seawater → more
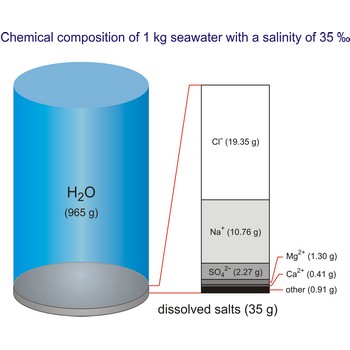
Seawater is a complex mixture of 96.5 % water, 3.5 % salts, and smaller amounts of other substances, including dissolved inorganic and organic materials, particulates, and a few atmospheric gases. The world's oceans cover nearly 71 % (361 840 000 km2) of the Earth's surface (510 100 000 km2), with an average depth of 3 682.2 m.
The density of seawater is higher than that of fresh water because of its higher salinity. Seawater's freezing point is lower than that of pure water and its boiling point is higher. The average salinity of the ocean is 35 ‰, which means that for every kilograms of water, there are 35 g of salt. The relative abundance of the major salts in seawater are constant regardless of the ocean. Only six elements and compounds comprise about 99 % of sea salts: chlorine (Cl-), sodium (Na+), sulfur (SO42-), magnesium (Mg2+), calcium (Ca2+), and potassium (K+).
silicon → silicij
Silicon was discovered by Jöns Jacob Berzelius (Sweden) in 1824. The origin of the name comes from the Latin word silicis meaning flint. Amorphous form of silicon is brown powder; crystalline form has grey metallic appearance. Solid form unreactive with oxygen, water and most acids. Dissolves in hot alkali. Silica dust is a moderately toxic acute irritant. Silicon makes up major portion of clay, granite, quartz and sand. Commercial production depends on a reaction between sand (SiO2) and carbon at a temperature of around 2200 °C. Used in glass as silicon dioxide (SiO2). Silicon carbide (SiC) is one of the hardest substances known and used in polishing. Also the crystalline form is used in semiconductors.
sodium → natrij
Sodium was discovered by Sir Humphry Davy (England) in 1807. The origin of the name comes from the Latin word natrium meaning sodium carbonate. It is soft silvery-white metal. Fresh surfaces oxidize rapidly. Reacts vigorously, even violently with water. Reacts with water to give off flammable gas. Burns in air with a brilliant white flame. Sodium is obtained by electrolysis of melted sodium chloride (salt), borax and cryolite. Metallic sodium is vital in the manufacture of organic compounds. Sodium chloride (NaCl) is table salt. Liquid sodium is used to cool nuclear reactors.
stratosphere → stratosfera
Stratosphere is the part of the earth’s atmosphere extending from the top of the troposphere (typically 10 km to 15 km above the surface) to about 50 km. It is characterised by an increase in temperature with increasing altitude.
tellurium → telurij
Tellurium was discovered by Franz Joseph Muller von Reichstein (Romania) in 1782. The origin of the name comes from the Latin word tellus meaning earth. It is silvery-white, brittle semi-metal. Unreactive with water or HCl; dissolves in HNO3; burns in air or oxygen. Tellurium is obtained as a by-product of copper and lead refining. Used to improve the machining quality of copper and stainless steel products and to colour glass and ceramics. Also in thermoelectric devices. Some is used in the rubber industry and it is a basic ingredient in manufacturing blasting caps.
thermosphere → termosfera
Thermosphere is the layer of the earth’s atmosphere extending from the top of the mesosphere (80 km - 90 km above the surface) to about 500 km. It is characterised by a rapid increase in temperature with increasing altitude up to about 200 km, followed by a levelling off in the 300 km - 500 km region.
titanium → titanij
Titanium was discovered by William Gregor (England) in 1791. Named after the Titans, the sons of the Earth goddess in Greek mythology. It is shiny, dark-grey metal. Powdered form burns in air. Exposed surfaces form oxide coating. It can be highly polished and is relatively immune to tarnishing. Unreactive with alkali and most acids. Titanium usually occurs in the minerals ilmenite (FeTiO3), rutile (TiO2) and iron ores. Pure metal produced by heating TiO2 with C and Cl2 to produce TiCl4 then heated with Mg gas in Ar atmosphere. Since it is strong and resists acids it is used in many alloys. Titanium dioxide (TiO2), a white pigment that covers surfaces very well, is used in paint, rubber, paper and many others.
troposphere → troposfera
Troposphere is the lowest part of the earth’s atmosphere, extending to 10 km to 15 km above the surface. It is characterized by a decrease in temperature with increasing altitude. The exact height varies with latitude and season.
tungsten → volfram
Tungsten was discovered by Fausto and Juan Jose de Elhuyar (Spain) in 1783. Named after the tungsten mineral wolframite. It is hard, steel-grey to white metal. Highest melting point of all metals. Resists oxygen, acids and alkalis. Tungsten occurs in the minerals scheelite (CaWO4) and wolframite [(Fe,Mn)WO4]. Made into filaments for vacuum tubes and electric lights. Also as contact points in cars. Tungsten carbide is extremely hard and is used for making cutting tools and abrasives.
vanadium → vanadij
Vanadium was discovered by A. M. del Rio (Spain) in 1801 and rediscovered by Nils Sefstrom (Sweden) in 1830. Named after Vanadis, the goddess of beauty in Scandinavian mythology. It is soft, ductile, silvery-white metal. Resistant to corrosion by moisture, air and most acids and alkalis at room temperature. Exposed surfaces form oxide coating. Reacts with concentrated acids. Vanadium is found in the minerals patronite (VS4), vanadinite [Pb5(VO4)3Cl] and carnotite [K2(UO2)2(VO4)2·3H2O]. Pure metal produced by heating with C and Cl to produce VCl3 which is heated with Mg in Ar atmosphere. It is mixed with other metals to make very strong and durable alloys. Vanadium pentoxide (V2O5) is used as a catalyst, dye and fixer-fixer.
Citing this page:
Generalic, Eni. "Dijatomejska zemlja." Croatian-English Chemistry Dictionary & Glossary. 29 June 2022. KTF-Split. {Date of access}. <https://glossary.periodni.com>.
Glossary
Periodic Table