entropy → entropija
Entropy (S) is a measure of the unavailability of a system’s energy to do work; in a closed system, an increase in entropy is accompanied by a decrease in energy availability. When a system undergoes a reversible change the entropy (S) changes by an amount equal to the energy (Q) transferred to the system by heat divided by the thermodynamic temperature (T) at which this occurs.
All real processes are to a certain extent irreversible changes and in any closed system an irreversible change is always accompanied by an increase in entropy.
Faraday’s laws of electrolysis → Faradayevi zakoni elektrolize
Faraday’s laws of electrolysis are two laws found by British chemist and physicist Michael Faraday (1791-1867) in his experiments on electrolysis:
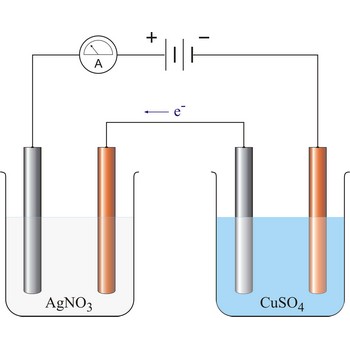
1. The quantity of matter extracted on the electrode is proportional to the quantity of charge (Q = I·t) which has flown in electrolysis time.
where z = number of electrons changed in reaction and F = Faraday’s constant which equals 96 487 C mol-1.
2. The masses of the elements liberated by the same quantity of electricity are directly proportional to their chemical equivalents.
96 487 C will discharge 1 mol Ag and 1/2 mol Cu. The relevant half reactions are:
permeability → permeabilnost
Permeability (Latin permeare, to pass through) is a passage or diffusion of a gas, vapour, liquid, or solid through a material without physically or chemically affecting it.
polymorphic transition → polimorfni prijelaz
Polymorphic transition is a reversible transition of a solid crystalline phase at a certain temperature and pressure to another phase of the same chemical composition with a different crystal structure. For examples, the transitions of quartz (SiO2) at 1 143 K to tridymite, and at 1 743 K to cristobalite.
fuel cell → gorivi članak
Fuel cell is a device that converts chemical energy into electrical energy. It is different from a battery in that the energy conversion continues as long as fuel and oxidising agent are fed to the fuel cell; that is, in principle indefinitely. (A battery is manufactured with a limited amount of chemicals, and it is exhausted when all the chemicals have reacted.) It is a galvanic cell where spontaneous chemical reactions occur at the electrodes. The fuel is oxidised at the anode, and the oxidising agent (almost always oxygen or air) is reduced at the cathode. Presently, the most commonly used fuel is hydrogen. More conventional fuels (e.g., petrol or natural gas) must be converted (reformed) into hydrogen before they can be utilised in a fuel cell.
Some fuel cells employ an aqueous solution as electrolyte, that can be either acidic or basic (alkaline), or an ion-exchange membrane soaked in aqueous solution can act as the electrolyte. These fuel cells operate at relatively low temperatures (from room temperature to not much above the boiling point of water). Some fuel cells employ molten salts (especially carbonates) as electrolytes and have to operate at temperatures of several hundred degrees centigrade (Celsius). Others employ ionically conductive solids as electrolyte and must operate close to 1 000 °C.
fugacity → fugacitet
Fugacity (f) is a thermodynamic function used in place of partial pressure in reactions involving real gases and mixtures. For a component of a mixture, it is defined by
where μ is the chemical potential.
The fugacity of a gas is equal to the pressure if the gas is ideal. The fugacity of a liquid or solid is the fugacity of the vapour with which it is in equilibrium. The ratio of the fugacity to the fugacity in some standard state is the activity.
potassium glass → kalijevo staklo
Potassium glass is a type of glass produced from potassium silicates and calcium with potassium carbonate. It dissolves harder than regular glass and it is used in production of chemical vessels.
Citing this page:
Generalic, Eni. "Kemijska promjena." Croatian-English Chemistry Dictionary & Glossary. 29 June 2022. KTF-Split. {Date of access}. <https://glossary.periodni.com>.
Glossary
Periodic Table