cetane number → cetanski broj
Cetane number is a measure of the ignition quality of diesel fuel. It denotes the volume fraction of cetane (C16H34) in a combustible mixture (containing cetane and 1-methylnapthalene) whose ignition characteristics match those of the diesel fuel being tested. Cetane is a collection of un-branched open chain alkane molecule that ignites very easily under compression, so it was assigned a cetane number of 100, while alpha-methyl naphthalene was assigned a cetane number of 0.
fatty acid → masna kiselina
Fatty acids are aliphatic monocarboxylic acids characterized by a terminal carboxyl group (R-COOH). The higher members of this series of acids occur in nature in the combined form of esters of glycerol (fats), and hence all acids of this family are called fatty acids. Natural fatty acids commonly have a chain of 4 to 28 carbons (usually unbranched and even-numbered), which may be saturated or unsaturated. The most important of saturated fatty acids are butyric (C4), lauric (C12), palmitic (C16), and stearic (C18). The most common unsaturated acids are oleic, linoleic, and linolenic (all C18).
The physical properties of fatty acids are determined by the chain length, degree of unsaturation, and chain branching. Short-chain acids are pungent liquids, soluble in water. As the chain length increases, melting points are raised and water-solubility decreases. Unsaturation and chain branching tend to lower melting points.
gasoline → motorni benzin
Gasoline is a complex mixture of volatile hydrocarbons that may have between 5 to 12 carbons. The major components are branched-chain paraffins, cycloparaffins, and aromatics. Gasoline is most often produced by the fractional distillation of crude oil as the fraction of hydrocarbons in petroleum boiling between 30 °C and 200 °C. The quality of a fuel is measured with its octane number. Octane number is the measure of the resistance of gasoline against detonation or preignition of the fuel in the engine. The higher the octane number, the more compression the fuel can withstand before detonating. The octane number is determined by comparing the characteristics of a gasoline to isooctane with good knocking properties (octane number of 100) and heptane with bad (octane number of 0).
mineralogy → mineralogija
Mineralogy is a branch of geology that studies minerals: their structure and properties and the ways of distinguishing them.
quantum chemistry → kvantna kemija
Quantum chemistry is a theoretical branch of chemistry that concerns the application of quantum mechanics to chemical problems.
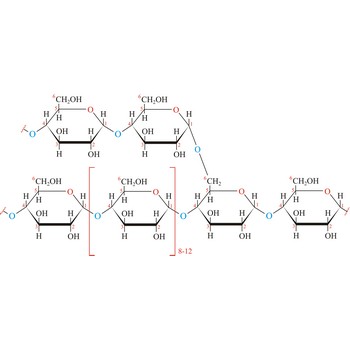
glycogen → glikogen
Glycogen (animal starch) is a polysaccharide that serves the same energy storage function in animals that starch serves in plants. Dietary carbohydrates not needed for immediate energy are converted by the body to glycogen for long term storage (principally in muscle and liver cells). Like amylopectin found in starch, glycogen is a polymer of α(1→4)-linked subunits of glucose, with α(1→6)-linked branches. Glycogen molecules are larger than those of amylopectin (up to 100 000 glucose units) and contain even more branches. Branch points occur about every 10 residues in glycogen and about every 25 residues in amylopectin. The branching also creates lots of ends for enzyme attack and provides for rapid release of glucose when it is needed.
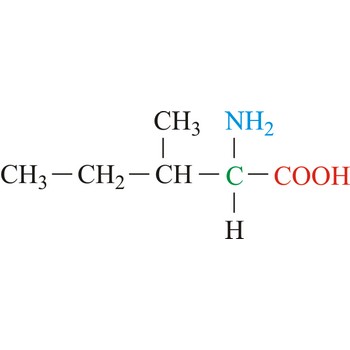
isoleucine → izoleucin
Isoleucine is hydrophobic amino acids with aliphatic side chain. It is one of the three amino acids having branched hydrocarbon side chains. The side chains of these amino acids are not reactive but, these residues are critically important for ligand binding to proteins, and play central roles in protein stability. Isoleucine is an essential amino acid, which means that humans cannot synthesize it, so it must be ingested.
- Abbreviations: Ile, I
- IUPAC name: 2-amino-3-methylpentanoic acid
- Molecular formula: C6H13NO2
- Molecular weight: 131.12 g/mol
Knudsen’s pipette → Knudsenova pipeta
Kudsen's automatic pipette, developed by the Danish physicist Martin Knudsen (1871-1949), allows quick and accurate transfer of a constant volume of liquid (sea water), usually around 15 mL. On the top of pipette is a double sided C vent that can establish flow between the body of the pipette and one of the branches (A or B), or isolate the body of the pipette from both of the branches. Sucking through the B branch the pipette is filled with liquid, it is closed with a twist of the C valve and the liquid is released by rotating the valve towards the A branch (so atmospheric air can enter the pipette). Emptying the pipette takes around 30 seconds. Before it's first use, the pipette must be calibrated with distilled water.
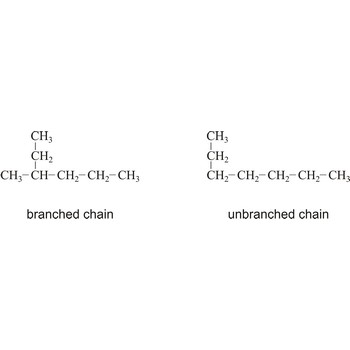
lateral chain → postranični lanac
Lateral chain is a shorter chain of hydrocarbons which is connected to the main chain of hydrocarbon.
Citing this page:
Generalic, Eni. "Branch." Croatian-English Chemistry Dictionary & Glossary. 29 June 2022. KTF-Split. {Date of access}. <https://glossary.periodni.com>.
Glossary
Periodic Table