elastic collision → elastični sudar
Elastic collision is a collision in which the total kinetic energy of the colliding bodies after collision is equal to their total kinetic energy before collision. Elastic collisions occur only if there is no conversion of kinetic energy into other forms, as in the collision of atoms. In the case of macroscopic bodies this will not be the case as some of the energy will become heat. In a collision between polyatomic molecules, some kinetic energy may be converted into vibrational and rotational energy of the molecules.
collision theory → teorija sudara
Collision theory is theory that explains how chemical reactions take place and why rates of reaction alter. For a reaction to occur the reactant particles must collide. Only a certain fraction of the total collisions cause chemical change; these are called successful collisions. The successful collisions have sufficient energy (activation energy) at the moment of impact to break the existing bonds and form new bonds, resulting in the products of the reaction. Increasing the concentration of the reactants and raising the temperature bring about more collisions and therefore more successful collisions, increasing the rate of reaction.
activation energy → energija aktivacije
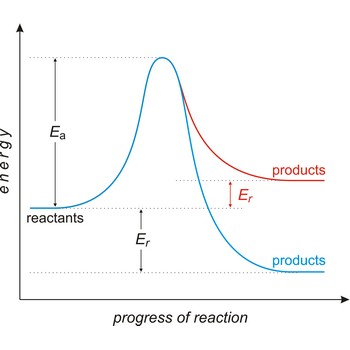
Activation energy (Ea) is the energy that must be added to a system in order for a process to occur, even though the process may already be thermodynamically possible. In chemical kinetics, the activation energy is the height of the potential barrier separating the products and reactants. It determines the temperature dependence on the reaction rate.
Brownian motion → Braunovo gibanje
Brownian motion is the continuous random movement of small particles suspended in a fluid, which arise from collisions with the fluid molecules. First observed by the British botanist R. Brown (1773-1858) when studying pollen particles. The effect is also visible in particles of smoke suspended in a gas.
cellulose → celuloza
Cellulose, (C6H10O5)n, is a polysaccharide that consists of a long unbranched chain of glucose units linked by (1→4)-β-glycoside bonds. Nature uses cellulose primarily as a structural material to impart strength and rigidity to plants. Leaves, grasses, and cotton are primarily cellulose. The fibrous nature of extracted cellulose has led to its use in textile industry for the production of cotton, artificial silk, etc. Cellulose also serves as raw material for the manufacture of cellulose acetate, known commercially as acetate rayon, and cellulose nitrate, known as guncotton. Gunncotton is the major ingredient in smokeless powder, the explosive propellant used in artillery shells and in ammunition for firearms.
glass transition temperature → temperatura staklastog prijelaza
Glass transition temperature (Tg) is the temperature at which an amorphous polymer is transformed, in a reversible way, from a viscous or rubbery condition to a hard and relatively brittle one.
harmonic motion → harmoničko gibanje
Harmonic motion is caused by restoring force, acting on a body that is displaced from its equilibrium position. This force tries to put the body back in equilibrium. Usual examples are the motion of a body attached to elastic spring (see: Hooke’s law) and the motion of mathematical pendulum. The body undergoes periodic motion around the equilibrium point.
mean free path → srednji slobodni put
Mean free path is the average distance a gas molecule travels between collisions.
vulcanisation → vulkanizacija
Vulcanisation (vulcanisation of rubber) is a process of combining rubber with sulphur or other substances that causes the polymer chains to crosslink, making them stronger and more elastic.
Hooke’s law → Hookeov zakon
Hooke’s law stating that the deformation of a body is proportional to the magnitude of the deforming force, provided that the body’s elastic limit (see elasticity) is not exceeded. If the elastic limit is not reached, the body will return to its original size once the force is removed. The law was discovered by English physicist Robert Hooke in 1676.
If a body on elastic spring is displaced from its equilibrium position (i.e. if the spring is stretched or compressed), a restitution force tries to return the body back in its equilibrium position. The magnitude of that force is proportional to the displacement of the body
Where F is the restitutional (elastic) force, x is the displacement of the body and k is the spring constant, which depends on dimensions, shape and material of the spring.
Citing this page:
Generalic, Eni. "Elastični sudar." Croatian-English Chemistry Dictionary & Glossary. 29 June 2022. KTF-Split. {Date of access}. <https://glossary.periodni.com>.
Glossary
Periodic Table