boron → bor
Boron compounds have been known for thousands of years, but the element was not discovered until 1808 by Sir Humphry Davy (England) and independently by Joseph-Louis Gay-Lussac (France) and L. J. Thenard (France). The origin of the name comes from the Arabic word buraq and the Persian word burah meaning boraks. It is hard, brittle, lustrous black semimetal. Unreactive with oxygen, water, alkalis or acids. Combines with most metals to form borides. Boron is obtained from kernite, a kind of borax (Na2B4O7·10H2O). High purity boron is produced by electrolysis of molten potassium fluroborate and potassium chloride (KCl). Amorphous boron is used in pyrotechnic flares to provide a distinctive green color and in rockets as an igniter.
calomel electrode → kalomel elektroda
Calomel electrode is a type of half cell in which the electrode is mercury coated with calomel (Hg2Cl2) and the electrolyte is a solution of potassium chloride and saturated calomel. In the calomel half cell the overall reaction is
Table: Dependence of potential of calomel electrode upon temperature and concentration of KCl according to standard hydrogen electrode
| Potential vs. SHE / V | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| t / °C | 0.1 mol dm-3 | 3.5 mol dm-3 | sat. solution |
| 15 | 0.3362 | 0.254 | 0.2511 |
| 20 | 0.3359 | 0.252 | 0.2479 |
| 25 | 0.3356 | 0.250 | 0.2444 |
| 30 | 0.3351 | 0.248 | 0.2411 |
| 35 | 0.3344 | 0.246 | 0.2376 |
carbohydrate → ugljikohidrat
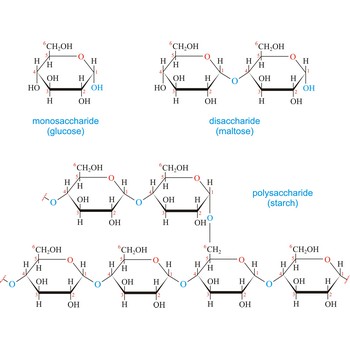
Carbohydrates (often called carbs for short) are polyhydroxy aldehydes or ketones, or substances that yield such compounds on hydrolysis. They are also known as saccharides, a term derived from the Latin word saccharum for sugar. Carbohydrates are the most abundant class of compounds in the biological world, making up more than 50 % of the dry weight of the Earth’s biomass. Every type of food we eat can have its energy traced back to a plant. Plants use carbon dioxide and water to make glucose, a simple sugar, in photosynthesis. Other carbohydrates such as cellulose and starch are made from the glucose. Light from the sun is absorbed by chlorophyll and this is converted to the energy necessary to biosynthesize carbohydrates
The term carbohydrate was applied originally to monosaccharides, in recognition of the fact that their empirical composition can be expressed as Cx(H2O)y. Later structural studies revealed that these compounds were not hydrates but the term carbohydrate persists.
Carbohydrates are generally classed as either simple or complex. Simple sugars, or monosaccharides, are carbohydrates that can’t be converted into smaller subunits by hydrolysis. Complex carbohydrates are made of two (disaccharides) or more (oligosaccharides, polysaccharides) simple sugars linked together by acetal (glycosidic) bonds and can be split into the former by hydrolysis.
chemical change → kemijska promjena
Chemical change is a process which results in the production of one or more new materials. The system within which the process takes place is called a chemical system. A chemical change is also known as a chemical reaction, where one substance is converted into one or more different substances. When sodium and chlorine react to produce sodium chloride, a chemical reaction has taken place.
derivative → derivat
Derivative is a compound that is derived from some other compound and usually maintains its general structure, e.g. trichlormethane (chloroform) is a derivative of methane.
mineral acid → mineralna kiselina
Mineral acid is an acid made from minerals by chemical reaction, e.g. hydrochloric acid is produced from sodium chloride and sulphuric acid is made from sulphur.
monodentate ligand → monodentantni ligand
Monodentate ligand is a ligand that has only one atom that coordinates directly to the central atom in a complex. For example, ammonia and chloride ion are monodentate ligands of copper in the complexes [Cu(NH3)6]2+ and [CuCl6]2+.
colloid ion → koloidni ion
Colloid ions emerge when colloid particles adsorb certain type of ion from solution and thus become charged with the same charge. The charge can also originate form a chemical reaction of colloid particle’s surface. Colloid ions formed by absorption of silver chloride particle can be show as follows:
Adsorbed layer is monomolecular (one molecule thick) and which type of ion will be formed depends upon which ions are present in a greater number in the solution in. Because of this colloid particles are charged with the same charge, mutual repelling occurs, and the colloid solution becomes stable. Colloid charge can be determined by electrophoresis.
Citing this page:
Generalic, Eni. "Chloe." Croatian-English Chemistry Dictionary & Glossary. 29 June 2022. KTF-Split. {Date of access}. <https://glossary.periodni.com>.
Glossary
Periodic Table