ideal gas law → jednadžba stanja idealnog plina
The generalized ideal gas law is derived from a combination of the laws of Boyle and Charles. Ideal gas law is the equation of state
which defines an ideal gas, where p is pressure, V molar volume, T temperature, and R the molar gas constant (8.314 JK-1mol-1).
ideal solution → idealna otopina
Ideal solution is a solution in which solvent-solvent and solvent-solute interactions are identical, so that properties such as volume and enthalpy are exactly additive. Ideal solutions follow Raoult’s law, which states that the vapour pressure pi of component i is pi = xi pi*, where xi is the mole fraction of component i and pi* the vapour pressure of the pure substance i.
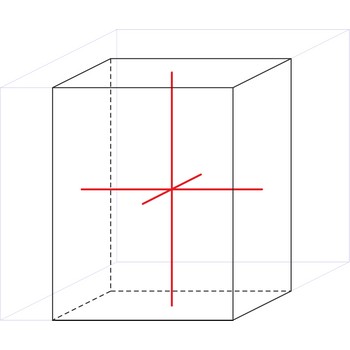
monoclinic crystal system → monoklinski kristalni sustav
Minerals of the monoclinic crystal system are referred to three unequal axes. Two of these axes (a and c) are inclined toward each other at an oblique angle; these are usually depicted vertically. The third axis (b) is perpendicular to the other two and is called the ortho axis. The two vertical axes therefore do not intersect one another at right angles, although both are perpendicular to the horizontal axis.
a ≠ b ≠ c
α = γ = 90° ≠ β
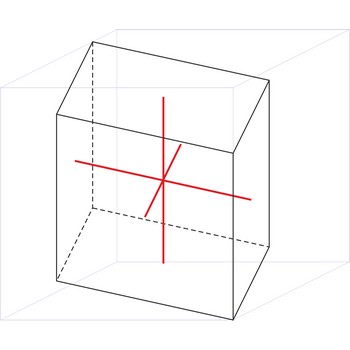
orthorhombic crystal system → ortorompski kristalni sustav
Orthorhombic crystal system is also known as the rhombic system. Minerals of the orthorhombic crystal system are referred to three mutually perpendicular axes, each of which is of a different length than the others.
a ≠ b ≠ c
α = β = γ = 90°
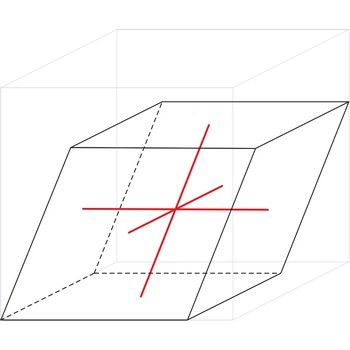
rhombohedral crystal system → romboedarski kristalni sustav
Rhombohedral crystal system is also known as the trigonal system. The crystallographic axes used in this system are of equal length. None of the axes are perpendicular to any other axis.
a = b = c
α= β = γ ≠ 90°
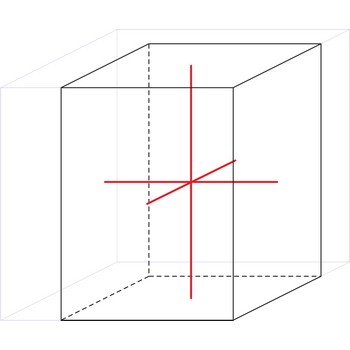
tetragonal crystal system → tetragonski kristalni sustav
Minerals of the tetragonal crystal system are referred to three mutually perpendicular axes. The two horizontal axes are of equal length, while the vertical axis is of different length and may be either shorter or longer than the other two.
a = b ≠ c
α = β = γ = 90°
triclinic crystal system → triklinski kristalni sustav
Minerals of the triclinic crystal system are referred to three unequal axes, all of which intersect at oblique angles. None of the axes are perpendicular to any other axis.
a ≠ b ≠ c
α ≠ β ≠ γ ≠ 90°
activated charcoal → aktivni ugljen
Activated charcoal or activated carbon is charcoal that has been activated for adsorption by steaming or by heating in a vacuum. Charcoal is obtained by burning wood, nutshells, coconut husks or other materials. Charcoal becomes activated by heating it with steam to approximately 1000 °C in the absence of oxygen.
The chemical nature of amorphous carbon, combined with a high surface area makes it an ideal medium for the adsorption of organic chemicals. A single gram of such material can have 400 m2 to 1 200 m2 square meters of surface area. Activated charcoal is widely used to decolorize liquids, recover solvents, and remove toxins from water and air.
activity → aktivitet
Activity (a) is a thermodynamic function used in place of concentration in equilibrium constants for reactions involving nonideal gases and solutions. For the species i activity is defined as
where ai is the activity of the species i, ci is its molar concentration, and fi is a dimensionless quantity called the activity coefficient.
activity coefficient → koeficijent aktiviteta
Activity coefficient (γ or f) is a fractional number which, when multiplied by the molar concentration of a substance in solution, yields the chemical activity. This term gives an idea of how much interaction exists between molecules at higher concentration.
In solutions of very low ionic strength, when m is less than 0.01, the Debye-Hückel limiting law can be used to calculate approximate activity coefficients
where γi = activity coefficient of the species i, zi = charge on the species i and μ = ionic strength of the solution.
Citing this page:
Generalic, Eni. "Idealni kristal." Croatian-English Chemistry Dictionary & Glossary. 29 June 2022. KTF-Split. {Date of access}. <https://glossary.periodni.com>.
Glossary
Periodic Table