Haber process → Haberov proces
Haber process is an industrial process for producing ammonia by reaction of nitrogen with hydrogen:
The reaction is reversible and exothermic, so that a high yield of ammonia is favoured by low temperature. However, the rate of reaction would be too slow for equilibrium to be reached at normal temperatures, so an optimum temperature of about 450 °C is used, with a catalyst of iron containing potassium aluminium oxide promoters. The higher the pressure the greater the yield, although there are technical difficulties in using very high pressures. A pressure of about 250 atmospheres is commonly employed. The removal of ammonia from the batch as soon as it is formed ensures that an equilibrium favouring product formation is maintained. The nitrogen is obtained from air. Formerly, the hydrogen was from water gas and the water-gas shift reaction (the Bosch process) but now the raw material (called synthesis gas) is obtained by steam reforming natural gas.
The process is of immense importance for the fixation of nitrogen for fertilisers and explosives. It was developed in 1908 by German chemist Fritz Haber (1868-1934) and was developed for industrial use by Carl Bosch (1874-1940), hence the alternative name Haber-Bosch process.
hafnium → hafnij
Hafnium was discovered by Dirk Coster (Denmark) and Georg Karl von Hevesy (Hungary) in 1923. The origin of the name comes from the Latin name Hafnia meaning Copenhagen. It is silvery, ductile metal. Exposed surfaces form oxide film. Resists alkalis and acids (except HF). Toxic. Metal ignites and burns readily. Hafnium is obtained from mineral zircon or baddeleyite. Used in reactor control rods because of its ability to absorb neutrons.
Kjeldahl flask → Kjeldahlova tikvica
Kjeldahl flask is a round bottom flask with a long wide neck that is used in the determination of nitrogen by Kjeldahl’s method. The method was developed by the Danish chemist Johan Kjeldahl (1849-1900).
Kjeldahl’s method → Kjeldahlov postupak
Kjeldahl’s method is an analytical method for determination of nitrogen in certain organic compounds. The method was developed by the Danish chemist Johan Kjeldahl (1849-1900).
It involves addition of a small amount of anhydrous potassium sulphate to the test compound, followed by heating the mixture with concentrated sulphuric acid, often with a catalyst such as copper sulphate. As a result ammonia is formed. After alkalyzing the mixture with sodium hydroxyde, the ammonia is separated by distillation, collected in standard acid, and the nitrogen determined by back-titration.
- Kjeldahl flask for decomposition (500 ml – macro or 100 ml - micro)
- funnel for alkaline solution
- Wagner tube (drop catcher)
- condenser
- absorption flask with known volume of standard acid
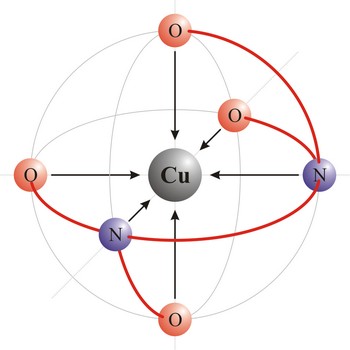
ligand → ligand
Ligand is an ion (F-, Cl-, Br-, I-, S2-, CN-, NCS-, OH-, NH2-) or molecule (NH3, H2O, NO, CO) that donates a pair of electrons to a metal atom or ion in forming a coordination complex. The main way of classifying ligands is by the number of points at which they are attached to, or bound to, the metal center. This is the denticity. Ligands with one potential donor atom are monodentate. Polydentate ligand is a ligand that is attached to a central metal ion by bonds from two or more donor atoms. Ligands with more than one potential donor atom are known as ambidentate, such as the thiocyanate ion, NCS-, which can bind to the metal center with either the nitrogen or sulphur atoms. Chelating ligands are those polydentate ligands which can form a ring including the metal atom.
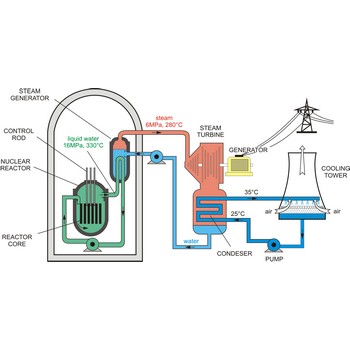
nuclear reactor → nuklearni reaktor
Nuclear reactor is an assembly of fissionable material (uranium-235 or plutonium-239) designed to produce a sustained and controllable chain reaction for the generation of electric power.
The essential components of a nuclear reactor are:
- The core, metal rods containing enough fissionable material to maintain a chain reaction at the necessary power level (as much as 50 t of uranium may be required).
- A source of neutrons to initiate the reaction (such as a mixture of polonium and beryllium)
- A moderator to reduce the energy of fast neutrons for more efficient fission (material such as graphite, beryllium, heavy water, and light water are used)
- A coolant to remove the fission-generated heat (water, sodium, helium, and nitrogen may be used)
- A control system such as rods of boron or cadmium that have high capture cross sections (to absorb neutrons)
- Adequate shielding, remote-control equipment, and appropriate instrumentation are essential for personnel safety and efficient operation.
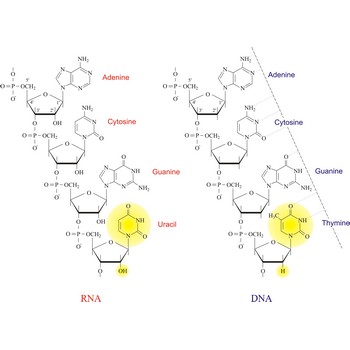
nucleic acid → nukleinska kiselina
Nucleic acids are a complex, high-molecular-weight biochemical macromolecules composed of nucleotide chains that convey genetic information. The most common nucleic acids are deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) and ribonucleic acid (RNA). Each nucleic acid chain is composed of subunits called nucleotides, each containing a sugar, a phosphate group, and nitrogenous base. DNA was first discovered in 1869 by the Swiss biochemist Friedrich Miescher (1844-1895).
Both DNA and RNA contain the two major purine bases adenine (A) and guanine (G) and one of the major pyrimidines, cytosine (C). Of the other two pyrimidines, thymine (T) is found in DNA and uracil (U) is found in RNA. There are two major pentoses in nucleic acids:2'-deoxy-D-ribose in DNA and D-ribose in RNA.
Nucleotides are linked together in both DNA and RNA in a polymeric fashion via covalent bonds. These bonds exist through phosphate-group bridges in which the 5' hydroxyl group of one nucleotide unit is joined to the 3' hydroxyl group of the next nucleotide. RNA is usually a single-stranded molecule, whereas DNA is usually double-stranded.
nucleotide → nukleotid
Nucleotides are the components that made up nucleic acids. They have three major components: the first component is a nitrogenous base, which is derivative of one of two parent compounds, pyrimidine or purine; the second is a pentose, or five carbon sugar group; the third is a unit of phosphate. Each group of three nucleotides in a gene is known as a codon. Whenever the phosphate group is not present, a nucleotide becomes a nucleoside.
organic → organski
1. Organic refers to any chemical compound based on carbon (C) with the exception of some of the simple compounds of carbon, such as carbon dioxide, which are frequently classified as inorganic compounds. Additional elements that are commonly found in organic compounds are hydrogen (H), nitrogen (N), oxygen (O), phosphorus (P) and sulfur (S).
2. Organic or organically-grown foods are grown or raised without synthetic fertilizers, pesticides, growth stimulators, or antibiotics and other drugs. Pests are controlled by cultivation techniques and the use of pesticides derived from natural sources and the use of natural fertilizers. In addition, organically grown foods must also be stored without the use of chemicals such as artificial additives and preservatives, and without food irradiation.
Ostwald’s process → Ostwaldov proces
Ostwald’s process is a process by which the nitric acid can be obtained in three degrees. In the first stage ammonia and oxygen react (with platinum-rhodium as a catalyst), whereby the nitrogen monoxide and water emerge
In the second stage nitrogen monoxide reacts with oxygen whereby nitrogen dioxide emerges
and in the third stage nitrogen dioxide dissolves in water, in the presence of air, giving the nitric acid
Citing this page:
Generalic, Eni. "Dušik." Croatian-English Chemistry Dictionary & Glossary. 29 June 2022. KTF-Split. {Date of access}. <https://glossary.periodni.com>.
Glossary
Periodic Table