extraction → ekstrakcija
Extraction is the separation of a component from its mixture by selective solubility. When a solution of one substance in one solvent is brought in with another solvent dissolved substance will distribute between the two solutants because of different solubility. Extraction is an efficient and fast method used for separating and concentrating matters. Extraction is best done several times in a succession, with smaller amount of solvent in it the matter is better dissolved. For example, caffeine can be separated from coffee beans by washing the beans with supercritical fluid carbon dioxide; the caffeine dissolves in the carbon dioxide, but flavour compounds do not. Vanillin can be extracted from vanilla beans by shaking the beans with an organic solvent, like ethanol.
face-centered cubic lattice → plošno centrirana kubična rešetka
Face-centered cubic lattice (fcc or cubic-F), like all lattices, has lattice points at the eight corners of the unit cell plus additional points at the centers of each face of the unit cell. It has unit cell vectors a =b =c and interaxial angles α=β=γ=90°.
The simplest crystal structures are those in which there is only a single atom at each lattice point. In the fcc structures the spheres fill 74 % of the volume. The number of atoms in a unit cell is four (8×1/8 + 6×1/2 = 4). There are 26 metals that have the fcc lattice.
face-centered orthorhombic lattice → plošno centrirana ortorompska rešetka
Face-centered orthorhombic lattice (orthorhombic-F), like all lattices, has lattice points at the eight corners of the unit cell plus additional points at the centers of each face of the unit cell. It has unit cell vectors a≠b≠c and interaxial angles α=β=γ=90°.
Fahrenheit scale → Fahrenheitova skala
Fahrenheit scale is the temperature scale in which 212 degrees is the boiling point of water and 32 degrees is the freezing point of water. The scale was invented in 1714 by the German physicist G.D. Fahrenheit (1686-1736).
32 °F = 0 °C
212 °F = 100 °C
1 °F =(5/9) °C
T(°C) = (5/9)[T(°F) - 32]
T(°F) = (9/5)T(°C) + 32
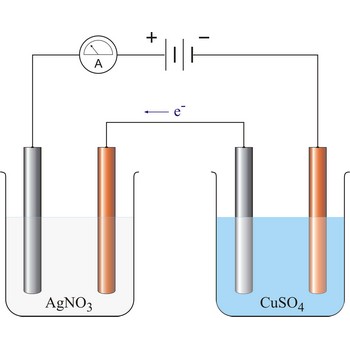
Faraday’s laws of electrolysis → Faradayevi zakoni elektrolize
Faraday’s laws of electrolysis are two laws found by British chemist and physicist Michael Faraday (1791-1867) in his experiments on electrolysis:
1. The quantity of matter extracted on the electrode is proportional to the quantity of charge (Q = I·t) which has flown in electrolysis time.
where z = number of electrons changed in reaction and F = Faraday’s constant which equals 96 487 C mol-1.
2. The masses of the elements liberated by the same quantity of electricity are directly proportional to their chemical equivalents.
96 487 C will discharge 1 mol Ag and 1/2 mol Cu. The relevant half reactions are:
fat → mast
Fats are esters of glycerol and long chain carboxylic acids. Fats occur widely in plants and animals as a means of storing food energy, having twice the calorific value of carbohydrates. Fats derived from plants and fish generally have a greater proportion of unsaturated fatty acids than those from mammals. Fats may be either solid or liquid at room temperature, depending on their structure and composition. Unsaturated fats are liquid at room temperature.
Plant oils may be hardened by the addition of hydrogen atoms, converting double bonds to single bonds. This process is known as hydrogenation. Hydrogenated vegetable oils are often present in margarine and other processed foods.
Alkali hydrolysis of fat with sodium hydroxide it gives glycerol and soap (i.e. a mixture of the sodium salts of the fatty acids).
fatty acid → masna kiselina
Fatty acids are aliphatic monocarboxylic acids characterized by a terminal carboxyl group (R-COOH). The higher members of this series of acids occur in nature in the combined form of esters of glycerol (fats), and hence all acids of this family are called fatty acids. Natural fatty acids commonly have a chain of 4 to 28 carbons (usually unbranched and even-numbered), which may be saturated or unsaturated. The most important of saturated fatty acids are butyric (C4), lauric (C12), palmitic (C16), and stearic (C18). The most common unsaturated acids are oleic, linoleic, and linolenic (all C18).
The physical properties of fatty acids are determined by the chain length, degree of unsaturation, and chain branching. Short-chain acids are pungent liquids, soluble in water. As the chain length increases, melting points are raised and water-solubility decreases. Unsaturation and chain branching tend to lower melting points.
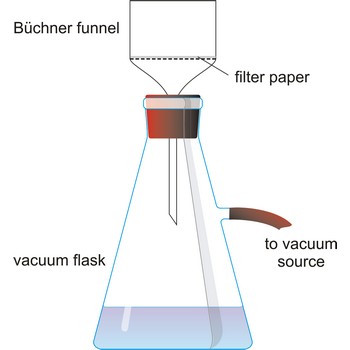
filter flask → boca za odsisavanje
Filter flask, also known as a vacuum flask, is a flask with a side arm to which a vacuum can be applied. It usually have heavy side walls to withstand high vacuum.
filter paper → filtar papir
Filter paper is a quantitative paper used for filtering and made of pure cellulose treated with hydrochloric and hydrofluoric acid. This kind of paper burns out practically without any remains (less than 0.0001 g ashes). Different types of paper are marked with numbers; qualitative bears marking 595 or 597 and quantitative 589 or 590. Dependable upon precipitate character, different types of filter paper are used:
- black band (5891) - 100 mL of fluid flows through it in 20 s to 30 s. It is used for filtering of gelatinous precipitates.
- white band (5892) - 100 mL of fluid flows through it in 40 s to 60 s. It is used for coarse crystalline precipitates filtration.
- blue band (5893) - 100 mL of fluid flows through it in 200 s to 400 s. It is used for fine crystalline precipitates.
filtration → filtriranje
Filtration is a procedure in which liquids are separated from the precipitate by passing a suspension through the filter. The precipitate remains on the filter and through it the filtrate passes. Gaseous heterogeneous mixtures can also be filtrated.
Citing this page:
Generalic, Eni. "Curtain rod width." Croatian-English Chemistry Dictionary & Glossary. 29 June 2022. KTF-Split. {Date of access}. <https://glossary.periodni.com>.
Glossary
Periodic Table