microscope → mikroskop
Microscope is an instrument that produces enlarged images of small objects. The optical microscopes (light microscope) use visible light and a system of lenses to magnify images. Typical magnification of a light microscope is up to 1500× ("1500 times")with a theoretical resolution limit of around 200 nm. Instead of using light, electron microscopes transmit a beam of electrons through, or onto the surface of, a specimen. An electron beam has a much shorter wavelength than does light, and can reveal structures as small as 2 nm.
monosaccharide → monosaharid
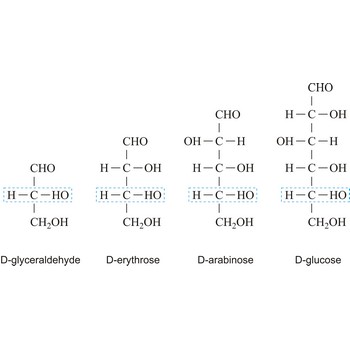
Monosaccharides are carbohydrates, with the general formula Cn(H2O)n, that cannot be decomposed to a simpler carbohydrates by hydrolysis.
Depending on whether the molecule contains an aldehyde group (-CHO) or a ketone group (-CO-) monosaccharide can be a polyhydroxy aldehyde (aldose) or a polyhydroxy ketone (ketose). These aldehyde and ketone groups confer reduction properties on monosaccharides. They are also classified according to the number of carbon atoms they contain: trioses have three carbon atoms, tetroses four, pentoses five, hexoses six, heptoses seven, etc. These two systems of classification are often combined. For example, a six-carbon polyhydroxy aldehyde such as D-glucose is an aldohexose, whereas a six-carbon polyhydroxy ketone such as D-fructose is a ketohexose.
The notations D and L are used to describe the configurations of carbohydrates. In Fischer projections of monosaccharides, the carbonyl group is always placed on top (in the case of aldoses) or as close to the top as possible (in the case of ketoses). If the OH group attached to the bottom-most asymmetric carbon (the carbon that is second from the bottom) is on the right, then the compound is a D-sugar. If the OH group is on the left, then the compound is an L-sugar. Almost all sugars found in nature are D-sugars.
Monosaccharides can exist as either straight-chain or ring-shaped molecules. During the conversion from straight-chain form to cyclic form, the carbon atom containing the carbonyl oxygen, called the anomeric carbon, becomes a chiral center with two possible configurations (anomers), α and β. When the stereochemistry of the first carbon matches the stereochemistry of the last stereogenic center the sugar is the α-anomer when they are opposite the sugar is the β-anomer.
niobium → niobij
Niobium was discovered by Charles Hatchett (England) in 1801. The origin of the name comes from the Greek word Niobe meaning daughter of Tantalus in Greek mythology (tantalum is closely related to niobium in the periodic table). It is shiny white, soft, ductile metal. Exposed surfaces form oxide film. Niobium occurs in a mineral columbite. It is used in stainless steel alloys for nuclear reactors, jets and missiles. Used as an alloy with iron and nickel. It can be used in nuclear reactors and is known to be superconductive when alloyed with tin, aluminium or zirconium.
nuclear magnetic resonance → nuklearna magnetska rezonancija
Nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) is a type of radio-frequency spectroscopy based on the magnetic field generated by the spinning of electrically charged atomic nuclei. This nuclear magnetic field is caused to interact with a very large (1 T - 5 T) magnetic field of the instrument magnet. NMR techniques have been applied to studies of electron densities and chemical bonding and have become a fundamental research tool for structure determinations in organic chemistry.
pipette → pipeta
Pipettes are glass tubes which are tapers towards at both ends into narrow opened tubes. According to their design two types of pipettes can be distinguished:
Volumetric pipettes
Volumetric pipettes (transfer or belly pipette) are used in volumetric analysis, when there is a need for taking exact smaller volume of a sample solution or reagent. The upper tube of volumetric pipette has a ringlike marking (mark) which marks its calibrated volume. Pipettes calibrated to deliver (TD or Ex) the indicated volume. By sucking in (with mouth, propipette or a water pump) the liquid is pulled in a little bit above the mark and the opening of the pipet is closed with a forefingertip. Outer wall of pipet is wiped and, with a slight forefinger loosening, the liquid is released until it reaches the mark. Mark must figure as a tangent on a lower edge of the liquid meniscus. A pipette is emptied out by lifting the forefinger off and letting the liquid flow out of the pipette freely. After another 15 s and the tip of the pipette is pulled onto the inner wall of the vessel. It is absolutely forbidden to blow out the contents of the pipette
Graduated pipettes
Graduated pipettes (Mohr pipette) have a scale divided into units of one and of 1/10th of a millilitre. Because of their wide necks it is less accurate than the volumetric pipette. They are used when taking volume of solutions in which accuracy does not have to be very high. They are filled in the same way as volumetric ones and liquid can be gradually released.
polydentant ligand → polidentantni liganad
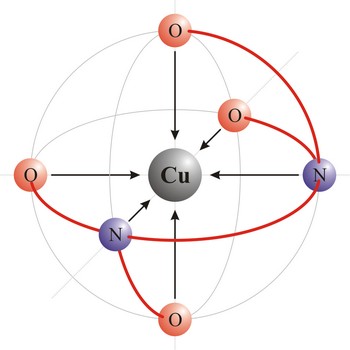
Polydentant ligands contain more co-ordination points (can give more electron pairs) and they form complex ringlike structures (celate complexes) by replacing two or more monodentant ligands. That kind of ligand is EDTA which has 6 co-ordinational points and with metals it creates complexes, always in 1:1 ratio.
polymer → polimer
Polymer is a substance composed of molecules of high relative molecular mass (molecular weight), the structure of which essentially comprises the multiple repetition of units derived, actually or conceptually, from molecules of low relative molecular mass (monomers). In most cases the number of monomers is quite large and is often not precisely known. A single molecule of a polymer is called a macromolecule. Polystyrene is light solid material obtained by polymerisation of styrene (vinyl benzene).
polymorphism → polimorfija
Polymorphism is the ability of a solid substance to crystallise into more than one different crystal structure. Different polymorphs have different arrangements of atoms within the unit cell, and this can have a profound effect on the properties of the final crystallised compound. The change that takes place between crystal structures of the same chemical compound is called polymorphic transformation.
The set of unique crystal structures a given compound may form are called polymorphs. Calcium carbonate is dimorphous (two forms), crystallizing as calcite or aragonite. Titanium dioxide is trimorphous; its three forms are brookite, anatase, and rutile. The prevailing crystal structure depends on both the temperature and the external pressure.
Iron is a metal with polymorphism structure. Each structure stable in the range of temperature, for example, when iron crystallizes at 1 538 °C it is bcc (δ-iron), at 1 394 °C the structure changes to fcc (γ-iron or austenite), and at 912 °C it again becomes bcc (α-iron or ferrite).
Polymorphism of an element is called allotropy.
polystyrene → polistiren
Polystyrene is a vinyl polymer. Structurally, it is a long hydrocarbon chain, with a phenyl group attached to every other carbon atom. Polystyrene is produced by free radical vinyl polymerization, from the monomer styrene. Polystyrene or Styrofoam is used in the construction industry as insulating material and for production of containers.
Citing this page:
Generalic, Eni. "Cubic close-packed structure." Croatian-English Chemistry Dictionary & Glossary. 29 June 2022. KTF-Split. {Date of access}. <https://glossary.periodni.com>.
Glossary
Periodic Table