potentiometric titration → potenciometrijska titracija
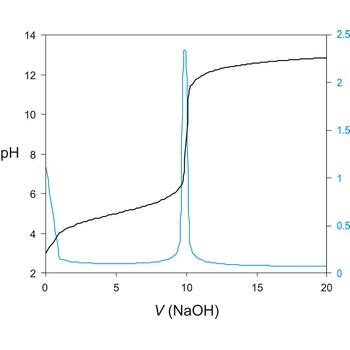
Potentiometric titration is a volumetric method in which the potential between two electrodes is measured (referent and indicator electrode) as a function of the added reagent volume. Types of potentiometric titrations for the determination of analytes in photoprocessing solutions include acid-base, redox, precipitation, and complexometric.
Potentiometric titrations are preferred to manual titrations, since they are more accurate and precise. They are also more easily adapted to automation, where automated titration systems can process larger volumes of samples with minimal analyst involvement.
A titration curve has a characteristic sigmoid curve. The part of the curve that has the maximum change marks the equivalence point of the titration. The first derivative, ΔE/ΔV, is the slope of the curve, and the endpoint occurs at the volume, V', where ΔE/ΔV has the maximum value.
precision balance → tehnička vaga
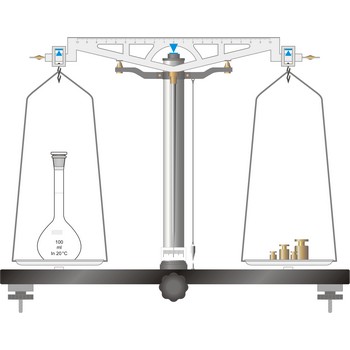
Precision balances typically display results from three to one decimal places (0.001 g up to 0.1 g). The readability precision balances are reduced when compared to analytical balances but, precision balances accommodate higher capacities (up to several kilograms). In its traditional form, it consists of a pivoted horizontal lever of equal length arms, called the beam, with a weighing pan, also called scale, suspended from each arm.
In electronic top pan, or toploader balances, mass is determined not by mechanical deflection but by electronically controlled compensation of an electric force. The signal generated enables the mass to be read from a digital display. The mass of the empty container can be stored in the balance’s computer memory and automatically deducted from the mass of the container plus its contents.
proline → prolin
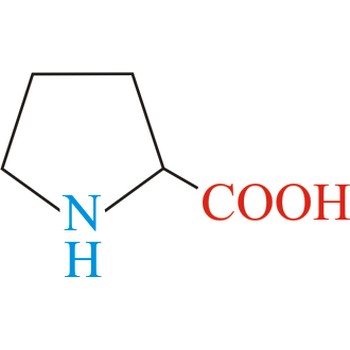
Proline has an aliphatic side chain with a distinctive cyclic structure. It is unusual because it is conformationally restricted. The secondary amino (imino) group of proline residues is held in a rigid conformation that reduces the structural flexibility of polypeptide regions containing proline. It is not an essential amino acid, which means that the human body can synthesize it.
- Abbreviations: Pro, P
- IUPAC name: pyrrolidine-2-carboxylic acid
- Molecular formula: C5H9NO2
- Molecular weight: 115.13 g/mol
sacrificial protection → zaštita žrtvovanom elektrodom
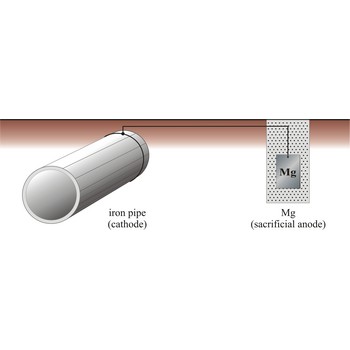
Sacrificial protection is the protection of iron or steel against corrosion by using a more reactive metal. Pieces of zinc or magnesium alloy are attached to pump bodies and pipes. The protected metal becomes the cathode and does not corrode. The anode corrodes, thereby providing the desired sacrificial protection. These items are known as sacrificial anodes and "attract" the corrosion to them rather than the iron/steel. The sacrificial anodes must be replaced periodically as they corrode.
The iron pipe will be connected to a more reactive metal such as magnesium through cooper wires, the magnesium will donate its electrons to the iron preventing it from rusting. Iron which is oxidises will immediately be reduced back to iron.
standard electrode potential → standardni elektrodni potencijal
Standard electrode potential (E°) (standard reduction potentials) are defined by measuring the potential relative to a standard hydrogen electrode using 1 mol solution at 25 °C. The convention is to designate the cell so that the oxidised form is written first. For example,
The e.m.f. of this cell is -0.76 V and the standard electrode potential of the Zn2+|Zn half cell is -0.76 V.
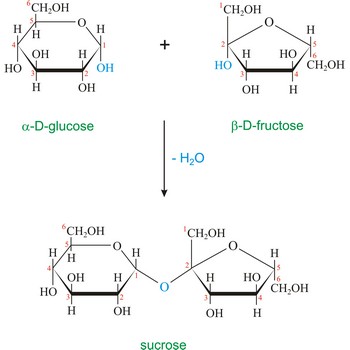
sucrose → saharoza
Sucrose (saccharose), or ordinary table sugar, is a disaccharide in which α-D-glucopyranose and β-D-fructofuranose are joined at their anomeric carbons by a glycosidic bond. There are no hemiacetals remaining in the sucrose and therefore sucrose is not a reducing sugar and does not exhibit mutarotation. Sugar is a white crystalline sweet compound found in many plants and extracted from sugar cane and sugar beet. It is used as a sweetening agent in food and drinks. If heated to 200 °C, sucrose becomes caramel. When sucrose is hydrolyzed it forms an equimolar mixture of glucose and fructose. This mixture of monosaccharides is called invert sugar. Honeybees have enzymes called invertases that catalyze the hydrolysis of sucrose. Honey, in fact, is primarily a mixture of glucose, fructose, and sucrose.
vanadium → vanadij
Vanadium was discovered by A. M. del Rio (Spain) in 1801 and rediscovered by Nils Sefstrom (Sweden) in 1830. Named after Vanadis, the goddess of beauty in Scandinavian mythology. It is soft, ductile, silvery-white metal. Resistant to corrosion by moisture, air and most acids and alkalis at room temperature. Exposed surfaces form oxide coating. Reacts with concentrated acids. Vanadium is found in the minerals patronite (VS4), vanadinite [Pb5(VO4)3Cl] and carnotite [K2(UO2)2(VO4)2·3H2O]. Pure metal produced by heating with C and Cl to produce VCl3 which is heated with Mg in Ar atmosphere. It is mixed with other metals to make very strong and durable alloys. Vanadium pentoxide (V2O5) is used as a catalyst, dye and fixer-fixer.
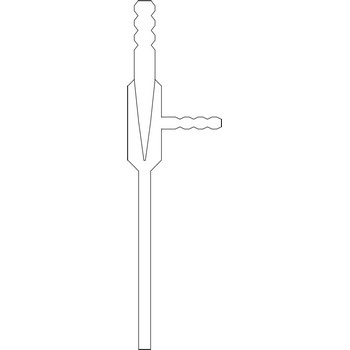
water jet vacuum pump → vodena sisaljka
The water jet vacuum pump or vacuum aspirator is one of the most popular devices that produces vacuum in laboratories. The rapid flow of water through the device creates a vacuum in a side-arm that is connected to a vacuum application such a Buchner flask. The water jet vacuum pump creates a vacuum by means of Venturi effect named after the Italian physicist Giovanni Battista Venturi (1746–1822). The Venturi effect is the reduction in fluid pressure that results when a fluid flows through a constricted section of pipe. Water jet pumps are manufactured of glass, plastic or metal, depending on the conditions in which they are used.
water hardness → tvrdoća vode
Hardness is defined as the concentrations of calcium and magnesium ions expressed in terms of calcium carbonate. These minerals in water can cause some everyday problems. They react with soap and produce a deposit called soap curd that remains on the skin and clothes and, because it is insoluble and sticky, cannot be removed by rinsing.
Hard water may also shorten the life of plumbing and water heaters. When water containing calcium carbonate is heated, a hard scale is formed that can plug pipes and coat heating elements. Scale is also a poor heat conductor. With increased deposits on the unit, heat is not transmitted to the water fast enough and overheating of the metal causes failure. Build-up of deposits will also reduce the efficiency of the heating unit, increasing the cost of fuel.
There are two types of water hardness, temporary and permanent.
Temporary Hardness is due to the bicarbonate ion, HCO3-, being present in the water. This type of hardness can be removed by boiling the water to expel the CO2, as indicated by the following equation:
Permanent hardness is due to calcium and magnesium nitrates, sulphates, and chlorides etc. This type of hardness cannot be eliminated by boiling.
| Water supply classification | |
|---|---|
| Hardness | Concentration of Calcium carbonate (mg/L) |
| Soft Water | 0 to 75 |
| Medium Hard Water | 75 to 150 |
| Hard Water | 150 to 300 |
| Very Hard Water | over 300 |
Heyrovsky-Ilkovic equation → Heyrovsky-Ilkovičeva jednadžba
The Heyrovsky-Ilkovic equation describes the entire current-potential curve (polarographic wave) of a reversible redox system in polarography
where R is the gas constant, T is the absolute temperature, F is the Faraday constant, n denotes the number of electrons taking part in the electrode reaction. E1/2 is a unique potential (for a given reaction and supporting electrolyte) termed the half-wave potential.
In order to obtain E1/2 from the above equation, we plot a graph of ln[(id-i)/i] against E. The intercept on the x-axis gives then an accurate value of E1/2. The slope of the obtained straight line is equal to nF/RT from which n is determined.
Citing this page:
Generalic, Eni. "Elektroda prvog reda." Croatian-English Chemistry Dictionary & Glossary. 29 June 2022. KTF-Split. {Date of access}. <https://glossary.periodni.com>.
Glossary
Periodic Table