metallic glass → metalno staklo
Certain alloys can solidify by extremely rapid cooling out of melt without formation of a crystal lattice, that is in the amorphous form - such, amorphous alloys are so called metallic glasses. The alloy of zirconium, beryllium, titanium, copper, and nickel is one of the first metallic glasses that can be made in bulk and formed into strong, hard, useful objects.
Unlike pure metals and most metal alloys, metallic glasses have no regular crystalline structure. This lack of long range order or microstructure is related to such desirable features as strength and low damping which is one reason why the premier use for zirconium-based metallic glass is in the manufacture of expensive golf club heads. Metallic glasses can be quite strong yet highly elastic, and they can also be quite tough (resistant to fracture). Even more interesting are the thermal properties; for instance, just like an oxide glass, there is a temperature (called the glass transition temperature) above which a metallic glass becomes quite soft and flows easily. This means that there are lots of opportunities for easily forming metallic glasses into complex shapes.
potential energy → potencijalna energija
Potential energy (Ep) is the energy stored in a body or system as a consequence of its position, shape, or state (this includes gravitation energy, electrical energy, nuclear energy, and chemical energy). Gravitational potential energy is the energy associated with the state of separation between bodies that attracts each other via gravitational force. Elastic potential energy is the energy associated with the state of compression or extension of an elastic object. Thermal energy is associated with the random motions of atoms and molecules in a body.
tin → kositar
Tin has been known since ancient times. The origin of the name comes from the Latin word stannum meaning tin. It is silvery-white, soft, malleable and ductile metal. Exposed surfaces form oxide film. Resists oxygen and water. Dissolves in acids and bases. Organic tin compounds may be highly toxic. Tin is principally found in the ore cassiterite (SnO2) and stannine (Cu2FeSnS4). Used as a coating for steel cans since it is non-toxic and non-corrosive. Also in solder (33 %Sn:67 %Pb), bronze (20 %Sn:80 %Cu) and pewter. Stannous fluoride (SnF2), a compound of tin and fluorine is used in some toothpaste.
vanadium → vanadij
Vanadium was discovered by A. M. del Rio (Spain) in 1801 and rediscovered by Nils Sefstrom (Sweden) in 1830. Named after Vanadis, the goddess of beauty in Scandinavian mythology. It is soft, ductile, silvery-white metal. Resistant to corrosion by moisture, air and most acids and alkalis at room temperature. Exposed surfaces form oxide coating. Reacts with concentrated acids. Vanadium is found in the minerals patronite (VS4), vanadinite [Pb5(VO4)3Cl] and carnotite [K2(UO2)2(VO4)2·3H2O]. Pure metal produced by heating with C and Cl to produce VCl3 which is heated with Mg in Ar atmosphere. It is mixed with other metals to make very strong and durable alloys. Vanadium pentoxide (V2O5) is used as a catalyst, dye and fixer-fixer.
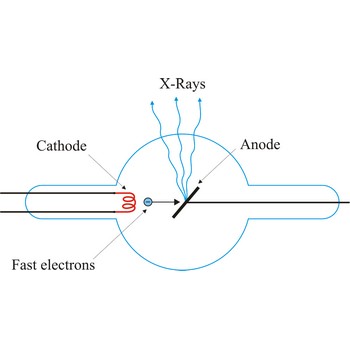
X-ray tube → rendgenska cijev
X-ray tube is a cathode ray tube that focuses energetic streams of electrons on a metal target, causing the metal to emit X-rays. The basic principle of the X-ray tube has not changed significantly since Roentgen's 1895 discovery. Current applied to a metal cathode (about 50 000 V) produces free electrons. The X-rays are produced when the rapidly moving electrons are suddenly stopped as they strike the metal target of the tube.
Citing this page:
Generalic, Eni. "Elastični sudar." Croatian-English Chemistry Dictionary & Glossary. 29 June 2022. KTF-Split. {Date of access}. <https://glossary.periodni.com>.
Glossary
Periodic Table