Schiff base → Schiffova baza
Schiff base is a class of compounds derived by the chemical reaction (condensation) of aldehydes or ketones with aromatic amines, for example
They were named after the German chemist Hugo Schiff (1834-1915).
fugacity → fugacitet
Fugacity (f) is a thermodynamic function used in place of partial pressure in reactions involving real gases and mixtures. For a component of a mixture, it is defined by
where μ is the chemical potential.
The fugacity of a gas is equal to the pressure if the gas is ideal. The fugacity of a liquid or solid is the fugacity of the vapour with which it is in equilibrium. The ratio of the fugacity to the fugacity in some standard state is the activity.
theories of catalysis → teorije katalize
Theories of catalysis explain the influence of the catalysts upon the rate of a reaction by describing the detailed mechanism by which the catalyst is involved in the steps of the chemical reaction.
thermit welding → termitno zavarivanje
Thermit welding is a group of welding processes in which fusion is produced by heating with superheated liquid metal resulting from a chemical reaction between a metal oxide and aluminium.
thermochemistry → termokemija
Termochemistry is the study of heat absorbed or released during chemical changes.
valence shell → valentna ljuska
Valence shell is the shell corresponding to the highest value of principal quantum number in the atom. The valence electrons in this shell are on average farther from the nucleus than other electrons. They are often directly involved in chemical reaction.
Hesse’s law → Hessov zakon
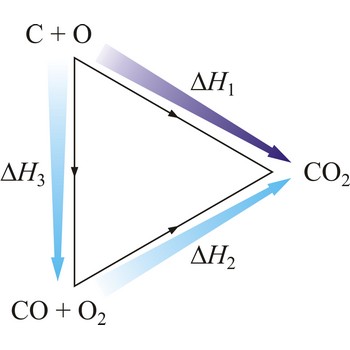
Hesse’s law says that reaction heat of some chemical change does not depend on the way in which the reaction is conducted, but only on starting and ending system state. Hesse’s law is also known as the law of constant heat summation. Hesse’s law is also known as the law of constant heat summation. The law was first put forward in 1840 by the Swiss-born Russian chemist Germain Henri Hess (1802-1850).
Hesse’s law can be used to obtain thermodynamic data that cannot be measured directly. For example, it is very difficult to control the oxidation of graphite to give pure CO. However, enthalpy for the oxidation of graphite to CO2 can easily be measured. So can the enthalpy of oxidation of CO to CO2. The application of Hess’s law enables us to estimate the enthalpy of formation of CO.
| C(s) + O2(g) →← CO2(g) | ΔrH1 = -393 kJ mol-1 |
| CO(g) + 1/2O2(g) →← CO2(g) | ΔrH2 = -283 kJ mol-1 |
| C(s) + 1/2O2(g) →← CO(g) | ΔrH3 = -110 kJ mol-1 |
The equation shows the standard enthalpy of formation of CO to be -110 kJ/mol.
hydrolysis → hidroliza
Hydrolysis is a chemical reaction in which water reacts with another substance to form two or more new substances. This involves ionisation of the water molecule, as well as splitting of the compound hydrolysed, e.g.
Examples are conversion of starch to glucose by water in the presence of suitable catalysts and a reaction of the ions of a dissolved salt to form various products, such as acids, complex ions, etc.
indicator → indikator
Indicator is a substance used to show the presence of a chemical substance or ion by its colour. Acid-base indicators are compounds, such as phenolphtaleine and methyl orange, which change colour reversibly, depending on whether the solution is acidic or basic. Oxidation-reduction indicators are substances that show a reversible colour change between oxidised and reduced forms.
law of conservation of mass → zakon o očuvanju mase
Law of conservation of mass states that no detectable gain or loss in mass occurs in chemical reactions. The state of a substance may change in a chemical reaction, for example, from a solid to a gas, but its total mass will not change. Note that the energy released (exothermic) or adsorbed (endothermic) in a chemical reaction is a result of energy transfer between atoms and their environment.
Citing this page:
Generalic, Eni. "Jednadžba kemijske reakcije." Croatian-English Chemistry Dictionary & Glossary. 29 June 2022. KTF-Split. {Date of access}. <https://glossary.periodni.com>.
Glossary
Periodic Table