absolute error → apsolutna pogreška
Absolute error is a difference between the obtained value (O) and the real value (μ). It is shown in employed for measuring (g, cm3, ...). For example, if three replicate weights for an object are 1.00 g, 1.05 g, and 0.95 g, the absolute error can be expressed as ±0.05 g. Absolute error is also used to express inaccuracies; for example, if the "true value" is 1.11 g and the measured value is 1.00 g, the absolute error could be written as 1.00 g - 1.11 g = -0.11 g. Note that when absolute errors are associated with indeterminate errors, they are preceded by "±"; when they are associated with determinate errors, they are preceded by their sign.
relative mistake → relativna pogreška
Relative mistake is a relation between absolute mistake (O-μ) and the real value (μ). It is expressed in percentage (%).
absolute temperature → apsolutna temperatura
Absolute temperature denoting a temperature measured on the absolute scale, a scale of temperature based on absolute zero as the lowest temperature.
absolute zero → apsolutna nula temperature
Absolute zero is theoretically, the lowest attainable temperature. It is the energy at which the kinetic energy of atom and molecules is minimal and is equivalent to -273.15 °C.
systematic error → sustavna pogreška
Systematic errors have an identifiable cause and affect the accuracy of results.
absolute volume → apsolutni volumen
Absolute volume is the total volume of the particles in a granular material, including both permeable and impermeable voids but excluding spaces between particles.
significant figures → značajne znamenke
Measurements are not infinitely accurate: we must estimate measurement uncertainty. The number of significant figures is all of the certain digits plus the first uncertain digit.
Rules for significant figures:
- Disregard all initial zeros.
- Disregard all final zeros unless they follow a decimal point.
- All remaining digits including zeros between nonzero digits are significant.
| 0.0023 | has two significant figures |
| 0.109 | has three significant figures |
| 2.00 | has three significant figures |
| 70 | has one significant figure |
In addition and subtraction, the number of significant figures in the answer depends on the original number in the calculation that has the fewest digits to the right of the decimal point.
In multiplication and division, the number of significant figures in a calculated result is determined by the original measurement that has the fewest number of significant digits.
In a logarithm of a number, keep as many digits to the right of the decimal point as there are significant figures in the original number.
In an antilogarithm of a number, keep as many digits as there are digits to the right of the decimal point in the original number.
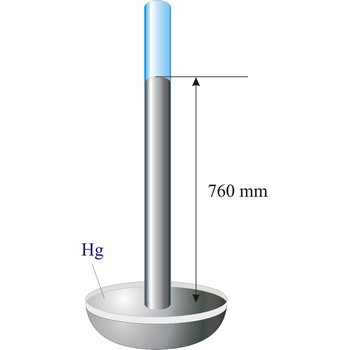
barometer → barometar
Barometer is an instrument that measures atmospheric pressure. A mercury barometer is a closed tube filled with mercury inverted in a mercury reservoir. The height of the mercury column indicates atmospheric pressure (with 1 atm = 760 mm of mercury). An aneroid barometer consists of an evacuated container with a flexible wall. When atmospheric pressure changes, the wall flexes and moves a pointer which indicates the changing pressure on a scale.
calibration → kalibracija
Calibration is correcting a measuring instrument by measuring values whose true values are known. Calibration minimises systematic error.
Citing this page:
Generalic, Eni. "Apsolutna pogreška." Croatian-English Chemistry Dictionary & Glossary. 29 June 2022. KTF-Split. {Date of access}. <https://glossary.periodni.com>.
Glossary
Periodic Table