effervescence → pjenušanje
Effervescence is the formation of gas bubbles in a liquid by a chemical reaction. An example of effervescence is the release of carbon dioxide which bubbles as a gas from the liquid when limestone chips, which are composed of calcium carbonate, are added to dilute hydrochloric acid.
cerium → cerij
Cerium was discovered by Martin Heinrich Klaproth (Germany) and by Jöns Jacob Berzelius (Sweden) in 1803 and Wilhelm von Hisinger (Germany) in 1814. Named after the asteroid Ceres this discovered two years before the element. It is malleable, ductile, iron-grey metal. Tarnishes in air; reacts easily with water. Dissolves in acids; ignites when heated. Metal ignites and burns readily. Strong reductant. Cerium is most abundant rare earth metal. Found in many minerals like monazite sand [Ce(PO4)]. Its oxides are used in the optics and glass-making industries. Its salts are used in the photography and textile industry. Used in high-intensity carbon lamps and as alloying agents in special metals.
chemical compound formula → formula kemijskog spoja
Chemical elements are represented by their symbols, and chemical compounds are represented by a group of symbols of those elements from which the compound is composed. That group of symbols, which shows which atoms and in which number relation they are present in certain compound is called a chemical compound formula.
In a formula chemical symbols show which element is present in a certain compound, and its index shows how much of that element there is in a certain compound. From sulphuric acid formula H2SO4 we can see that one molecule of sulphuric acid consists of two atoms of hydrogen, one atom of sulphur and four atoms of oxygen.
chromium → krom
Chromium was discovered by Louis-Nicholas Vauquelin (France) in 1797. The origin of the name comes from the Greek word chroma meaning colour. It is very hard, crystalline, steel-grey metal. The pure metal has a blue-white colour. It is hard, brittle and corrosion-resistant at normal temperatures. Hexavalent compounds toxic by skin contact. The most important chromium mineral is chromite [Fe,Mg(CrO4)]. Produced commercially by heating its ore in the presence of silicon or aluminium. Used to make stainless steel. It gives the colour to rubies and emeralds. Iron-nickel-chromium alloys in various percentages yield an incredible variety of the most important metals in modern technology.
glyceride → glicerid
Glycerides are esters of glycerol (propane-1,2,3-triol) with fatty acids, widely distributed in nature. They are by a long-established custom subdivided into triglycerides, 1,2- or 1,3-diglycerides, and 1- or 2- monoglycerides, according to the number and positions of acyl groups.
cobalt → kobalt
Cobalt was discovered by Georg Brandt (Germany) in 1735. The origin of the name comes from the German word kobald meaning goblin or evil spirit. It is hard, ductile, lustrous bluish-grey metal. Surfaces stable in air. Reacts over time with dilute acids. It has remarkable magnetic properties. Cobalt occurs in compounds with arsenic and sulfur as in cobaltine (CoAsS) and linneite (Co3S4). Pure cobalt is obtained as a by-product of refining nickel, copper and iron. Used in many hard alloys; for magnets, ceramics and special glasses. Radioactive cobalt-60 is used in cancer therapy.
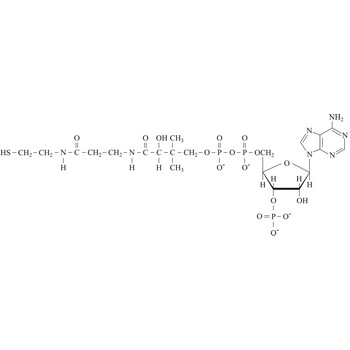
coenzyme a → koenzim a
Coenzyme A (CoA) is an essential metabolic cofactor synthesized from cysteine, pantothenate (vitamin B5), and ATP. CoA plays important roles in many metabolic pathways, including the tricarboxylic acid (TCA) cycle, and the synthesis and oxidation of fatty acids. One of the main functions of CoA is the carrying and transfer of acyl groups. Acylated derivatives (acetyl-CoA) are critical intermediates in many metabolic reactions.
contact procedure → kontaktni postupak
Contact procedure is an industrial procedure used for the production of sulphuric acid, where a dry and clean sulphur dioxide and air go over a catalyst made of vanadium pentoxide at 450 °C by which sulphur trioxide is gained, then we add concentrated sulphuric acid by which we obtain smoking sulphuric acid which is now diluted to sulphuric acid.
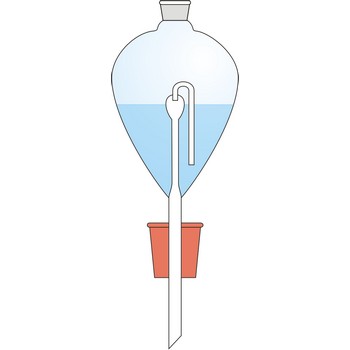
Contat-Gockel’s valve → Contat-Gockelov ventil
Contat-Göckel’s valve is used for maintenance of inert atmosphere in a flask. The valve is filled with a saturated solution of sodium bicarbonate (NaHCO3) so that the end of the tube is covered. Solution inside the valve keeps the flask contents away from the oxygen influence from air. If low pressure is created inside the flask (when the flask is cooled), the solution will penetrate inside it from funnel and in a reaction with acid CO2 is generated which fills up the flask.
Solution from the funnel will keep penetrating until CO2 pressure in the flask is equalised with the outer pressure.
Citing this page:
Generalic, Eni. "Kisela kiša." Croatian-English Chemistry Dictionary & Glossary. 29 June 2022. KTF-Split. {Date of access}. <https://glossary.periodni.com>.
Glossary
Periodic Table