thermal resistance → toplinski otpor
Heat always flows from a higher to a lower temperature level. The driving force for the heat flux lies in the temperature difference ΔT between two temperature levels. Analogous to Ohm’s law, the following holds:
where H = dQ/dt is heat flux, measured in watts, ΔT is temperature difference across the thermal resistance, measured in kelvin, and Rth is thermal resistance, measured in K/W.
For example, suppose there were two houses with walls of equal thickness; one is made of glass and the other of asbestos. On a cold day, heat would pass through the glass house much faster. The thermal restistance of asbestos is then higher than of glass.
If the thermal Ohm’s law is divided by the heat capacity C, Newton’s law of cooling is obtained:
where dT/dt is rate of cooling or heating, measured in K s-1, and C is heat capacity, measured in J K-1.
transition metal → prijelazni element
This group of metals is distinguished from other metals not by their physical properties, but by their electronic structure. Transition metals are elements characterized by a partially filled d subshell. The First Transition Series comprises scandium (Sc), titanium (Ti), vanadium (V), chromium (Cr), manganese (Mn), iron (Fe), cobalt (Co), nickel (Ni) and copper (Cu). The Second and Third Transition Series include the lanthanides and actinides, respectively.
The transition metals are noted for their variability in oxidation state. Thus, manganese has two electrons in its outside shell and five electrons in the next shell down, and exhibits oxidation states of +1, +2, +3, +4, +5, +6, and +7.
They are also characterised by the fact that well into the series, going from left to right, the properties of the succeeding metals do not differ greatly from the preceding ones.
tungsten → volfram
Tungsten was discovered by Fausto and Juan Jose de Elhuyar (Spain) in 1783. Named after the tungsten mineral wolframite. It is hard, steel-grey to white metal. Highest melting point of all metals. Resists oxygen, acids and alkalis. Tungsten occurs in the minerals scheelite (CaWO4) and wolframite [(Fe,Mn)WO4]. Made into filaments for vacuum tubes and electric lights. Also as contact points in cars. Tungsten carbide is extremely hard and is used for making cutting tools and abrasives.
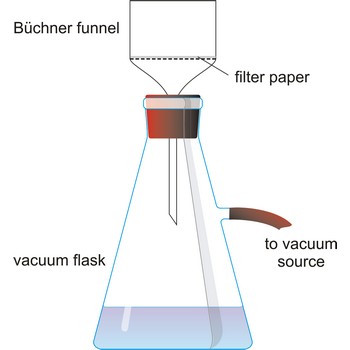
vacuum filtration → vakuum filtracija
Vacuum filtration is a technique for separating a solid product from a liquid. The mixture of solid and liquid is poured through a filter paper in a Buchner funnel. The solid is trapped by the filter and the liquid is drawn through the funnel into the flask below, by a vacuum.
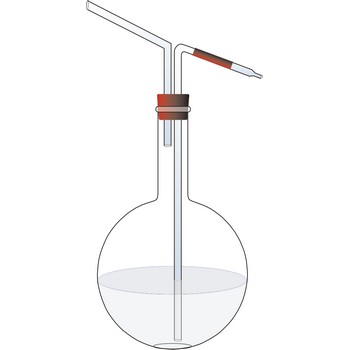
wash bottle → boca štrcaljka
Plastic wash bottle is a squeeze bottle made of low density polyethylene (LDPE) whose contents can be forced out through a narrow hole at the top by squeezing the bottle.
Glass wash bottle is a bottle fitted with two glass tubes pass through the cap, so that on blowing into one of the tubes a stream of water issuing from the other may be directed upon anything to be washed or rinsed, as a precipitate upon a filter.
X-rays → X-zrake
X-rays are electromagnetic radiation of shorter wavelength than ultraviolet radiation (10-11 m to 10-9 m or 0.01 nm to 1 nm) produced by bombardment of atoms by high-quantum-energy particles. X-rays can pass through many forms of matter and they are therefore used medically and industrially to examine the internal structure.

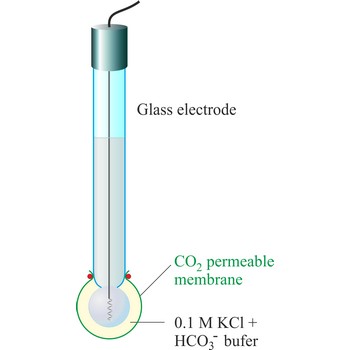
CO2 ion selective electrode → CO2 ion selektivna elektroda
The carbon dioxide ion selective electrode uses a gas-permeable membrane to separate the sample solution from the electrode internal solution. Dissolved carbon dioxide in the sample solution diffuses through the membrane until an equilibrium is reached between the partial pressure of CO2 in the sample solution and the CO2 in the internal filling solution. In any given sample the partial pressure of carbon dioxide will be proportional to the concentration of carbon dioxide. The diffusion across the membrane affects the level of hydrogen ions in the internal filling solution:
The hydrogen level of the internal filling solution is measured by the pH electrode located behind the membrane. The internal filling solution contains a high concentration of sodium bicarbonate (e.g. 0.1 mol/L NaHCO3) so that the bicarbonate level can be considered constant.
Schrotter apparatus for determination of CO2 → Schrotterova aparatura za određivanje CO2
Schrötter decomposition apparatus (Schrötter's alkalimeter) is used to determining the carbonate content in samples of limestone, gypsum, dolomite, or baking powder by loss of weight. The apparatus is named after the Austrian chemist Anton Schrötter von Kristelli (1802-1875), who devised it in 1871. The size of the filled apparatus (apparatus is 16 cm high) is such that it weights less than 75 g, and can be placed on the pan of an analytical balance.
Procedure: Weigh about 0.5 g of the powdered carbonate sample and introduce it into the decomposition flask C. Pour into the drying tube A 2-3 mL of concentrated sulphuric acid (H2SO4), and to the dropping funnel B add about 10-15 mL of hydrochloric acid (w(HCl) = 15 %). Weigh the whole apparatus. Open the upper taps of both parts and allow the hydrochloric acid from B to run slowly down on to the powdered sample. The evolved CO2 escapes through the strong sulphuric acid and is thus thoroughly dried. When further addition of acid produces no more evolution of CO2, warm the apparatus up to 80 °C so as to expel the CO2 from the solution. Connect the upper tap of the drying tube A to a water pump and draw a slow current of air through the apparatus until completely cool. Open the upper taps for a moment to equalize the internal and external pressure and weight the apparatus again. The weight loss is equal to the weight of carbon dioxide liberated from the carbonates.
Citing this page:
Generalic, Eni. "Krom." Croatian-English Chemistry Dictionary & Glossary. 29 June 2022. KTF-Split. {Date of access}. <https://glossary.periodni.com>.
Glossary
Periodic Table