ligand field theory → teorija ligandnog polja
Ligand field theory is a description of the structure of crystals containing a transition metal ion surrounded by nonmetallic ions (ligands). It is based on the construction of molecular orbitals involving the d-orbitals of the central metal ion and combinations of atomic orbitals of the ligands.
metalloid → polumetal
Metalloid (semimetal) is any of a class of chemical elements intermediate in properties between metals and nonmetals. The classification is not clear cut, but typical metalloids are boron (B), silicon (Si), germanium (Ge), arsenic (As), and tellurium (Te). They are electrical semiconductors and their oxides are amphoteric.
dipole moment → dipolni moment
Electric dipole moment (μ) is a product of the positive charge and the distance between the charges. Dipole moments are often stated in debyes; The SI unit is the coulomb metre. In a diatomic molecule, such as HCl, the dipole moment is a measure of the polar nature of the bond; i.e. the extent to which the average electron charges are displaced towards one atom (in the case of HCl, the electrons are attracted towards the more electronegative chlorine atom). In a polyatomic molecule, the dipole moment is the vector sum of the dipole moments of the individual bonds. In a symmetrical molecule, such as tetrafluoromethane (CF4) there is no overall dipole moment, although the individual C-F bonds are polar.
micelle → micele
Micelle is an electrically charged colloidal particle, usually organic in nature, composed of aggregates of large molecules, e.g., in soaps and surfactants. For aqueous solutions, the hydrophilic end of the molecule is on the surface of the micelle, while the hydrophobic end (often a hydrocarbon chain) points toward the centre.
electrochemical cell → elektrokemijski članak
Electrochemical cell is a device that converts chemical energy into electrical energy or vice versa when a chemical reaction is occurring in the cell. It consist of two electronically conducting phases (e.g., solid or liquid metals, semiconductors, etc) connected by an ionically conducting phase (e.g. aqueous or non-aqueous solution, molten salt, ionically conducting solid). As an electric current passes, it must change from electronic current to ionic current and back to electronic current. These changes of conduction mode are always accompanied by oxidation/reduction reactions.
An essential feature of the electrochemical cell is that the simultaneously occurring oxidation-reduction reactions are spatially separated. E.g., in a spontaneous chemical reaction during the oxidation of hydrogen by oxygen to water, electrons are passed directly from the hydrogen to the oxygen.
In contrast, in the spontaneous electrochemical reaction in a galvanic cell the hydrogen is oxidised at the anode by transferring electrons to the anode and the oxygen is reduced at the cathode by accepting electrons from the cathode. The ions produced in the electrode reactions, in this case positive hydrogen ions and the negative hydroxyl (OH-) ions, will recombine in the solution to form the final product of the reaction: water. During this process the electrons are conducted from the anode to the cathode through an outside electric circuit where the electric current can drive a motor, light a light bulb, etc. The reaction can also be reversed: water can be decomposed into hydrogen and oxygen by the application of electrical power in an electrolytic cell.
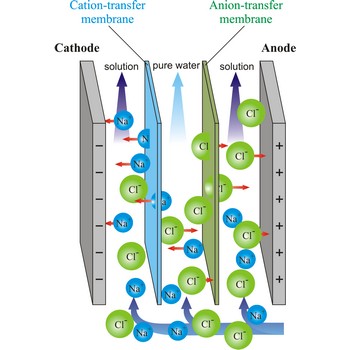
electrodialysis → elektrodijaliza
Electrodialysis is a procedure of dialysis accelerated with an electric field. Dialyser is divided into three sections. Solution flows through the middle section, between two semipermeable membranes alternately to positive ions and negative ions. An electrodes are placed in the neighbouring sections. Under the influence of electric field, positive ions will travel towards the cathode (the negative electrode), and negative ions towards the anode (the positive electrode), whereby travelling of ions through the membrane is accelerated. In this way, the feed water is separated into two streams: one of pure water and the other of more concentrated solution.
Citing this page:
Generalic, Eni. "Električna otpornost." Croatian-English Chemistry Dictionary & Glossary. 29 June 2022. KTF-Split. {Date of access}. <https://glossary.periodni.com>.
Glossary
Periodic Table