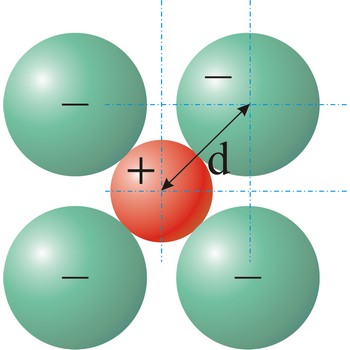
ionic radius → ionski radijus
Ionic radius is the radius of anions and cations in crystalline ionic compounds, as determined by consistently partitioning the center-to-center distance of ions in those compounds. In general, negative ions have larger ionic radii than positive ions.
water ion product → ionski produkt vode
Water ion product (Kw) is a concentration product of hydrogen and hydroxide ions. For the reaction:
the equilibrium expression would be:
Note that all pure liquid terms are omitted, hence H2O does not appear in the denominator. At 25 °C, Kw = 1.0×10-14 mol2dm-6 = (Ka)(Kb)
conditional electrode potential → uvjetni elektrodni potencijal
Conditional or formal electrode potential (E°’) is equal to electrode potential (E) when overall concentrations of oxidised and reduced form in all its forms in a solution are equal to one. Conditional electrode potential includes all effects made by reactions that do not take part in the electron exchange, but lead to change of ion power, changes of pH, hydrolysis, complexing, precipitating, etc.
At 298 K (25 °C) and by converting natural (Napierian) logarithms into decimal (common, or Briggian) logarithms, Nernst’s equation for electrode potential can be written as follows:
deionised water → deionizirana voda
Deionised water is water from which ionic salts have been removed by ion-exchange. It is used for many purposes as an alternative to distilled water.
| Type of water | Conductivity / µScm-1 |
|---|---|
| Ultrapure water | 0.05 |
| Distilled water | 0.5 |
| Tap water | 50 |
| Ocean water | 50 000 |
regeneration → regeneracija
Regeneration is the process of restoring an ion exchange medium to a usable state after exhaustion. The cation exchanger is normally regenerated with hydrochloric acid and the anion exchanger with sodium hydroxide.
water softening → omekšavanje vode
Water softening is a process in which calcium and magnesium ions are removed from water. It is usually done by ion exchanger which exchanges removed ions with sodium ones.
glass electrode → staklena elektroda
Glass electrode is a hydrogen-ion responsive electrode usually consisting of a bulb, or other suitable form, of special glass attached to a stem of high resistance glass complete with internal reference electrode and internal filling solution system. Glass electrode is also available for the measurement of sodium ions.
The glass electrode, which consists of a thin wall glass bulb, has an extremely high electrical resistance. The membrane of a typical glass electrode (with a thickness of 0.03 mm to 0.1 mm) has an electrical resistance of 30 MΩ to 600 MΩ. The surface of a glass membrane must be hydrated before it will function as a pH electrode. When a glass surface is immersed in an aqueous solution then a thin solvated layer (gel layer) is formed on the glass surface in which the glass structure is softer. This applies to both the outside and inside of the glass membrane.
The simplest explanation for the working of the thin glass electrode is that the glass acts as a weak acid (Glass-H).
The hydrogen ion activity of the internal solution is held constant. When a solution of different pH from the inside comes in contact with the outside of the glass membrane, the glass is either deprotonated or protonated relative to the inside of the glass. The difference in pH between solutions inside and outside the thin glass membrane creates electromotive force in proportion to this difference in pH.
zeolite → zeolit
Zeolite is a natural or synthetic hydrated aluminosilicate with an open three-dimensional crystal structure, in which water molecules are held in cavites in the latice. The water can be driven off by heating and the zeolite can then absorb other molecules of suitable size. Zeolites are used for separating mixtures by selective absorption.
activity coefficient → koeficijent aktiviteta
Activity coefficient (γ or f) is a fractional number which, when multiplied by the molar concentration of a substance in solution, yields the chemical activity. This term gives an idea of how much interaction exists between molecules at higher concentration.
In solutions of very low ionic strength, when m is less than 0.01, the Debye-Hückel limiting law can be used to calculate approximate activity coefficients
where γi = activity coefficient of the species i, zi = charge on the species i and μ = ionic strength of the solution.
adiabatic process → adijabatski proces
Adiabatic process is a thermodynamic process in which no heat enters or leaves the system. In general, an adiabatic change involves a fall or rise in temperature of the system.
Citing this page:
Generalic, Eni. "Ionska izmjena." Croatian-English Chemistry Dictionary & Glossary. 29 June 2022. KTF-Split. {Date of access}. <https://glossary.periodni.com>.
Glossary
Periodic Table