dioxin → dioksin
Dioxin is a general term that describes a group of hundreds of chemicals that are highly persistent in the environment. The most toxic compound is 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin or TCDD. The toxicity of other dioxins and chemicals like PCBs that act like dioxin are measured in relation to TCDD. Dioxin is formed as an unintentional by-product of many industrial processes involving chlorine such as waste incineration, chemical and pesticide manufacturing and pulp and paper bleaching. Dioxin was the primary toxic component of Agent Orange, found at Love Canal in Niagara Falls, NY and was the basis for evacuations at Times Beach, MO and Seveso, Italy.
Dioxin is formed by burning chlorine-based chemical compounds with hydrocarbons. The major source of dioxin in the environment comes from waste-burning incinerators of various sorts and also from backyard burn-barrels. Dioxin pollution is also affiliated with paper mills which use chlorine bleaching in their process, with the production of Polyvinyl Chloride (PVC) plastics, and with the production of certain chlorinated chemicals (like many pesticides).
magnetochemistry → magnetokemija
Magnetochemistry is a branch of physical chemistry which studies relations between magnetism and the chemical structure of matter.
dissociation → disocijacija
Dissociation is the process by which a chemical combination breaks up into simpler constituents as a result of either added energy (dissociated by heat), or the effect of a solvent on a dissolved polar compound (electrolytic dissociation). It may occur in the gaseous, solid, or liquid state, or in a solution.
An example of dissociation is the reversible reaction of hydrogen iodide at high temperatures
The term dissociation is also applied to ionisation reactions of acids and bases in water. For example
which is often regarded as a straightforward dissociation into ions
electric cell → električni članak
Electric cell (battery) is a device that is capable of changing some form of energy, such as chemical, nuclear or radiant energy, into electricity. A solar cell, for example, consists of a semiconductor junction that converts sunlight directly into electricity. A dry cell battery converts chemical energy into electricity.
electrochemical cell → elektrokemijski članak
Electrochemical cell is a device that converts chemical energy into electrical energy or vice versa when a chemical reaction is occurring in the cell. It consist of two electronically conducting phases (e.g., solid or liquid metals, semiconductors, etc) connected by an ionically conducting phase (e.g. aqueous or non-aqueous solution, molten salt, ionically conducting solid). As an electric current passes, it must change from electronic current to ionic current and back to electronic current. These changes of conduction mode are always accompanied by oxidation/reduction reactions.
An essential feature of the electrochemical cell is that the simultaneously occurring oxidation-reduction reactions are spatially separated. E.g., in a spontaneous chemical reaction during the oxidation of hydrogen by oxygen to water, electrons are passed directly from the hydrogen to the oxygen.
In contrast, in the spontaneous electrochemical reaction in a galvanic cell the hydrogen is oxidised at the anode by transferring electrons to the anode and the oxygen is reduced at the cathode by accepting electrons from the cathode. The ions produced in the electrode reactions, in this case positive hydrogen ions and the negative hydroxyl (OH-) ions, will recombine in the solution to form the final product of the reaction: water. During this process the electrons are conducted from the anode to the cathode through an outside electric circuit where the electric current can drive a motor, light a light bulb, etc. The reaction can also be reversed: water can be decomposed into hydrogen and oxygen by the application of electrical power in an electrolytic cell.
metabolism → metabolizam
Metabolism is a sum of all chemical and physiological processes by which the body builds and maintains itself. It is a process of building the body’s molecular structures from nutrients (anabolism) and breaking them down for energy (catabolism).
electrochemical series → elektrokemijski niz
Electrochemical series is a series of chemical elements arranged in order of their standard electrode potentials. The hydrogen electrode
is taken as having zero electrode potential. An electrode potential is, by definition, a reduction potential.
Elements that have a greater tendency than hydrogen to lose electrons to their solution are taken as electropositive; those that gain electrons from their solution are below hydrogen in the series and are called electronegative.
The series shows the order in which metals replace one another from their salts; electropositive metals will replace hydrogen from acids.
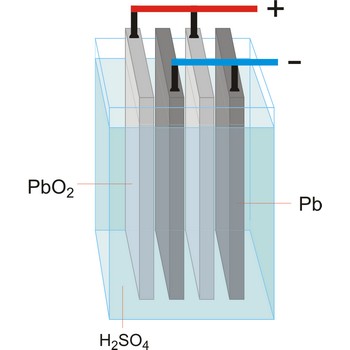
electrolytic cell → elektrolitska ćelija
Electrolytic cell is an electrochemical cell that converts electrical energy into chemical energy. The chemical reactions do not occur spontaneously at the electrodes when they are connected through an external circuit. The reaction must be forced by applying an external electric current. It is used to store electrical energy in chemical form (rechargeable battery). It is also used to decompose or produce (synthesise) new chemicals by the application of electrical power. This process is called electrolysis, e.g., water can be decomposed into hydrogen gas and oxygen gas. The free energy change of the overall cell reaction is positive.
electronegativity → elektronegativnost
Electronegativity is a parameter originally introduced by L. Pauling which describes, on a relative basis, the power of an atom to attract electrons. For example, in hydrogen chloride, the chlorine atom is more electronegative than the hydrogen and the molecule is polar, with a negative charge on the chlorine atom.
There are various ways of assigning values for the electronegativity of an element. Pauling electronegativities are based on bond dissociation energies using a scale in which fluorine, the most electronegative element, has the value 4 and francium, the lowest electronegative element, has the value 0.7.
energy → energija
Energy (E, U) is the characteristic of a system that enables it to do work. Like work itself, it is measured in joules (J).
The internal energy of a body is the sum of the potential energy and the kinetic energy of its component atoms and molecules.
Potential energy is the energy stored in a body or system as a consequence of its position, shape, or state (this includes gravitation energy, electrical energy, nuclear energy, and chemical energy).
Kinetic energy is the energy of motion and is usually defined as the work that will be done by a body possessing the energy when it is brought to rest. For a body of mass m having a speed v, the kinetic energy is mv2/2. Kinetic energy is most clearly exhibited in gases, in which molecules have much greater freedom of motion than in liquids and solids.
In an isolated system energy can be transferred from one form to another but the total energy of the system remains constant.
Citing this page:
Generalic, Eni. "Kemijsko oružje." Croatian-English Chemistry Dictionary & Glossary. 29 June 2022. KTF-Split. {Date of access}. <https://glossary.periodni.com>.
Glossary
Periodic Table