magnesium → magnezij
Magnesium was discovered by Sir Humphry Davy (England) in 1808. The origin of the name comes from the Greek word Magnesia, a district of Thessaly. It is lightweight, malleable, silvery-white metal. Burns in air with a brilliant white flame and reacts with water as temperature elevates. Can ignite in air. React violently with oxidants. Magnesium is found in large deposits in the form of magnesite, dolomite and other minerals. It is usually obtained by electrolysis of melted magnesium chloride (MgCl2) derived from brines, wells and sea water. Used in alloys to make airplanes, missiles and other uses for light metals. Have structural properties similar to aluminium.
manganese → mangan
Manganese was discovered by Johann Gahn (Sweden) in 1774. The origin of the name comes from the Latin word magnes meaning magnet, or magnesia nigri meaning black magnesia (MnO2). It is hard, brittle, grey-white metal with a pinkish tinge. Impure forms are reactive. Rusts like iron in moist air. Manganese is most abundant ores are pyrolusite (MnO2), psilomelane [(Ba,H2O)2Mn5O10] and rhodochrosite (MnCO3). Pure metal produced by mixing MnO2 with powered Al and ignited in a furnace. Used in steel, batteries and ceramics. The steel in railroad tracks can contain as much as 1.2 % manganese. It is crucial to the effectiveness of vitamin B1.
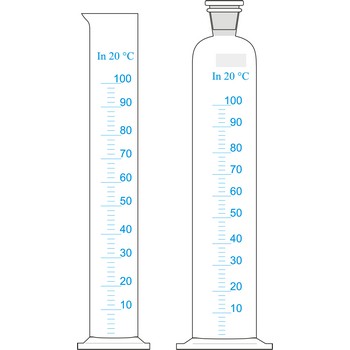
measuring cylinder → menzura
Measuring cylinders (graduated cylinders) are graduated glass cylinders with a capacity from 2 mL to 2 L. They are used when reagent solutions for volume measuring are prepared when accuracy is not of great relevance. The larger the measuring cylinder, the bigger the measuring error.
molybdenum → molibden
Molybdenum was discovered by Carl William Scheele (Sweden) in 1778. The origin of the name comes from the Greek word molybdos meaning lead. It is silvery white, very hard metal, but is softer and more ductile than tungsten. Molybdenum is found in the minerals molybdenite (MoS2) and wulfenite (MoO4Pb). Its alloys are used in aircraft, missiles and protective coatings in boiler plate.
neodymium → neodimij
Neodymium was discovered by Carl F. Auer von Welsbach (Austria) in 1885. The origin of the name comes from the Greek words neos didymos meaning new twin. It is silvery-white, rare-earth metal that oxidizes easily in air. Reacts slowly in cold water, more rapidly as heated. Metal ignites and burns readily. Neodymium is made from electrolysis of its halide salts, which are made from monazite sand. Used in making artificial ruby for lasers. Also in ceramics and for a special lens with praseodymium. Also to produce bright purple glass and special glass that filters infrared radiation. Misch metal, used in the manufacture of pyrophoric alloys for cigarette lighters, contains about 18 % neodymium metal. (Typically composition of misch metal are Ce:Nd:Pr:La:Other rare earth=50:18:6:22:4). Neodymium is used to create some of the most powerful permanent magnets on Earth, known as NIB magnets they consist of neodymium, iron, and boron.
niobium → niobij
Niobium was discovered by Charles Hatchett (England) in 1801. The origin of the name comes from the Greek word Niobe meaning daughter of Tantalus in Greek mythology (tantalum is closely related to niobium in the periodic table). It is shiny white, soft, ductile metal. Exposed surfaces form oxide film. Niobium occurs in a mineral columbite. It is used in stainless steel alloys for nuclear reactors, jets and missiles. Used as an alloy with iron and nickel. It can be used in nuclear reactors and is known to be superconductive when alloyed with tin, aluminium or zirconium.
nitrogen → dušik
Nitrogen was discovered by Daniel Rutherford (Scotland) in 1772. The origin of the name comes from the Greek words nitron genes meaning nitre and forming and the Latin word nitrum (nitre is a common name for potassium nitrate, KNO3). It is colourless, odourless, generally inert gas. Minimally reactive at room temperature. A component of many organic and inorganic compounds. Makes up about 78 % of earth’s atmosphere. Nitrogen is obtained from liquid air by fractional distillation. Primarily to produce ammonia and other fertilizers. Also used in making nitric acid, which is used in explosives. Also used in welding and enhanced oil recovery.
oil of vitriol → vitriolno ulje
Oil of vitriol is an obsolete name for sulfuric acid (H2SO4). Very old way of making sulfuric acid is by heating green vitriol (FeSO4*7H2O) to decomposition and collecting the acid vapors evolved.
orbital → orbitala
Orbital is the area in space about an atom or molecule in which the probability of finding an electron is greatest.
The possible atomic orbitals correspond to subshells of the atom. Thus there is one s-orbital for each shell (orbital quantum number l = 0). There are three p-orbitals (corresponding to the three values of l) and five d-orbitals. The shapes of orbitals depend on the value of l.
osmium → osmij
Osmium was discovered by Smithson Tennant (England) in 1803. The origin of the name comes from the Greek word osme meaning smell. It is hard fine black powder or hard, lustrous, blue-white metal. Unaffected by air, water and acids. Characteristic acrid, chlorine like odour due to tetroxide compound. Osmium tetroxide highly toxic. Osmium is obtained from the same ores as platinum. Used to tip gold pen points, instrument pivots, to make electric light filaments. Used for high temperature alloys and pressure bearings. Very hard and resists corrosion better than any other.
Citing this page:
Generalic, Eni. "Grej." Croatian-English Chemistry Dictionary & Glossary. 29 June 2022. KTF-Split. {Date of access}. <https://glossary.periodni.com>.
Glossary
Periodic Table