cell potential → potencijal članka
Cell potential (E) is difference between anode and cathode potential. If the cell potential is positive, then the reaction is spontaneous.
equivalent → ekvivalent
Equivalent (eq) is a unit for describing the amount of a chemical species. In contrast to the mole, the amount of a substance contained in one equivalent can vary from reaction to reaction.
chemical change → kemijska promjena
Chemical change is a process which results in the production of one or more new materials. The system within which the process takes place is called a chemical system. A chemical change is also known as a chemical reaction, where one substance is converted into one or more different substances. When sodium and chlorine react to produce sodium chloride, a chemical reaction has taken place.
chemical equation → kemijska jednadžba
Chemical equation is a way of denoting a chemical reaction using the symbol for the participating particles (atoms, molecules, ions, etc.); for example,
The single arrow is used for an irreversible reaction; double arrows are used for reversible reactions. When reactions involve different phases, it is usual to put the phase in brackets after the symbol.
| s | = | solid |
| l | = | liquid |
| g | = | gas |
| aq | = | aqueous |
The numbers a, b, c, and d, showing the relative numbers of molecules reacting, are called the stoichiometric coefficients. The convention is that stoichiometric coefficients are positive for reactants and negative for products. If the sum of the coefficients is zero, the equation is balanced.
equivalent weight → ekvivalentna masa
Equivalent weight of a substance participating in a neutralization reaction is that mass of substance (molecule, ion, or paired ion) that either reacts with or supplies 1 mol of hydrogen ions in that reaction.
Equivalent weight of a substance participating in an oxidation/reduction reaction is that weight which directly or indirectly produces or consumes 1 mol of electrons.
fermentation → fermentacija
Fermentation is a class of biochemical reactions that break down complex organic molecules (such as carbohydrates) into simpler materials (such as ethanol, carbon dioxide, and water). Fermentation reactions are catalyzed by enzymes.
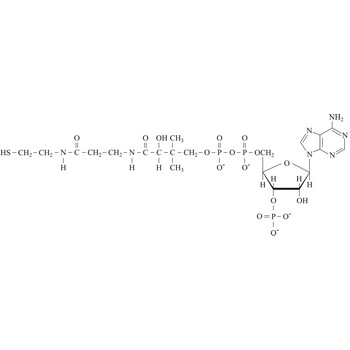
coenzyme a → koenzim a
Coenzyme A (CoA) is an essential metabolic cofactor synthesized from cysteine, pantothenate (vitamin B5), and ATP. CoA plays important roles in many metabolic pathways, including the tricarboxylic acid (TCA) cycle, and the synthesis and oxidation of fatty acids. One of the main functions of CoA is the carrying and transfer of acyl groups. Acylated derivatives (acetyl-CoA) are critical intermediates in many metabolic reactions.
collision theory → teorija sudara
Collision theory is theory that explains how chemical reactions take place and why rates of reaction alter. For a reaction to occur the reactant particles must collide. Only a certain fraction of the total collisions cause chemical change; these are called successful collisions. The successful collisions have sufficient energy (activation energy) at the moment of impact to break the existing bonds and form new bonds, resulting in the products of the reaction. Increasing the concentration of the reactants and raising the temperature bring about more collisions and therefore more successful collisions, increasing the rate of reaction.
Citing this page:
Generalic, Eni. "Egzotermna reakcija." Croatian-English Chemistry Dictionary & Glossary. 29 June 2022. KTF-Split. {Date of access}. <https://glossary.periodni.com>.
Glossary
Periodic Table