allomerism → alomerija
Allomerism is the appearance of substances with different chemical composition but the same crystalline form.
antioxidant → antioksidans
Antioxidants are compounds that slow down oxidation processes that degrade foods, fuels, rubber, plastic, and other materials. Antioxidants like butylated hydroxyanisole (BHA), are added to food to prevent fats from becoming rancid and to minimize decomposition of vitamins and essential fatty acids; they work by scavenging destructive free radicals from the food.
activated charcoal → aktivni ugljen
Activated charcoal or activated carbon is charcoal that has been activated for adsorption by steaming or by heating in a vacuum. Charcoal is obtained by burning wood, nutshells, coconut husks or other materials. Charcoal becomes activated by heating it with steam to approximately 1000 °C in the absence of oxygen.
The chemical nature of amorphous carbon, combined with a high surface area makes it an ideal medium for the adsorption of organic chemicals. A single gram of such material can have 400 m2 to 1 200 m2 square meters of surface area. Activated charcoal is widely used to decolorize liquids, recover solvents, and remove toxins from water and air.
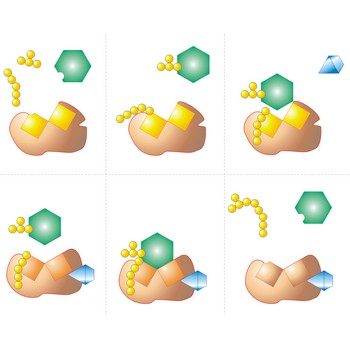
active site → aktivno mjesto
Active site is a pocket or crevice on an enzyme molecule that fits reactant molecules like a hand in a glove. The active site lowers the activation energy for reaction
azo compounds → azo-spojevi
Azo compounds are organic compounds containing the group -N=N- linking two other groups. They can be formed by reaction of a diazonium ion with a benzene ring.
Citing this page:
Generalic, Eni. "Jednadžba kemijske reakcije." Croatian-English Chemistry Dictionary & Glossary. 29 June 2022. KTF-Split. {Date of access}. <https://glossary.periodni.com>.
Glossary
Periodic Table