isomorphism → izomorfija
Isomorphism is the existence of two or more substances that have the same crystal structure, so that they form solid solutions.
isotropic crystal → izotropni kristal
The measured properties of an isotropic crystal are independent of the axis of testing. Opposite of anisotropic.
isotropy → izotropija
Isotropy is the property of molecules and materials of having identical physical properties in all directions.
cysteine → cistein
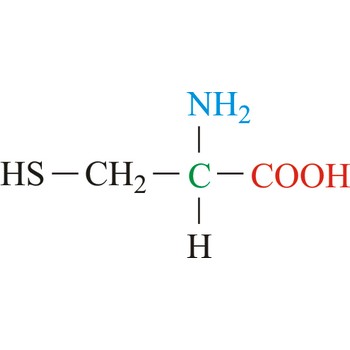
Cysteine is neutral amino acids with polar side chains. Because of its high reactivity, the thiol group of cysteine has numerous biological functions. It serves as a potent nucleophile and metal ligand (particularly for iron and zinc), but is best known for its ability to form disulfide bonds, which often make an important contribution to the stability of extracellular proteins. Cysteine is a non-essential amino acid, which means that it is biosynthesized in humans.
- Abbreviations: Cys, C
- IUPAC name: 2-amino-3-sulfanylpropanoic acid
- Molecular formula: C3H7NO2S
- Molecular weight: 121.16 g/mol
deoxyribonucleic acid → dezoksiribonukleinska kiselina
Deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) is a nucleic acid with 2-deoxy-D-ribose as the sugar in its nucleotides. DNA contains encoded genetic information, specifically templates for the synthesis of all of an organism’s proteins and enzymes.
DNA was first identified in the 1869 by Swiss chemist Friedrich Miescher (1844-1895). In 1953, American biologist James Dewey Watson (1928-) and English physicist Francis Harry Compton Crick (1916–2004) had discovered that DNA occurs in the cell as a double helix, with two long strands of the molecule wound around each other, and further that the chemical structure of the molecule dictates that adenine (A) always aligns or pairs with thymine (T), and cytosine (C) always pairs with guanine (G). It is this base pairing that allows DNA in a cell to copy itself, and transfer its information to a new cell. The diameter of the helix is 2.0 nm and there is a residue on each chain every 0.34 nm in the z direction. The angle between each residue on the same strand is 36°, so that the structure repeats after 10 residues (3.4 nm) on each strand.
law of definite composition → zakon o određenom sastavu
Law of definite composition states that the elements in a given compound are always combined in the same proportion by mass. This law form the basis for the definition of a chemical compound.
differential thermal analysis → diferencijalna termalna analiza
Differential thermal analysis (DTA) is a technique that is often used to analyze materials that react or decompose at higher temperatures. The difference in temperature between the sample and an inert reference material is monitored as both are heated in a furnace. Phase transitions and chemical reactions taking place in the sample on heating cause the temperature difference to become larger, at temperatures that are characteristic of the sample.
dioxin → dioksin
Dioxin is a general term that describes a group of hundreds of chemicals that are highly persistent in the environment. The most toxic compound is 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin or TCDD. The toxicity of other dioxins and chemicals like PCBs that act like dioxin are measured in relation to TCDD. Dioxin is formed as an unintentional by-product of many industrial processes involving chlorine such as waste incineration, chemical and pesticide manufacturing and pulp and paper bleaching. Dioxin was the primary toxic component of Agent Orange, found at Love Canal in Niagara Falls, NY and was the basis for evacuations at Times Beach, MO and Seveso, Italy.
Dioxin is formed by burning chlorine-based chemical compounds with hydrocarbons. The major source of dioxin in the environment comes from waste-burning incinerators of various sorts and also from backyard burn-barrels. Dioxin pollution is also affiliated with paper mills which use chlorine bleaching in their process, with the production of Polyvinyl Chloride (PVC) plastics, and with the production of certain chlorinated chemicals (like many pesticides).
Lewis acid → Lewisova kiselina
Lewis acid is an agent capable of accepting a pair of electrons to form a coordinate bond.
Citing this page:
Generalic, Eni. "Kemijsko svojstvo." Croatian-English Chemistry Dictionary & Glossary. 29 June 2022. KTF-Split. {Date of access}. <https://glossary.periodni.com>.
Glossary
Periodic Table