Results 1–4 of 4 for cysteine
cysteine → cistein
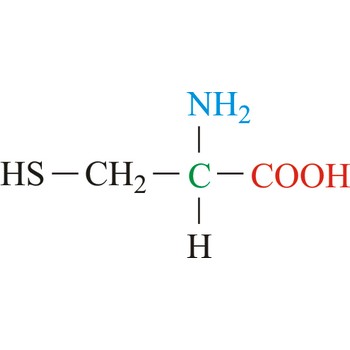
Cysteine is neutral amino acids with polar side chains. Because of its high reactivity, the thiol group of cysteine has numerous biological functions. It serves as a potent nucleophile and metal ligand (particularly for iron and zinc), but is best known for its ability to form disulfide bonds, which often make an important contribution to the stability of extracellular proteins. Cysteine is a non-essential amino acid, which means that it is biosynthesized in humans.
- Abbreviations: Cys, C
- IUPAC name: 2-amino-3-sulfanylpropanoic acid
- Molecular formula: C3H7NO2S
- Molecular weight: 121.16 g/mol
coenzyme a → koenzim a
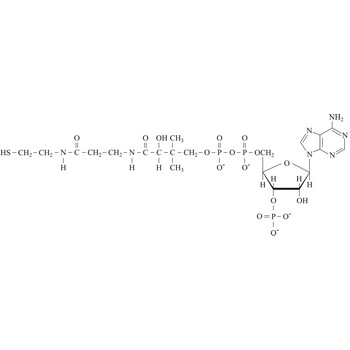
Coenzyme A (CoA) is an essential metabolic cofactor synthesized from cysteine, pantothenate (vitamin B5), and ATP. CoA plays important roles in many metabolic pathways, including the tricarboxylic acid (TCA) cycle, and the synthesis and oxidation of fatty acids. One of the main functions of CoA is the carrying and transfer of acyl groups. Acylated derivatives (acetyl-CoA) are critical intermediates in many metabolic reactions.
cross-linking → umrežavanje
Cross-linking is an attachment of two chains of polymer molecules by bridges, composed of either an element, a group, or a compound, that join certain carbon atoms of the chains by primary chemical bonds, as indicated in the schematic diagram
Cross-linking occurs in nature in substances made up of polypeptide chains that are joined by the disulfide bonds of the cysteine residue, as in keratins or insulin. Cross-linking can be artificially effected, either adding a chemical substance (cross-linking agent), or by subjecting the polymer to high-energy radiation. Examples are: vulcanisation of rubber with sulphur, cross-linking of polystyrene with divinylbenzene, or cross-linking of polyethylene by means of high-energy radiation.
Cross-linking has the effect of changing a plastic from thermoplastic to thermosetting. Thus, it also increases strength, heat and electrical resistance, and especially resistance to solvents and other chemicals.
Cystine → Cistin
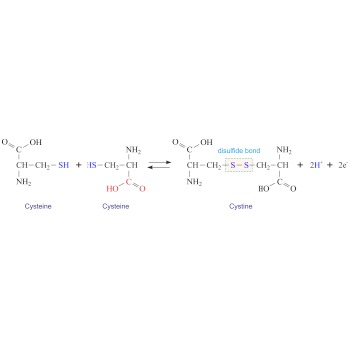
Cystine (C6H12N2O4S2) is a dimer of cysteine. It is formed by the oxidation of the thiol groups (-SH) of two cysteines generating a disulphide bridge (-S-S-). Cystine is a white crystalline solid that is slightly soluble in water. Cystine is particularly abundant in skeletal and connective tissues and in hair, horn, and wool.
Citing this page:
Generalic, Eni. "Cysteine." Croatian-English Chemistry Dictionary & Glossary. 29 June 2022. KTF-Split. {Date of access}. <https://glossary.periodni.com>.
Glossary
Periodic Table