transition metal → prijelazni element
This group of metals is distinguished from other metals not by their physical properties, but by their electronic structure. Transition metals are elements characterized by a partially filled d subshell. The First Transition Series comprises scandium (Sc), titanium (Ti), vanadium (V), chromium (Cr), manganese (Mn), iron (Fe), cobalt (Co), nickel (Ni) and copper (Cu). The Second and Third Transition Series include the lanthanides and actinides, respectively.
The transition metals are noted for their variability in oxidation state. Thus, manganese has two electrons in its outside shell and five electrons in the next shell down, and exhibits oxidation states of +1, +2, +3, +4, +5, +6, and +7.
They are also characterised by the fact that well into the series, going from left to right, the properties of the succeeding metals do not differ greatly from the preceding ones.
triols → trioli
Trihydric alcohols (i.e. Triols) are organic compounds containing three hydroxyl groups. The simplest trihydric alcohol is 1,2,3-propane-triol, CH2(OH)CH(OH)CH2(OH), which is also known as glycerol (from the Greek glykys meaning sweet) or glycerin. Glycerol is commercially produced by the hydrolysis of fats.
Glycerol is a by-product in the soap industry and is recovered by suitable means.
tyrosine → tirozin
Tyrosine is hydrophobic amino acids with aromatic side chain. Tyrosine is large aromatic residue that is normally found buried in the interior of a protein and is important for protein stability. Tyrosine has special properties since its hydroxyl side chain may function as a powerful nucleophile in an enzyme active site (when ionized) and is a common site for phosphorylation in cell signaling cascades. Tyrosine absorbs ultraviolet radiation and contributes to the absorbance spectra of proteins. It is not essential (or semi-essential) to the human diet, since it is synthesized in the body from other metabolites.
- Abbreviations: Tyr, Y
- IUPAC name: 2-amino-3-(4-hydroxyphenyl)propanoic acid
- Molecular formula: C9H11NO3
- Molecular weight: 181.19 g/mol
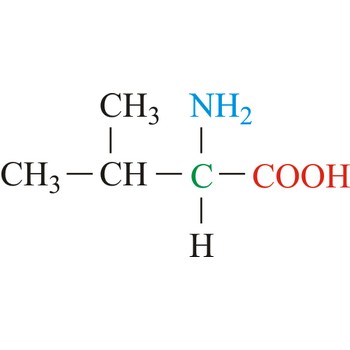
valine → valin
Valine is hydrophobic amino acids with aliphatic side chain. It is a member of the branched-chain amino acid family, along with leucine and isoleucine. Valine differs from threonine by replacement of the hydroxyl group with a methyl substituent, but they are of roughly the same shape and volume. The nonpolar hydrophobic amino acids tend to cluster together within proteins, stabilizing protein structure by means of hydrophobic interactions. Valine is an essential amino acid, which means that it cannot be synthesized in the body and must be obtained through dietary sources.
- Abbreviations: Val, V
- IUPAC name: 2-amino-3-methylbutanoic acid
- Molecular formula: C5H11NO2
- Molecular weight: 117.15 g/mol
yttrium → itrij
Yttrium was discovered by Carl Gustaf Mosander (Sweden) in 1843. Named after Ytterby, a village in Sweden. It is silvery, ductile, fairly reactive metal. Exposed surfaces form oxide film. Easily combustible, reacts with oxygen in water to release hydrogen. Yttrium is found in minerals such as monazite, xenotime and yttria. Combined with europium to make red phosphors for colour TV’s. Yttrium oxide and iron oxide combine to form a crystal garnet used in radar.
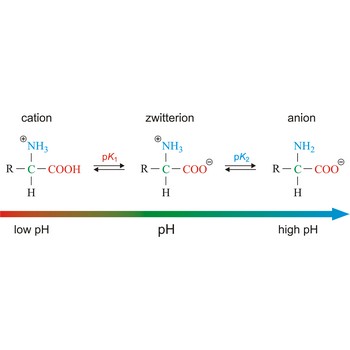
zwitterion → dipolarni ion
Zwitterion, also known as inner salt or dipolar ion, is an ion with a positive and a negative electrical charge at different locations within a molecule. As the molecule contains two opposite charges, it is electrically neutral. The term zwitterion is derived from the German word zwitter, meaning a hybrid, hermaphrodite. Zwitterions can be formed from compounds that contain both acid groups and base groups in their molecules (ampholytes).
All of the common amino acids found in proteins are ampholytes because they contain a carboxyl group (-COOH) that acts as an acid and an amino group (-NH2) that acts as a base. In the solid state, amino acids exist in the dipolar or zwitterion form. If acid is added to a solution containing the zwitterion, the carboxylate group captures a hydrogen (H+) ion, and the amino acid becomes positively charged. If base is added, ion removal of the H+ ion from the amino group of the zwitterion produces a negatively charged amino acid.
Chitosan → Kitozan
Chitosan is a linear polysaccharide composed of randomly distributed N-acetyl D-glucosamine and D-glucosamine units. It can be easily derived from partial deacetylation of natural polymer chitin. At a minimum deacetylization level of 60 % (amount of free amino groups in the polymer) it is considered to be chitosan. Thanks to the amino groups of D-glucosamine, chitosan can be protonated and turned into polycation, which is one of the sources of unique properties of chitosan as biopolymer, like aqueous solubility, antibacterial properties, biodegradability with non-toxic residues and biocompatibility.
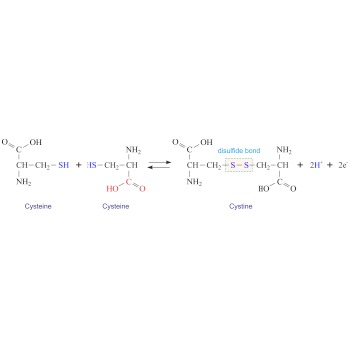
Cystine → Cistin
Cystine (C6H12N2O4S2) is a dimer of cysteine. It is formed by the oxidation of the thiol groups (-SH) of two cysteines generating a disulphide bridge (-S-S-). Cystine is a white crystalline solid that is slightly soluble in water. Cystine is particularly abundant in skeletal and connective tissues and in hair, horn, and wool.
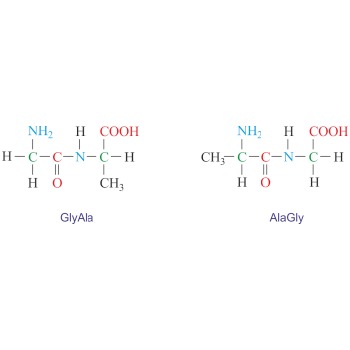
Dipeptide → Dipeptid
Dipeptide is an organic compound formed when two amino acids are joined by a peptide bond. Depending on which groups of amino acids are involved in the peptide bond four dipeptides can be formed from two different amino acids. For example, glycine (Gly) and alanine (Ala) can give two symmetrical dipeptides (GlyGly and AlaAla) and two unsymmetrical dipeptides (GlyAla and AlaGly). The naming is done by reading the sequence from the N-terminus to the C-terminus.
Citing this page:
Generalic, Eni. "Glikozidna skupina." Croatian-English Chemistry Dictionary & Glossary. 29 June 2022. KTF-Split. {Date of access}. <https://glossary.periodni.com>.
Glossary
Periodic Table