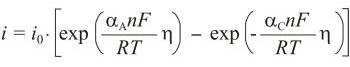blackbody radiation → zračenje crnog tijela
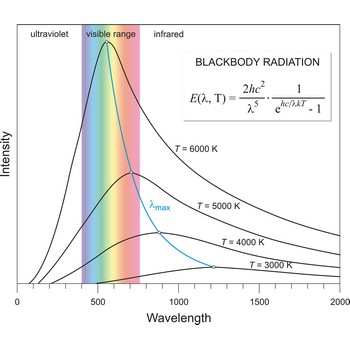
Blackbody radiation is the radiation emitted by a perfect blackbody, i.e., a body which absorbs all radiation incident on it and reflects none. The primary law governing blackbody radiation is the Planck Radiation Law, which governs the intensity of radiation emitted by unit surface area into a fixed direction (solid angle) from the blackbody as a function of wavelength for a fixed temperature. The Planck Law can be expressed through the following equation
where λ is the wavelength, h is Planck’s constant, c is the speed of light, k is the Boltzmann constant, and T is the temperature.
coherence → koherentnost
If two overlapping light waves are to interfere detectably, the phase difference between them must remain constant with time, i.e. the waves must be coherent.
Bohr magneton → Bohrov magneton
Bohr magneton (μB) is the atomic unit of magnetic moment, defined as
where h is Planck’s constant, me the electron mass, and e the elementary charge. It is the moment associated with a single electron spin.
covalentity → kovalentnost
Covalentity is a maximum number of covalent bond that one atom can make, it is equal to the number of hydrogen atoms that are combined with other atoms. It is usually constant.
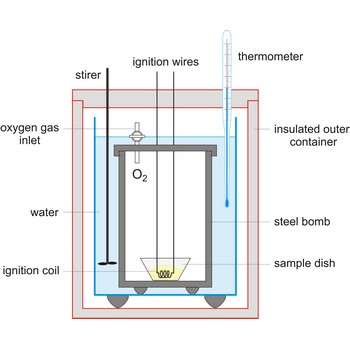
bomb calorimeter → kalorimetrijska bomba
Bomb calorimeter is a type of constant-volume calorimeter used in measuring the heat of combustion of samples which can be burned in oxygen. Four essential parts are required in any bomb calorimeter:
- a bomb or vessel in which the combustible charges can be burned,
- a bucket or container for holding the bomb in a measured quantity of water, together with a stirring mechanism,
- an insulating jacket to protect the bucket from transient thermal stresses during the combustion process, and
- a thermometer or other sensor for measuring temperature changes within the bucket.
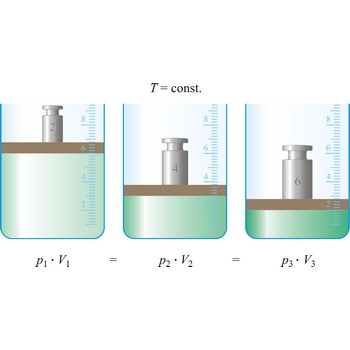
Boyle’s law → Boyleov zakon
Boyle’s law (sometimes referred to as the Boyle-Mariott’s law) is the empirical law, exact only for an ideal gas, which states that the volume of a gas is inversely proportional to its pressure at constant temperature.
Butler-Volmer equation → Butler-Volmerova jednadžba
Butler-Volmer equation is an activation controlled reaction, the one for which the rate of reaction is controlled solely by the rate of the electrochemical charge transfer process, which is in turn an activation-controlled process. This gives rise to kinetics that are described by the Butler-Volmer equation:
where io is exchange current density, η is overpotential (η = E - Eo), n is number of electrons, αA is anodic transfer coefficient, and αC is cathodic transfer coefficient
equation of state → jednadžba stanja
Equation of state is an equation relating the pressure, volume, and temperature of a substance or system. Equation of state for ideal gas
where p is pressure, V molar volume, T temperature, and R the molar gas constant (8.314 JK-1mol-1).
free energy → slobodna energija
Free energy is an energy that is actually available to do useful work. A decrease in free energy accompanies any spontaneous process. Free energy does not change for systems that are at equilibrium.
galvanostat → galvanostat
Galvanostat is an electronic instrument that controls the current through an electrochemical cell at a preset value, as long as the needed cell voltage and current do not exceed the compliance limits of the galvanostat.
Citing this page:
Generalic, Eni. "Konstanta ravnoteže." Croatian-English Chemistry Dictionary & Glossary. 29 June 2022. KTF-Split. {Date of access}. <https://glossary.periodni.com>.
Glossary
Periodic Table