solid state → čvrsto agregatno stanje
Solid state is characterised by a constant shape and volume. Particles are placed very close to one another and have efect one on another with great attraction forces. Solid bodies do not assume the shape of the container in which they are put.
spin → spin
Spin is the intrinsic angular momentum of an elementary particle, or system of particles such as nucleus, that is also responsible for the magnetic moment; or, a particle or nucleus possessing such a spin. The spins of nuclei have characteristic fixed values. Pairs of neutrons and protons align to cancel out their spins, so that nuclei with an odd number of neutrons and/or protons will have a net non-zero rotational component characterized by a non-zero quantum nuclear spin number.
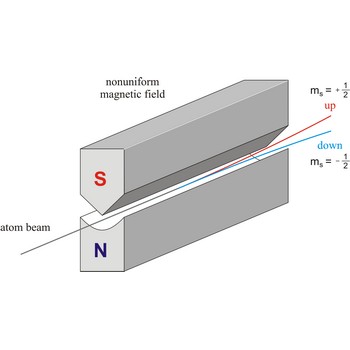
Stern-Gerlach experiment: a beam of silver atoms is split into two beams when it traverses a nonuniform magnetic field. Atoms with spin quantum number ms=+1/2 follow one trajectory, and those with ms=+1/2 follow another.
stoichiometry → stehiometrija
Stoichiometry is the relative proportions elements from compounds or in which substances react. Every chemical reaction has its characteristic proportions. For example, when methane unites with oxygen in complete combustion, 1 mol of methane requires 2 mol of oxygen.
At the same time, 1 mol of carbon dioxide and 2 mol of water are formed as reaction products.
Alternatively, 16 g of methane and 64 g of oxygen produce 44 g of carbon dioxide and 36 g of water.
The stoichiometric relationship between the products and reactants can be used to in calculations.
starch → škrob
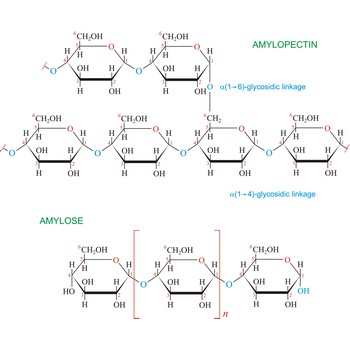
Starch (C6H10O5)x is a polysaccharide used by plants to stockpile glucose molecules. It is the major component of flour, potatoes, rice, beans, corn, and peas. Starch is a mixture of two different polysaccharides: amylose (about 20 %), which is insoluble in cold water, and amylopectin (about 80 %), which is soluble in cold water. Amylose is composed of unbranched chains of D-glucose units joined by α(1→4)-glycosidic linkages. Unlike amylose, which are linear polymers, amylopectin contains α(1→6)-glycoside branches approximately every 25 glucose units.
Starch digestion begins in the mouth via the action of amylase, a digestive enzyme present in saliva. The process is completed in the small intestine by the pancreatic amylase. The final products of starch digestion, glucose molecules, are absorbed into the intestinal bloodstream and transported to the liver. Like most enzymes, glycosidases are highly selective in their action. They hydrolyze only the α-glycoside links in starch and leave the β-glycoside links in cellulose untouched. Starch is important food stuff and is used in adhesives, and sizes, in laundering, pharmacy and medicine.
stratosphere → stratosfera
Stratosphere is the part of the earth’s atmosphere extending from the top of the troposphere (typically 10 km to 15 km above the surface) to about 50 km. It is characterised by an increase in temperature with increasing altitude.
supercritical fluid chromatography → superkritična fluidna kromatografija
Supercritical fluid chromatography (SFC) is a hybrid of gas and liquid chromatography. SFC is of importance because it permits the separation and determination of a group of compounds that are not conveniently handled by either gas or liquid chromatography. These compounds are either nonvolatile or thermally labile so that gas chromatography cannot be used and they do not contain functional groups that make possible detection by liquid chromatography. SFC has been applied to a wide variety of materials including natural prodcuts, drugs, foods, pesticides and herbicides, fossil fuels, explosives and propellants.
superfluid helium → superfluidni helij
Superfluidity in helium-4 was discovered in 1938 by the Soviet physicist Pyotr Leonidovich Kapitsa. Helium-4 exhibits superfluidity when it is cooled below 2.18 K (-270.97 C), which is called the lambda (λ) point. At these temperatures, helium-4 exhibits the characteristics of two distinct fluids, one of which appears to flow without friction. An extensive series of experiments showed that in this state of helium, called helium II (He II), there is an apparent enormous rise in heat conductivity, at an increase rate of about three million. Another unusual property of He II is its mobile, rapid flow through capillaries or over the rim of its containment vessel as a thin film that exhibits no measurable viscosity and appears unaffected by the forces of gravity or evaporation and condensation.
Tafel plot → Tafelov dijagram
Tafel plot is the graph of the logarithm of the current density j against the overpotential η in electrochemistry in the high overpotential limit. An electrode when polarised frequently yields a current potential relationship over a region which can be approximated by:
where η is change in open circuit potential, i is the current density, B and i0 is constants. B is known as the Tafel Slope. If this behaviour is observed a plot of the semilogarithmic components is known as the Tafel line and the diagram is called the Tafel diagram.
thermal expansion → toplinsko rastezanje
Thermal expansion is a change in dimensions of a material resulting from a change in temperature. All objects change size with changes in temperature. The change ΔL in any linear dimension L is given by
in which α is the thermal coefficient of linear expansion, Lo is the initial or reference dimension at temperature To (reference temperature) and ΔT is change in temperature which causes the change in dimension.
The change ΔV in the volume of a sample of solid or liquid is
Here γ is coefficient of volume expansion, Vo is the volume of the sample at temperature To and ΔV is the change in volume over the temperature range ΔT. With isotropic substances, the coefficient of volume expansion can be calculated from the coefficient of linear expansion: γ = 3α.
thermodynamic laws → termodinamički zakoni
Thermodynamic laws are the foundation of the science of thermodynamics:
First law: The internal energy of an isolated system is constant; if energy is supplied to the system in the form of heat dq and work dw, then the change in energy dU = dq + dw.
Second law: No process is possible in which the only result is the transfer of heat from a reservoir and its complete conversion to work.
Third law: The entropy of a perfect crystal approaches zero as the thermodynamic temperature approaches zero.
Citing this page:
Generalic, Eni. "Hera chan tvb." Croatian-English Chemistry Dictionary & Glossary. 29 June 2022. KTF-Split. {Date of access}. <https://glossary.periodni.com>.
Glossary
Periodic Table