antioxidant → antioksidans
Antioxidants are compounds that slow down oxidation processes that degrade foods, fuels, rubber, plastic, and other materials. Antioxidants like butylated hydroxyanisole (BHA), are added to food to prevent fats from becoming rancid and to minimize decomposition of vitamins and essential fatty acids; they work by scavenging destructive free radicals from the food.
activated charcoal → aktivni ugljen
Activated charcoal or activated carbon is charcoal that has been activated for adsorption by steaming or by heating in a vacuum. Charcoal is obtained by burning wood, nutshells, coconut husks or other materials. Charcoal becomes activated by heating it with steam to approximately 1000 °C in the absence of oxygen.
The chemical nature of amorphous carbon, combined with a high surface area makes it an ideal medium for the adsorption of organic chemicals. A single gram of such material can have 400 m2 to 1 200 m2 square meters of surface area. Activated charcoal is widely used to decolorize liquids, recover solvents, and remove toxins from water and air.
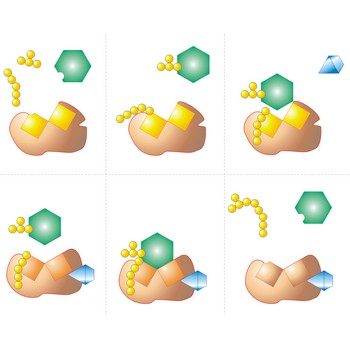
active site → aktivno mjesto
Active site is a pocket or crevice on an enzyme molecule that fits reactant molecules like a hand in a glove. The active site lowers the activation energy for reaction
azo compounds → azo-spojevi
Azo compounds are organic compounds containing the group -N=N- linking two other groups. They can be formed by reaction of a diazonium ion with a benzene ring.
biochemistry → biokemija
Biochemistry is the study of the chemistry of living organisms, especially the structure and function of their chemical components (principally proteins, carbohydrates, lipids and nucleic acids).
bioelement → bioelement
Bioelement is any chemical element that is found in the molecules and compounds that make up living organism.
Boudouard’s equilibrium → Boudouardova ravnoteža
Boudouard’s equilibrium is established when carbon dioxide reacts with carbon. Because of reactions endothermity the temperature increase shifts the reaction rightwards and the temperature reduction leftwards.
adenosine triphosphate → adenozin trifosfat
Adenosine triphosphate (ATP) is nucleotide that is of fundamental importance as a carrier of chemical energy in all living organisms. It consists of adenin linked to D-ribose).
alkaline earth metal → zemnoalkalijski metal
Alkali earth metal is a term that refers to six elements: beryllium (Be), magnesium (Mg), calcium (Ca), strontium (Sr), barium (Ba), and radium (Ra). These elements make up group 2 of the periodic table of elements. They all exhibit a single oxidation state, +2. They are all light and very reactive. Barium and radium are the most reactive and beryllium is the least.
To denote slightly soluble metal oxides chemists formerly used the term "earth". The oxides of barium, strontium, and calcium resemble alumina (Al2O3), a typical "earth", but form alkaline mixtures with water. For this reason barium, strontium, and calcium were called alkaline earth metals. This name has now been extended to include all of the elements of group 2.
alkanes → alkani
Alkanes (paraffins) are acyclic branched or unbranched hydrocarbons having the general formula CnH2n+2, and therefore consisting entirely of hydrogen atoms and saturated carbon atoms. In the systematic chemical nomenclature alkane names end in the suffix -ane. They form a homologous series (the alkane series) methane (CH4), ethane (C2H6), propane (C3H8), butane (C4H10), etc. The lower members of the series are gases; the high-molecular mass alkanes are waxy solid. Generaly the alkanes are fairly unreactive. They form haloalkanes with halogens when irradiated with ultraviolet radiation. Alkanes are present in natural gas and petroleum.
Citing this page:
Generalic, Eni. "Kemijska reakcija." Croatian-English Chemistry Dictionary & Glossary. 29 June 2022. KTF-Split. {Date of access}. <https://glossary.periodni.com>.
Glossary
Periodic Table