unsaturated hydrocarbon → nezasićeni ugljikovodik
Unsaturated hydrocarbons are organic compounds containing double (alkenes) or triple (alkynes) bonds in their molecules.
fat → mast
Fats are esters of glycerol and long chain carboxylic acids. Fats occur widely in plants and animals as a means of storing food energy, having twice the calorific value of carbohydrates. Fats derived from plants and fish generally have a greater proportion of unsaturated fatty acids than those from mammals. Fats may be either solid or liquid at room temperature, depending on their structure and composition. Unsaturated fats are liquid at room temperature.
Plant oils may be hardened by the addition of hydrogen atoms, converting double bonds to single bonds. This process is known as hydrogenation. Hydrogenated vegetable oils are often present in margarine and other processed foods.
Alkali hydrolysis of fat with sodium hydroxide it gives glycerol and soap (i.e. a mixture of the sodium salts of the fatty acids).
omega-3 fatty acids → omega-3 masne kiseline
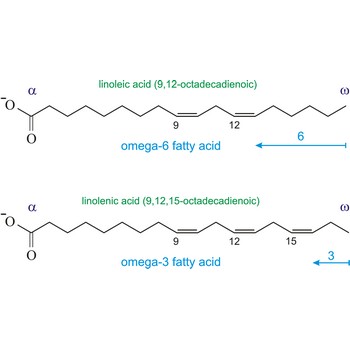
Omega-3 fatty acids are polyunsaturated fatty acids, meaning they contain more than one double bond. The name omega-3 indicates that the first double bond occurs on the third carbon atom (n-3) from the methyl (-CH3) end of the molecule (omega position). The three main omega-3 fatty acids are alpha-linolenic acid (ALA, 18:3n-3), eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA, 20:5n-3), and docosahexaenoic acid (DHA, 22:6n-3). ALA comes from plants. EPA and DHA come from fish.
Similarly, the first double bond in omega-6 fatty acids is located between the sixth and seventh carbon atom (n-6) from the methyl end of the fatty acid (omega end).
saturated fatty acid → zasićena masna kiselina
Saturated fatty acid is a fatty acid carrying the maximum possible number of hydrogen atoms (It doesn’t have any double bounds in the alkyl chain). The most important of these are:
| Butyric (butanoic acid) | CH3(CH2)2COOH |
| Lauric (dodecanoic acid) | CH3(CH2)10COOH |
| Myristic (tetradecanoic acid) | CH3(CH2)12COOH |
| Palmitic (hexadecanoic acid) | CH3(CH2)14COOH |
| Stearic (octadecanoic acid) | CH3(CH2)16COOH |
| Arachidic (eicosanoic acid) | CH3(CH2)18COOH |
unsaturated fatty acid → nezasićena masna kiselina
Unsaturated fatty acid is a fatty acid whose carbon chain can absorb additional hydrogen atoms. Their carbon chain has one or more double or triple valence bond per molecule. The most important of these are:
| Oleic (9-octadecenoic acid) | CH3(CH2)7CH=CH(CH2)7COOH |
| Linoleic (9,12-octadecadienoic acid) | CH3(CHCH2)3(CH2CH=CH)2(CHCH2)7COOH |
| Linolenic (9,12,15-octadecatrienoic acid) | CH3(CH2CH=CH)3(CHCH2)7COOH |
Citing this page:
Generalic, Eni. "Kumulirana dvostruka veza." Croatian-English Chemistry Dictionary & Glossary. 29 June 2022. KTF-Split. {Date of access}. <https://glossary.periodni.com>.
Glossary
Periodic Table