. he published five enormously influential papers, one on Brownian movement, one on the photoelectric effect, one on the special theory of relativity, and one on energy and inertia (which included the famous expression E = mc2). In 1915 he published the general theory of relativity, concerned mainly with gravitation. In 1921 he was awarded the Nobel Prize. In 1933, as a Jew, Einstein decided to remain in the USA (where he was lecturing), as Hitler had come to power. For the remainder of his life he sought a unified field theory. In 1939 he informed president Roosevelt that an atom bomb was feasible and that. Germany might be able to make one.
experiment → eksperiment
Experiment is direct observation under controlled conditions. Most experiments involve carefully changing one variable and observing the effect on another variable (for example, changing temperature of a water sample and recording the change volume that results).
filter paper → filtar papir
Filter paper is a quantitative paper used for filtering and made of pure cellulose treated with hydrochloric and hydrofluoric acid. This kind of paper burns out practically without any remains (less than 0.0001 g ashes). Different types of paper are marked with numbers; qualitative bears marking 595 or 597 and quantitative 589 or 590. Dependable upon precipitate character, different types of filter paper are used:
- black band (5891) - 100 mL of fluid flows through it in 20 s to 30 s. It is used for filtering of gelatinous precipitates.
- white band (5892) - 100 mL of fluid flows through it in 40 s to 60 s. It is used for coarse crystalline precipitates filtration.
- blue band (5893) - 100 mL of fluid flows through it in 200 s to 400 s. It is used for fine crystalline precipitates.
manganometry → manganometrija
Manganometry is a quantitative oxidimetric method based on measurement of potassium permanganate (KMnO4) spent for an oxidation of the matter in question.
Pauli exclusion principle → Paulijev princip zabrane
Pauli exclusion principle is the statement that two electrons in an atom cannot have identical all four quantum numbers. It was first formulated in 1925 by the Austrian-born Swiss physicst Wolfgang Ernst Pauli (1900-1958).
photon → foton
Photon is an elementary particle of zero mass and spin 1/2. The photon is involved in electromagnetic interactions and is the quantum of electromagnetic radiation. The photon may also be regarded as a unit of energy equal to
where h is Planck constant and ν is the frequency of the radiation.
gravimetry → gravimetrija
Gravimetry is the quantitative measurement of an analyte by weighing a pure, solid form of the analyte. Since gravimetric analysis is an absolute measurement, it is the principal method for analysing and preparing primary standards.
A typical experimental procedure to determine an unknown concentration of an analyte in a solution is as follows:
- quantitatively precipitate the analyte from the solution
- collect the precipitate by filtering and wash it to remove impurities
- dry the solid in an oven to remove the solvent
- weigh the solid on an analytical balance
- calculate the analyte concentration in the original solution based on the weight of the precipitate.
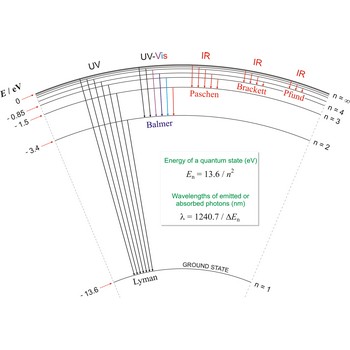
Lyman series → Lymanova serija
Lyman series is the series of lines in the spectrum of the hydrogen atom which corresponds to transitions between the ground state (principal quantum number n = 1) and successive excited states.
orbital → orbitala
Orbital is the area in space about an atom or molecule in which the probability of finding an electron is greatest.
The possible atomic orbitals correspond to subshells of the atom. Thus there is one s-orbital for each shell (orbital quantum number l = 0). There are three p-orbitals (corresponding to the three values of l) and five d-orbitals. The shapes of orbitals depend on the value of l.
Citing this page:
Generalic, Eni. "Kvant." Croatian-English Chemistry Dictionary & Glossary. 29 June 2022. KTF-Split. {Date of access}. <https://glossary.periodni.com>.
Glossary
Periodic Table