rare earth elements → elementi rijetkih zemalja
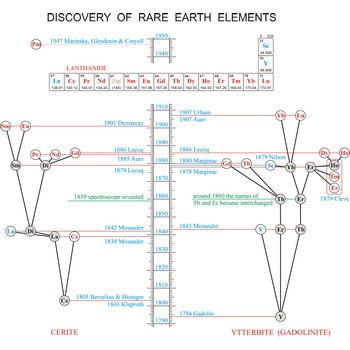
Rare earth elements (metals) are the elements scandium (Sc), yttrium (Y), and the lanthanides (La, Ce, Pr, Nd, Pm, Sm, Eu, Gd, Tb, Dy, Ho, Er, Tm, Yb, Lu). These elements got their name from the fact that chemists first isolated them in their oxide forms. These oxides somewhat resemble calcium, magnesium and aluminium oxides, sometimes called common earths. Do you want to know more?
redox potential → redoks potencijal
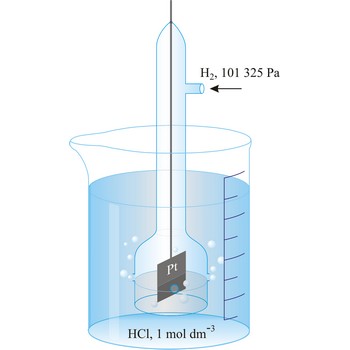
Redox potential is the potential of a reversible oxidation-reduction electrode measured with respect to a reference electrode, corrected to the hydrogen electrode, in a given electrolyte.
reflux condenser → povratno hladilo
Reflux condenser is used for repeated transformation of vapour in liquid in order to prevent the loss due to evaporation.
refractometer → refraktometar
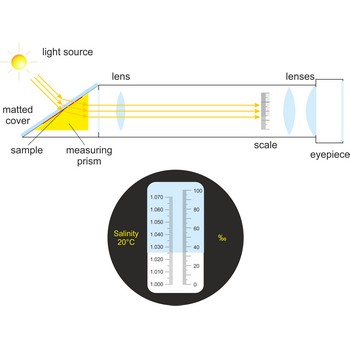
Refractometer is an optical device used from measurement of refractive index. A refractometer takes advantage of the fact that light bends as it passes through different materials. It can be used to measure the salinity of water or the amount of sugar in fresh grapes. Refractometers are available with or without automatic temperature compensation (ATC).
When using a conventional saltwater refractometer, a sample is placed on an optical prism in the sample window. As light shines through the sample, it is bent according to the salinity of the water, and casts a shadow on the scale that is visible through the eyepiece. Salinity is read directly through the eyepiece.
resonance → rezonancija
Resonance is a stabilising quality of certain molecules that can be represented by considering the electron distribution in an ion or molecule as a composite of two or more forms, in those cases where a single form is an inadequate representation; for example, benzene and the carbonate ion. A various canonical structures can be drawn to show how electron delocalisation will explain the discrepancy, the difference in electron density
retardation factor → faktor zaostajanja
Retardation factor, RF, (in planar chromatography) is a ratio of the distance travelled by the centre of the spot to the distance simultaneously travelled by the mobile phase:
The RF value is characteristic for any given compound on the same stationary phase using the same mobile phase for development of the plates. Hence, known RF values can be compared to those of unknown substances to aid in their identifications.
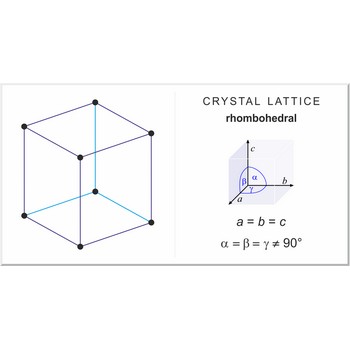
rhombohedral crystal system → romboedarski kristalni sustav
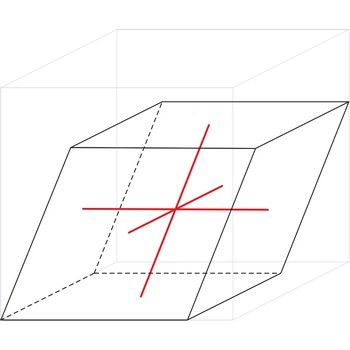
Rhombohedral crystal system is also known as the trigonal system. The crystallographic axes used in this system are of equal length. None of the axes are perpendicular to any other axis.
a = b = c
α= β = γ ≠ 90°
rhombohedral lattice → romboedarska rešetka
Rhombohedral (or trigonal) lattice has one lattice point at the each corner of the unit cell. It has unit cell vectors a=b=c and interaxial angles α=β=γ≠90°.
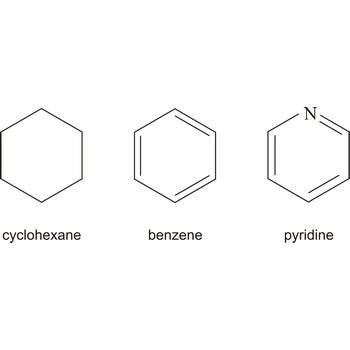
ringlike structure → prstenasta struktura
The ringlike structure is a structure by which the cycloalcanes and aromates are shown.
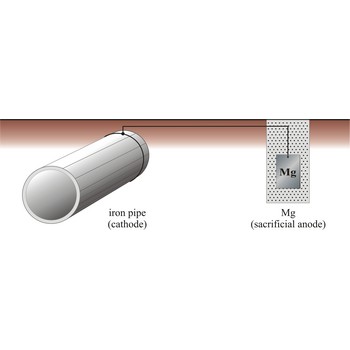
sacrificial protection → zaštita žrtvovanom elektrodom
Sacrificial protection is the protection of iron or steel against corrosion by using a more reactive metal. Pieces of zinc or magnesium alloy are attached to pump bodies and pipes. The protected metal becomes the cathode and does not corrode. The anode corrodes, thereby providing the desired sacrificial protection. These items are known as sacrificial anodes and "attract" the corrosion to them rather than the iron/steel. The sacrificial anodes must be replaced periodically as they corrode.
The iron pipe will be connected to a more reactive metal such as magnesium through cooper wires, the magnesium will donate its electrons to the iron preventing it from rusting. Iron which is oxidises will immediately be reduced back to iron.
Citing this page:
Generalic, Eni. "Blast furnace glossary." Croatian-English Chemistry Dictionary & Glossary. 29 June 2022. KTF-Split. {Date of access}. <https://glossary.periodni.com>.
Glossary
Periodic Table