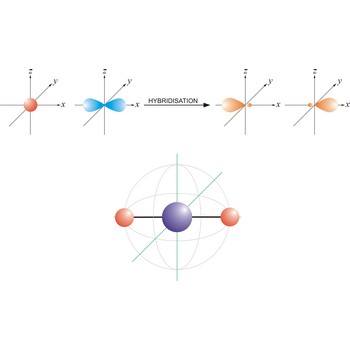
hybridization → hibridizacija
Hybridization is an internal linear combination of atomic orbitals, in which the wave functions of the atomic orbitals are added together to generate new hybrid wave functions. The new orbitals which are formed are hybrids of the originals and have properties (shape, size and energy) that are somewhere in between.
hybrid orbital → hibridne orbitale
Hybrid orbital is an orbital created by mixing together atomic orbitals to form an equal number of new hybrid atomic orbitals. For example, a common hybridization is sp3 where s orbital combine with a three p orbitals to form four new orbitals. After hybridization, all hybrid orbitals have the same energy, lower than p orbitals, but higher than s orbitals.
linear molecular geometry → linearna geometrija molekule
Linear molecule is a molecule in which atoms are deployed in a straight line (under 180° angle). Molecules with an linear electron pair geometries have sp hybridization at the central atom. An example of linear electron pair and molecular geometry are carbon dioxide (O=C=O) and beryllium hydride BeH2.
octahedral molecular geometry → oktaedarska geometrija molekule
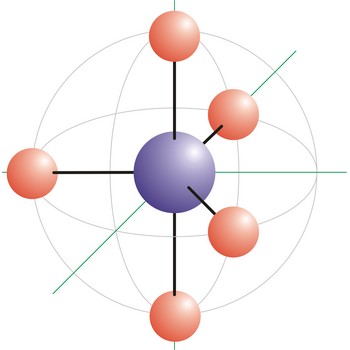
Octahedral molecular geometry (square bipyramidal shape) describes the shape of compounds where six atoms or ligands are symmetrically arranged around a central atom. The sulfur hexafluoride (SF6), with six bonding pairs, is predicted and found to be a regular octahedron. Four of the attachments are positioned in a square plane with 90° bond angles. The remaining two attachments are positioned perpendicular (90°) to the square plane at opposite ends of the central atom. Molecules with an octahedral electron pair geometries have sp3d2 (or d2sp3) hybridization at the central atom.
sp hybrid orbital → sp hibridna orbitala
An sp hybrid orbital is an orbital formed by the linear combination of one s and one p orbital of comparable energy (such 2s and 2p orbitals) on a same atom. The two sp hybrid orbitals are aligned in a straight line in opposite direction (bond angles are 180°). The remaining two p orbitals are at right angles to one another and to the line formed by the two sp orbitals.
sp2 hybrid orbital → sp2 hibridna orbitala
An sp2 hybrid orbital is an orbital formed by the linear combination of one s and two p orbitals of comparable energy (such 2s and 2p orbitals) on a same atom. The three sp2 hybrid orbitals lie in a plane with angle of 120°. The remaining p orbital remains unchanged and is perpendicular to the plane of the three sp2 orbitals.
sp3 hybrid orbital → sp3 hibridna orbitala
An sp3 hybrid orbital is an orbital formed by the linear combination of one s and three p orbitals of comparable energy (such 2s and 2p orbitals) on a same atom. The four sp3 hybrid orbitals point toward the corners of a regular tetrahedron with the bond angle of 109.5°.
T-shaped molecular geometry → T-oblik geometrije molekule
T-shape is a molecular geometry that results when there are 3 bonds and 2 lone pairs around the central atom in the molecule. The atoms bonded to the central atom lie at the ends of a T with 90° angles between them. Molecules with an trigonal bipyramidal electron pair geometries have sp3d (or dsp3) hybridization at the central atom. ICl3 has a T-shaped molecular geometry.
tetrahedral molecular geometry → tetraedarska geometrija molekule
Tetrahedral is a molecular shape that results when there are four bonds and no lone pairs around the central atom in the molecule. The atoms bonded to the central atom lie at the corners of a tetrahedron with 109.5° angles between them. Molecules with an tetrahedral electron pair geometries have sp3 hybridization at the central atom. The ammonium ion (NH4+) and methane (CH4) have a tetrahedral molecular geometry.
trigonal bipyramidal molecular geometry → trigonska bipiramidalna geometrija molekule
Trigonal bipyramidal (trigonal bipyramidal shape) is a molecular geometry that results when there are five bonds and no lone pairs on the central atom in the molecule. Three of the bonds are arranged along the atom’s equator, with 120° angles between them; the other two are placed at the atom’s axis. Axial bonds are at right angles to the equatorial bonds. Molecules with an trigonal bipyramidal electron pair geometries have sp3d (or dsp3) hybridization at the central atom. The PCl5 molecule has a trigonal bipyramidal molecular geometry.
Citing this page:
Generalic, Eni. "Hybridization." Croatian-English Chemistry Dictionary & Glossary. 29 June 2022. KTF-Split. {Date of access}. <https://glossary.periodni.com>.
Glossary
Periodic Table