irreversible galvanic cell → nepovrativi galvanski članak
Irreversible galvanic cell is a chemical source of direct current, in which reactions that take place on the electrodes are irreversible.
Dalton’s atomic theory → Daltonova atomska teorija
Dalton’s atomic theory is a theory of chemical combination, first stated by John Dalton in 1803. It involves the following postulates:
1. Elements consist of indivisible small particles (atoms).
2. All atoms of the same element are identical; different elements have different types of atom.
3. Atoms can neither be created nor destroyed.
4. ’Compound elements’ (i.e. compounds) are formed when atoms of different elements join in simple ratios to form ’compound atoms’ (i.e. molecules).
Dalton also proposed symbols for atoms of different elements (later replaced by the present notation using letters).
differential thermal analysis → diferencijalna termalna analiza
Differential thermal analysis (DTA) is a technique that is often used to analyze materials that react or decompose at higher temperatures. The difference in temperature between the sample and an inert reference material is monitored as both are heated in a furnace. Phase transitions and chemical reactions taking place in the sample on heating cause the temperature difference to become larger, at temperatures that are characteristic of the sample.
limiting reactant → mjerodavni reaktant
Limiting reactant is a reactant in a chemical reaction that limits the amount of product that can be formed. The reaction will stop when the entire limiting reagent is consumed. These other reactants are present in excess.
dissociation → disocijacija
Dissociation is the process by which a chemical combination breaks up into simpler constituents as a result of either added energy (dissociated by heat), or the effect of a solvent on a dissolved polar compound (electrolytic dissociation). It may occur in the gaseous, solid, or liquid state, or in a solution.
An example of dissociation is the reversible reaction of hydrogen iodide at high temperatures
The term dissociation is also applied to ionisation reactions of acids and bases in water. For example
which is often regarded as a straightforward dissociation into ions
mineral acid → mineralna kiselina
Mineral acid is an acid made from minerals by chemical reaction, e.g. hydrochloric acid is produced from sodium chloride and sulphuric acid is made from sulphur.
nascent state → nascentno stanje
Nascent state is an especially active state of an element in a moment when it is released from a compound during chemical reaction, e.g. nascent hydrogen.
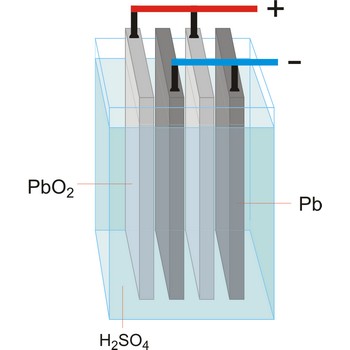
electrochemical cell → elektrokemijski članak
Electrochemical cell is a device that converts chemical energy into electrical energy or vice versa when a chemical reaction is occurring in the cell. It consist of two electronically conducting phases (e.g., solid or liquid metals, semiconductors, etc) connected by an ionically conducting phase (e.g. aqueous or non-aqueous solution, molten salt, ionically conducting solid). As an electric current passes, it must change from electronic current to ionic current and back to electronic current. These changes of conduction mode are always accompanied by oxidation/reduction reactions.
An essential feature of the electrochemical cell is that the simultaneously occurring oxidation-reduction reactions are spatially separated. E.g., in a spontaneous chemical reaction during the oxidation of hydrogen by oxygen to water, electrons are passed directly from the hydrogen to the oxygen.
In contrast, in the spontaneous electrochemical reaction in a galvanic cell the hydrogen is oxidised at the anode by transferring electrons to the anode and the oxygen is reduced at the cathode by accepting electrons from the cathode. The ions produced in the electrode reactions, in this case positive hydrogen ions and the negative hydroxyl (OH-) ions, will recombine in the solution to form the final product of the reaction: water. During this process the electrons are conducted from the anode to the cathode through an outside electric circuit where the electric current can drive a motor, light a light bulb, etc. The reaction can also be reversed: water can be decomposed into hydrogen and oxygen by the application of electrical power in an electrolytic cell.
oxidation → oksidacija
The term oxidation originally meant a reaction in which oxygen combines chemically with another substance. More generally, oxidation is a part of a chemical reaction in which a reactant loses electrons (increases oxidation number). Simultaneous reduction of a different reactant must occur (redox reaction).
electrolytic cell → elektrolitska ćelija
Electrolytic cell is an electrochemical cell that converts electrical energy into chemical energy. The chemical reactions do not occur spontaneously at the electrodes when they are connected through an external circuit. The reaction must be forced by applying an external electric current. It is used to store electrical energy in chemical form (rechargeable battery). It is also used to decompose or produce (synthesise) new chemicals by the application of electrical power. This process is called electrolysis, e.g., water can be decomposed into hydrogen gas and oxygen gas. The free energy change of the overall cell reaction is positive.
Citing this page:
Generalic, Eni. "Kemijska reakcija." Croatian-English Chemistry Dictionary & Glossary. 29 June 2022. KTF-Split. {Date of access}. <https://glossary.periodni.com>.
Glossary
Periodic Table