Einstein, Albert → Einstein, Albert
Albert Einstein (1879-1955) is a German born American physicist, who took Swiss nationality in 1901. A year later he went to work in the Bern patent office. In 1905. he published five enormously influential papers, one on Brownian movement, one on the photoelectric effect, one on the special theory of relativity, and one on energy and inertia (which included the famous expression E = mc2). In 1915 he published the general theory of relativity, concerned mainly with gravitation. In 1921 he was awarded the Nobel Prize. In 1933, as a Jew, Einstein decided to remain in the USA (where he was lecturing), as Hitler had come to power. For the remainder of his life he sought a unified field theory. In 1939 he informed president Roosevelt that an atom bomb was feasible and that. Germany might be able to make one.
elastic collision → elastični sudar
Elastic collision is a collision in which the total kinetic energy of the colliding bodies after collision is equal to their total kinetic energy before collision. Elastic collisions occur only if there is no conversion of kinetic energy into other forms, as in the collision of atoms. In the case of macroscopic bodies this will not be the case as some of the energy will become heat. In a collision between polyatomic molecules, some kinetic energy may be converted into vibrational and rotational energy of the molecules.
electric cell → električni članak
Electric cell (battery) is a device that is capable of changing some form of energy, such as chemical, nuclear or radiant energy, into electricity. A solar cell, for example, consists of a semiconductor junction that converts sunlight directly into electricity. A dry cell battery converts chemical energy into electricity.
electrochemical cell → elektrokemijski članak
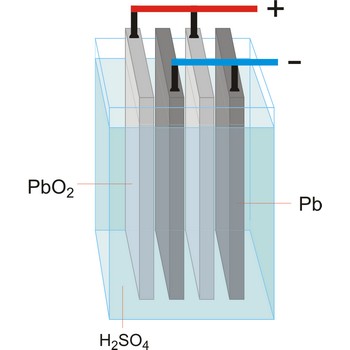
Electrochemical cell is a device that converts chemical energy into electrical energy or vice versa when a chemical reaction is occurring in the cell. It consist of two electronically conducting phases (e.g., solid or liquid metals, semiconductors, etc) connected by an ionically conducting phase (e.g. aqueous or non-aqueous solution, molten salt, ionically conducting solid). As an electric current passes, it must change from electronic current to ionic current and back to electronic current. These changes of conduction mode are always accompanied by oxidation/reduction reactions.
An essential feature of the electrochemical cell is that the simultaneously occurring oxidation-reduction reactions are spatially separated. E.g., in a spontaneous chemical reaction during the oxidation of hydrogen by oxygen to water, electrons are passed directly from the hydrogen to the oxygen.
In contrast, in the spontaneous electrochemical reaction in a galvanic cell the hydrogen is oxidised at the anode by transferring electrons to the anode and the oxygen is reduced at the cathode by accepting electrons from the cathode. The ions produced in the electrode reactions, in this case positive hydrogen ions and the negative hydroxyl (OH-) ions, will recombine in the solution to form the final product of the reaction: water. During this process the electrons are conducted from the anode to the cathode through an outside electric circuit where the electric current can drive a motor, light a light bulb, etc. The reaction can also be reversed: water can be decomposed into hydrogen and oxygen by the application of electrical power in an electrolytic cell.
electrolytic cell → elektrolitska ćelija
Electrolytic cell is an electrochemical cell that converts electrical energy into chemical energy. The chemical reactions do not occur spontaneously at the electrodes when they are connected through an external circuit. The reaction must be forced by applying an external electric current. It is used to store electrical energy in chemical form (rechargeable battery). It is also used to decompose or produce (synthesise) new chemicals by the application of electrical power. This process is called electrolysis, e.g., water can be decomposed into hydrogen gas and oxygen gas. The free energy change of the overall cell reaction is positive.
electromagnetic radiation spectrum → spektar elektromagnetskog zračenja
Wavelengths of electromagnetic waves can be shown with the help of electromagnetic radiation spectrum. Electromagnetic radiation spectrum is divided into several areas from γ-radiation of very short wavelengths and great energy to radio waves with wavelengths up to 1 000 m. The human eye can only see a narrow part of the electromagnetic spectrum - visible radiation.
electron affinity → elektronski afinitet
Electron affinity (EA) is the energy change occurring when an atom or molecule gains an electron to form a negative ion. For an atom or molecule X, it is the energy released for the electron-attachment reaction
This is often measured in electronvolts. Alternatively, the molar enthalpy change, ΔH, can be used.
electron microscope → elektronski mikroskop
Electron microscope is a form of microscope that uses a beam of electrons instead of a beam of light (as in the optical microscope) to form a large image of a very small object. In optical microscopes the resolution is limited by the wavelength of the light. High-energy electrons, however, can be associated with a considerably shorter wavelength than light; for example, electrons accelerated to energy of 105 electronvolts have a wavelength of 0.004 nm enabling a resolution of from 0.2 nm to 0.5 nm to be achieved.
molar enthalpy of melting → molarna entalpija taljenja
Molar enthalpy of melting (Δs lH) is a change of enthalpy during melting divided by the molarity of a solid matter, and is equal to the energy used when melting is conducted under constant pressure.
open system → otvoreni sustav
Open system is a system which can exchange matter and energy with the environment.
Citing this page:
Generalic, Eni. "Energija." Croatian-English Chemistry Dictionary & Glossary. 29 June 2022. KTF-Split. {Date of access}. <https://glossary.periodni.com>.
Glossary
Periodic Table