Gratzel solar cell → Gratzelova sunčeva ćelija
Grätzel solar cell is photoelectrochemical cell, developed by Michael Grätzel and collaborators, simulates some characteristics of the natural solar cell, which enables photosynthesis take place. In natural solar cell the chlorophyll molecules absorb light (most strongly in the red and blue parts of the spectrum, leaving the green light to be reflected). The absorbed energy is sufficient to knock an electron from the excited chlorophyll. In the further transport of electron, other molecules are involved, which take the electron away from chlorophyll. In Grätzel cell, the tasks of charge-carrier generation and transport are also assigned to different species.
His device consists of an array of nanometre-sized crystallites of the semiconductor titanium dioxide, welded together and coated with light-sensitive molecules that can transfer electrons to the semiconductor particles when they absorb photons. So, light-sensitive molecules play a role equivalent to chlorophyll in photosynthesis. In Grätzel cell, the light-sensitive molecule is a ruthenium ion bound to organic bipyridine molecules, which absorb light strongly in the visible range; titanium dioxide nanocrystals carry the received photoexcited electrons away from electron donors. On the other hand, a donor molecule must get back an electron, so that it can absorb another photon. So, this assembly is immersed in a liquid electrolyte containing molecular species (dissolved iodine molecules) that can pick up an electron from an electrode immersed in the solution and ferry it to the donor molecule. These cells can convert sunlight with efficiency of 10 % in direct sunlight and they are even more efficient in diffuse daylight.
Kjeldahl’s method → Kjeldahlov postupak
Kjeldahl’s method is an analytical method for determination of nitrogen in certain organic compounds. The method was developed by the Danish chemist Johan Kjeldahl (1849-1900).
It involves addition of a small amount of anhydrous potassium sulphate to the test compound, followed by heating the mixture with concentrated sulphuric acid, often with a catalyst such as copper sulphate. As a result ammonia is formed. After alkalyzing the mixture with sodium hydroxyde, the ammonia is separated by distillation, collected in standard acid, and the nitrogen determined by back-titration.
- Kjeldahl flask for decomposition (500 ml – macro or 100 ml - micro)
- funnel for alkaline solution
- Wagner tube (drop catcher)
- condenser
- absorption flask with known volume of standard acid
lanthanum → lantan
Lanthanum was discovered by Carl Gustaf Mosander (Sweden) in 1839. The origin of the name comes from the Greek word lanthanein meaning to lie hidden. It is soft, silvery-white, malleable, ductile metal. Readily tarnishes in air. Reaction with water releases hydrogen gas. Metal ignites and burns readily. Reacts with oxidants. Lanthanum is found with rare earths in monazite and bastnasite. Monazite sand typical contains 25 % lanthanum. It is used in the electrodes of high-intensity, carbon-arc lights. Because it gives glass refractive properties, it is used in expensive camera lenses.
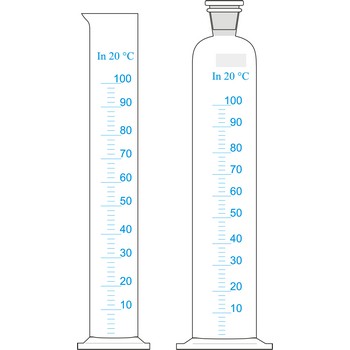
measuring cylinder → menzura
Measuring cylinders (graduated cylinders) are graduated glass cylinders with a capacity from 2 mL to 2 L. They are used when reagent solutions for volume measuring are prepared when accuracy is not of great relevance. The larger the measuring cylinder, the bigger the measuring error.
neodymium → neodimij
Neodymium was discovered by Carl F. Auer von Welsbach (Austria) in 1885. The origin of the name comes from the Greek words neos didymos meaning new twin. It is silvery-white, rare-earth metal that oxidizes easily in air. Reacts slowly in cold water, more rapidly as heated. Metal ignites and burns readily. Neodymium is made from electrolysis of its halide salts, which are made from monazite sand. Used in making artificial ruby for lasers. Also in ceramics and for a special lens with praseodymium. Also to produce bright purple glass and special glass that filters infrared radiation. Misch metal, used in the manufacture of pyrophoric alloys for cigarette lighters, contains about 18 % neodymium metal. (Typically composition of misch metal are Ce:Nd:Pr:La:Other rare earth=50:18:6:22:4). Neodymium is used to create some of the most powerful permanent magnets on Earth, known as NIB magnets they consist of neodymium, iron, and boron.
Petri dish → Petrijeva zdjelica
Petri dish is a shallow glass or plastic flat bottomed dish with a lid. Used primarily in laboratories for the culture of bacteria and other microorganisms on specially prepared media. It was named after the German bacteriologist Julius Richard Petri (1852-1921) who invented it in 1877.
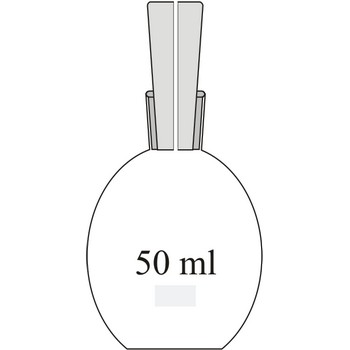
picnometer → piknometar
Picnometer is a special glass flask which is used for determining a relative density of liquids using the weight of a known volume. It usually has a glass faceted cork which is pierced in the centre like a thin capillary through which surplus of liquid runs out.
potassium → kalij
Potassium was discovered by Sir Humphry Davy (England) in 1807. The origin of the name comes from the Arabic word qali meaning alkali (the origin of the symbol K comes from the Latin word kalium). It is soft, waxy, silver-white metal. Fresh surface has silvery sheen. Quickly forms dull oxide coating on exposure to air. Reacts strongly with water. Reacts with water to give off flammable gas. Reacts violently with oxidants. Occurs only in compounds. Potassium is found in minerals like carnallite [(KMgCl3)·6H2O] and sylvite (KCL). Pure metal is produced by the reaction of hot potassium chloride and sodium vapours in a special retort. Used as potash in making glass and soap. Also as saltpetre, potassium nitrate (KNO3) to make explosives and to colour fireworks in mauve. Vital to function of nerve and muscle tissues.
pipette → pipeta
Pipettes are glass tubes which are tapers towards at both ends into narrow opened tubes. According to their design two types of pipettes can be distinguished:
Volumetric pipettes
Volumetric pipettes (transfer or belly pipette) are used in volumetric analysis, when there is a need for taking exact smaller volume of a sample solution or reagent. The upper tube of volumetric pipette has a ringlike marking (mark) which marks its calibrated volume. Pipettes calibrated to deliver (TD or Ex) the indicated volume. By sucking in (with mouth, propipette or a water pump) the liquid is pulled in a little bit above the mark and the opening of the pipet is closed with a forefingertip. Outer wall of pipet is wiped and, with a slight forefinger loosening, the liquid is released until it reaches the mark. Mark must figure as a tangent on a lower edge of the liquid meniscus. A pipette is emptied out by lifting the forefinger off and letting the liquid flow out of the pipette freely. After another 15 s and the tip of the pipette is pulled onto the inner wall of the vessel. It is absolutely forbidden to blow out the contents of the pipette
Graduated pipettes
Graduated pipettes (Mohr pipette) have a scale divided into units of one and of 1/10th of a millilitre. Because of their wide necks it is less accurate than the volumetric pipette. They are used when taking volume of solutions in which accuracy does not have to be very high. They are filled in the same way as volumetric ones and liquid can be gradually released.
praseodymium → praseodimij
Praseodymium was discovered by Carl F. Auer von Welsbach (Austria) in 1885. The origin of the name comes from the Greek words prasios didymos meaning green twin. It is silvery white, moderately soft, malleable, ductile metal. Reacts slowly with oxygen. Reacts rapidly with water. Metal ignites and burns readily. Praseodymium is obtained from same salts as neodymium. Used with neodymium to make lenses for glass maker’s goggles since it filters out the yellow light present in glass blowing. Alloyed with magnesium creates a high-strength metal used in aircraft engines. Misch metal, used in the manufacture of pyrophoric alloys for cigarette lighters, contains about 5 % praseodymium metal. (Typically composition of misch metal are Ce:Nd:Pr:La:Other rare earth=50:18:6:22:4).
Citing this page:
Generalic, Eni. "Kalijevo staklo." Croatian-English Chemistry Dictionary & Glossary. 29 June 2022. KTF-Split. {Date of access}. <https://glossary.periodni.com>.
Glossary
Periodic Table