psychoactive drug → psihoaktivna droga
Psychoactive drugs are natural (mescaline) or synthetic substances (LSD) which take effect on central nervous system causing euphoria, and by lengthened use they also cause addiction, gradually destroying the nervous system.
equilibrium constant → konstanta ravnoteže
The equilibrium constant (K) was originally introduced in 1863 by Norwegian chemists C.M. Guldberg and P. Waage using the law of mass action. For a reversible chemical reaction represented by the equation
chemical equilibrium occurs when the rate of the forward reaction equals the rate of the back reaction, so that the concentrations of products and reactants reach steady-state values.
The equilibrium constant is the ratio of chemical activities of the species A, B, C, and D at equilibrium.
To a certain approximation, the activities can be replaced by concentrations.
For gas reactions, partial pressures are used rather than concentrations
The units of Kp and Kc depend on the numbers of molecules appearing in the stoichiometric equation (a, b, c, and d).
The value equilibrium constant depends on the temperature. If the forward reaction is exothermic, the equilibrium constant decreases as the temperature rises. The equilibrium constant shows the position of equilibrium. A low value of K indicates that [C] and [D] are small compared to [A] and [B]; i.e. that the back reaction predominates.
The equilibrium constant is related to ΔrG°, the standard Gibbs free energy change in the reaction, by
resonant frequency → rezonantna frekvencija
All vibrating systems have one or more resonant frequencies, which depend on system characteristics. If an external force is applied on the system at that frequency, the vibrations will be much greater than at slight different frequencies.
freon → freon
Freon (chlorofluorocarbon, CFC) a type of compound in which some or all of the hydrogen atoms of hydrocarbon (usually an alkane) have been replaced by chlorine and fluorine atoms. Most CFC are chemically uncreative and are stable at high temperatures. They are used as aerosol propellants, refrigerants, and solvents, and in the manufacture of rigid packaging foam. CFC because of their chemical inertness, can diffuse unchanged into the upper atmosphere. Here, photochemical reactions cause them to break down and react with ozone. For his reason, their use has been discouraged.
Gibbs phase rule → Gibbsov zakon faza
Gibbs phase rule is the relationship used to determine the number of state variables, usually chosen from among temperature, pressure, and species composition in each phase, which must be specified to fix the thermodynamic state of a system in equilibrium:
where C is the number of components in a mixture, P is the number of phases, and F is the degrees of freedom, i.e., the number of intensive variables that can be changed independently without affecting the number of phases.
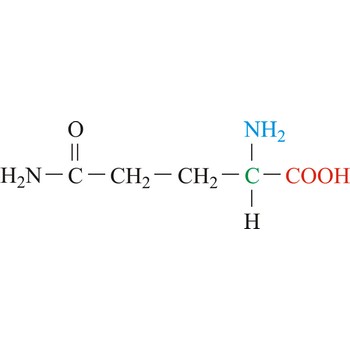
glutamine → glutamin
Glutamine is neutral amino acids with polar side chains. It serves as an important carrier of ammonia and contributes it to the formation of urea and purines. Glutamine is not recognized as an essential amino acid but may become conditionally essential in certain situations, including intensive athletic training or certain gastrointestinal disorders. It is synthesized by the enzyme glutamine synthetase from glutamate and ammonia.
- Abbreviations: Gln, Q
- IUPAC name: 2,5-diamino-5-oxopentanoic acid
- Molecular formula: C5H10N2O3
- Molecular weight: 146.14 g/mol
thermodynamic equilibrium → termodinmička ravnoteža
Thermodynamic equilibrium is a system equilibrium in which energy that it gains from its surroundings is exactly balanced by the energy that it loses, no matter how much time is allowed to pass.
Citing this page:
Generalic, Eni. "Inercijski referentni sustavi." Croatian-English Chemistry Dictionary & Glossary. 29 June 2022. KTF-Split. {Date of access}. <https://glossary.periodni.com>.
Glossary
Periodic Table