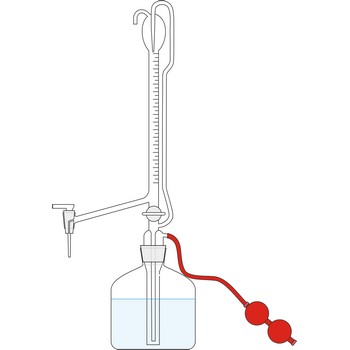
automatic burette → automatska bireta
Automatic burette is used for series of tests. It is connected with a bottle which contains the titration solution. The air is pumped into the bottle by a small rubber air pump, created the pressure in the bottle which the rises the solution to the top of burette. When the the burette is full, the valve is released, the pressure in the bottle falls and the burette automatically sets itself to zero. Work with automatic burettes is by far faster and the consumption of standard solution is smaller.
brass → mjed
Brasses are alloys of copper and zinc (generally 5 % to 40 %). Brass has been known to man since prehistoric times, long before zinc itself was discovered. It was produced by melting copper together with calamine, a zinc ore. Its ductility reaches a maximum with about 30 % zinc and its tensile strength with 45 % although this property varies greatly with the mechanical and heat treatment of the alloy. Typical applications included gears, plumbing ware fittings, adapters, valves and screw machine products. The French horn is a valved brass wind instrument.
Brass may contain small amounts of other alloying elements, such as aluminum, lead, tin, or nickel. Lead can be added as an alloying element resulting in a brass that can be rapidly machined and produces minimal tool wear. Additions of aluminium, iron and manganese to brass improve strength, whilst silicon additions improve wear resistance. Brass containing tin (< 2 % ) is less liable to corrosion in seawater; it is sometimes called naval brass and is used in naval construction.

calibration → kalibracija
Calibration is correcting a measuring instrument by measuring values whose true values are known. Calibration minimises systematic error.
chemical equation equalization → izjednačavanje kemijske jednadžbe
Chemical equation equalization is determining values of stechiometric coefficients of reactants and products in a chemical equation in a way that the number of atoms of each element is equal before and after the reaction.
bronze → bronca
Bronze is an alloy made primarily of copper and tin. It may contain as much as 25 % tin. Bronzes with 10 % or more tin are harder, stronger, and resistant to corrosion. As bronze weathers, a brown or green film forms on the surface. This film inhibits corrosion. Silicon or aluminium is often added to bronze to improve resistance to corrosion. Phosphorus, lead, zinc, and other metals may be added for special purposes. The alloy is hard and easily cast and is extensively used in bearings, valves and other machine parts.
Bronze was one of the first alloys developed by ancient metal workers. The Bronze Age occurred in Europe around 2200 to 700 BC. Bronze was used for weapons such as spearheads, swords, and knives. Since ancient times, bronze has been the most popular metal for casting statues and other art objects.

The term bronze has been adopted commercially for many copper-rich alloys that contain little or no tin but are similar in colour to bronze, including aluminium bronze, manganese bronze, and silicon bronze. Aluminium bronze is used to make tools and, because it will not spark when struck. Manganese bronze is actually a brass that contains manganese. It is often used to make ship propellers because it is strong and resists corrosion by sea water.
complexometry → kompleksometrija
Complexometry is a volumetric analytic method which is based on titration of metal ion solutions with a substance that, combined with metal ions yields complex compounds, e.g. EDTA. The stoichiometric ratio of EDTA-metal in complexometric analyses is always 1:1, whatever the valency of the metal
Fermi level → Fermijev nivo
Fermi level is the highest energy of occupied states in a solid at zero temperature. The Fermi level in conductors lies in the conduction band, in insulators it lies in the valence band, and in semiconductors it falls in the gap between the conduction band and the valence band. It was named after the Italian physicst Enrico Fermi (1901 - 1954).
dielectric constant → dielektrična konstanta
Dielectric constant or permittivity (ε) is an index of the ability of a substance to attenuate the transmission of an electrostatic force from one charged body to another. The lower the value, the greater the attenuation. The standard measurement apparatus utilises a vacuum whose dielectric constant is 1. In reference to this, various materials interposed between the charged terminal have the following value at 20 °C:
| vacuum | 1 |
| air | 1.00058 |
| glass | 3 |
| benzene | 2.3 |
| acetic acid | 6.2 |
| ammonia | 15.5 |
| ethanol | 25 |
| glycerol | 56 |
| water | 81 |
The exceptionally high value for water accounts for its unique behaviour as a solvent and in electrolytic solutions. Dielectric constant values decrease as the temperature rises.
electron → elektron
The electron is an elementary particle with a negative electric charge of (1.602 189 2±0.000 004 6)×10-19 C and a mass of 1/1837 that of a proton, equivalent to (9.109 534±0.000 047)×10-31 kg.
In 1897 the British physicist Joseph John (J.J.) Thomson (1856-1940) discovered the electron in a series of experiments designed to study the nature of electric discharge in a high-vacuum cathode-ray tube. Thomson interpreted the deflection of the rays by electrically charged plates and magnets as evidence of bodies much smaller than atoms that he calculated as having a very large value for the charge to mass ratio. Later he estimated the value of the charge itself.
Electrons are arranged in from one to seven shells around the nucleus; the maximum number of electrons in each shell is strictly limited by the laws of physics (2n2). The outer shells are not always filled: sodium has two electrons in the first shell (2×12 = 2), eight in the second (2×22 = 8), and only one in the third (2×32 = 18). A single electron in the outer shell may be attracted into an incomplete shell of another element, leaving the original atom with a net positive charge. Valence electrons are those that can be captured by or shared with another atom.
Electrons can be removed from the atoms by heat, light, electric energy, or bombardment with high-energy particles. Decaying radioactive nuclei spontaneously emit free electrons, called β particles.
geometrical optics → geometrijska optika
In most cases light can be described as an electromagnetic wave. Geometrical optics is an approximation in which the waves can be represented as straight-line rays. This approximation is valid if the light waves do not meet obstacles comparable in size to the wavelength of radiation.
Citing this page:
Generalic, Eni. "Amplituda vala." Croatian-English Chemistry Dictionary & Glossary. 29 June 2022. KTF-Split. {Date of access}. <https://glossary.periodni.com>.
Glossary
Periodic Table