coherence → koherentnost
If two overlapping light waves are to interfere detectably, the phase difference between them must remain constant with time, i.e. the waves must be coherent.
cosmic rays → kozmičke zrake
Cosmic rays are high energy (1015 eV- 1017 eV) nuclear particles, electrons, and photons, originating mostly outside the solar system, which continually bombard the Earth’s atmosphere.
Bohr magneton → Bohrov magneton
Bohr magneton (μB) is the atomic unit of magnetic moment, defined as
where h is Planck’s constant, me the electron mass, and e the elementary charge. It is the moment associated with a single electron spin.
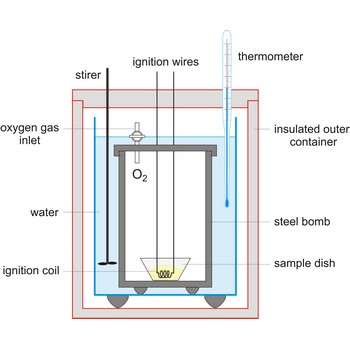
bomb calorimeter → kalorimetrijska bomba
Bomb calorimeter is a type of constant-volume calorimeter used in measuring the heat of combustion of samples which can be burned in oxygen. Four essential parts are required in any bomb calorimeter:
- a bomb or vessel in which the combustible charges can be burned,
- a bucket or container for holding the bomb in a measured quantity of water, together with a stirring mechanism,
- an insulating jacket to protect the bucket from transient thermal stresses during the combustion process, and
- a thermometer or other sensor for measuring temperature changes within the bucket.
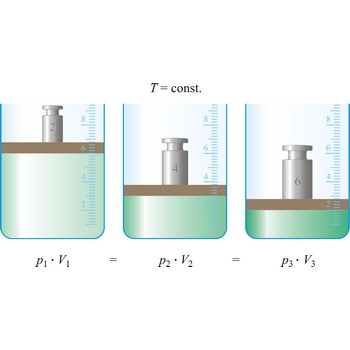
Boyle’s law → Boyleov zakon
Boyle’s law (sometimes referred to as the Boyle-Mariott’s law) is the empirical law, exact only for an ideal gas, which states that the volume of a gas is inversely proportional to its pressure at constant temperature.
covalentity → kovalentnost
Covalentity is a maximum number of covalent bond that one atom can make, it is equal to the number of hydrogen atoms that are combined with other atoms. It is usually constant.
equation of state → jednadžba stanja
Equation of state is an equation relating the pressure, volume, and temperature of a substance or system. Equation of state for ideal gas
where p is pressure, V molar volume, T temperature, and R the molar gas constant (8.314 JK-1mol-1).
cement → cement
Cement is any various substances used for bonding or setting to a hard material. Portland cement is a mixture of calcium silicates and aluminates made by heating limestone (CaCO3) with clay (containing aluminosilicates) in a kiln. The product is ground to a fine powder. When mixed with water it settles in a few hours and then hardens over a longer period of time due to the formation of hydrated aluminates and silicates.
Charles’ law → Charlesov zakon
The volume of a fixed mass of gas at a constant pressure expand by the constant fraction of its volume at 0 °C. For each Celsius or kelvin degree its temperature is raised. For any ideal gas fraction it is approximately 1/273. This can be expressed by the equation
were V° is the volume at 0°C and V is its volume at t°C.
This is equivalent to the statement that the volume of a fixed mass of gas at a constant pressure is proportional to its thermodynamic temperature
This law also know as Gay-Lussac’s law.
An equation similar to the one given above applies to pressures for ideal gases:
chemical equation → kemijska jednadžba
Chemical equation is a way of denoting a chemical reaction using the symbol for the participating particles (atoms, molecules, ions, etc.); for example,
The single arrow is used for an irreversible reaction; double arrows are used for reversible reactions. When reactions involve different phases, it is usual to put the phase in brackets after the symbol.
| s | = | solid |
| l | = | liquid |
| g | = | gas |
| aq | = | aqueous |
The numbers a, b, c, and d, showing the relative numbers of molecules reacting, are called the stoichiometric coefficients. The convention is that stoichiometric coefficients are positive for reactants and negative for products. If the sum of the coefficients is zero, the equation is balanced.
Citing this page:
Generalic, Eni. "Konstanta produkta topljivosti." Croatian-English Chemistry Dictionary & Glossary. 29 June 2022. KTF-Split. {Date of access}. <https://glossary.periodni.com>.
Glossary
Periodic Table