blast furnace → visoka peć
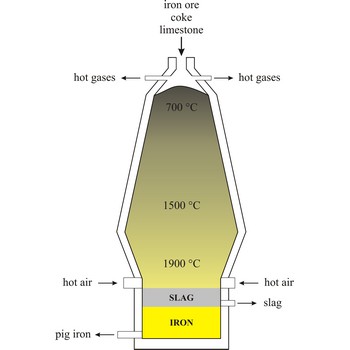
Blast furnace is a furnace for smelting of iron from iron oxide ores (hematite, Fe2O3 or magnetite, Fe3O4). Coke, limestone and iron ore are poured in the top, which would normally burn only on the surface. The hot air blast to the furnace burns the coke and maintains the very high temperatures that are needed to reduce the ore to iron. The reaction between air and the fuel generates carbon monoxide. This gas reduces the iron(III) oxide in the ore to iron.
Because the furnace temperature is in the region of 1500 °C, the metal is produced in a molten state and this runs down to the base of the furnace.
The production of iron in a blast furnace is a continuous process. The furnace is heated constantly and is re-charged with raw materials from the top while it is being tapped from the bottom. Iron making in the furnace usually continues for about ten years before the furnace linings have to be renewed.
basic Bessemer process → bazni Bessemerov proces
Basic Bessemer process is the process of steelmaking in a way that steel, melted iron and limestone are put in the blast-furnace after which the metal oxygen is released in gushes in order to oxidise the impurities.
Bessemer, Henry → Bessemer, Henry
Sir Henry Bessemer (1813-1898) is the British engineer who first introduced a process for converting pig iron from a blast furnace into steel
iron → željezo
Iron has been known since ancient times. The origin of the name comes from the Latin word ferrum meaning iron. It is malleable, ductile, silvery-white metal. Exposed surfaces form red-brown oxides. Forms very strong alloys (steel). Ferromagnetic. Metal dust flammable. Fourth most abundant element in the earth’s crust. Iron is obtained from iron ores. Pure metal produced in blast furnaces by layering limestone, coke and iron ore and forcing hot gasses into the bottom. This heats the coke red hot and the iron is reduced from its oxides and liquefied where it flows to the bottom. Iron is the most common metal in human society. More than 90 % of all metal refined in the world is iron. Used in steel and other alloys. It is the chief constituent of hemoglobin which carries oxygen in blood vessels. Its oxides are used in magnetic tapes and disks.
nickel → nikal
Nickel was discovered by Axel Fredrik Cronstedt (Sweden) in 1751. The origin of the name comes from the German word kupfernickel meaning Devil’s copper or St Nicholas’s (Old Nick’s) copper. It is hard, malleable, silvery-white metal. Soluble in acids, resist alkalis. It can be polished to a lustrous finish. Resists corrosion in air under normal conditions. Nickel is chiefly found in pentlandite [(Ni,Fe)9S8] ore. The metal is produced by heating the ore in a blast furnace which replaces the sulfur with oxygen. The oxides are then treated with an acid that reacts with the iron not the nickel. Used in electroplating and metal alloys because of its resistance to corrosion. Also in nickel-cadmium batteries, as a catalyst and for coins.
absorbance → apsorbancija
Absorbance (A) is a logarithm of the ratio of incident radiant power (Po) to transmitted radiant power (P) through a sample (excluding the effects on cell walls).
The absorption of light by a substance in a solution can be described mathematically by the Beer-Lambert law
where A is the absorbance at a given wavelength of light, ε is the molar absorbtivity or extinction coefficient (L mol-1 cm-1), unique to each molecule and varying with wavelength, b is the length of light path through the sample (cm), and c is the concentration of the compound in solution (mol L-1).
abundance of elements → rasprostranjenost elemenata
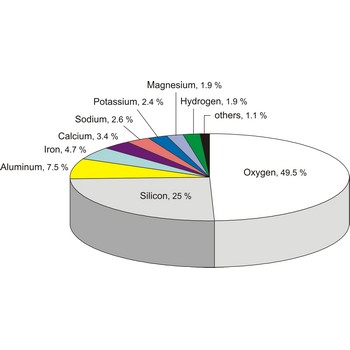
Elements in nature are mostly found in different compounds and, rarely, in the free (elementary) state. In Earth’s crust the most abundant of all elements is oxygen (with 49.5 %), then silicon (25 %), aluminium (7.5 %), iron (4.7 %), calcium (3.4 %), sodium (2.6 %), potassium (2.4 %), magnesium (1.9 %) and hydrogen (1.9 %). These nine elements make up almost 99 % of the Earth’s composition.
accumulator → akumulator
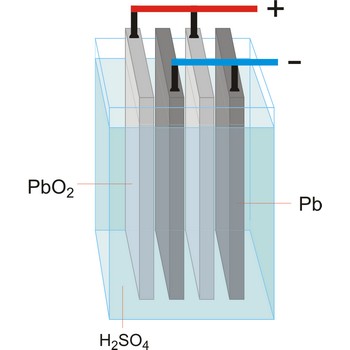
Accumulator (secondary cell, storage battery) is a type of voltaic cell or battery that can be recharged by passing current through it from an external D.C. supply. The charging current reverses the chemical reactions in the cell. The common types are the lead-acid accumulator and the nickel-cadmium cell.
Citing this page:
Generalic, Eni. "Blast furnace glossary." Croatian-English Chemistry Dictionary & Glossary. 29 June 2022. KTF-Split. {Date of access}. <https://glossary.periodni.com>.
Glossary
Periodic Table