aspartic acid → asparaginska kiselina
Aspartic acid is an electrically charged amino acids with acidic side chains. As a group the charged amino acids are relatively abundant and are generally located on the surface of the protein. Aspartic acid and glutamic acid play important roles as general acids in enzyme active centers, as well as in maintaining the solubility and ionic character of proteins. Aspartic acid (sometimes referred to as asparate depending on pH) is non-essential in mammals, being produced from oxaloacetate by transamination.
- Abbreviations: Asp, D
- IUPAC name: 2-aminobutanedioic acid
- Molecular formula: C4H7NO4
- Molecular weight: 133.10 g/mol
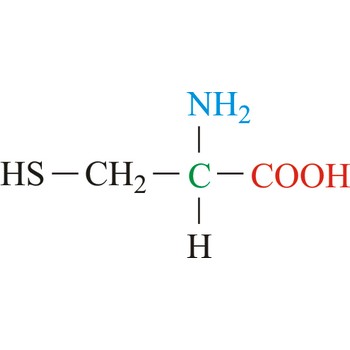
cysteine → cistein
Cysteine is neutral amino acids with polar side chains. Because of its high reactivity, the thiol group of cysteine has numerous biological functions. It serves as a potent nucleophile and metal ligand (particularly for iron and zinc), but is best known for its ability to form disulfide bonds, which often make an important contribution to the stability of extracellular proteins. Cysteine is a non-essential amino acid, which means that it is biosynthesized in humans.
- Abbreviations: Cys, C
- IUPAC name: 2-amino-3-sulfanylpropanoic acid
- Molecular formula: C3H7NO2S
- Molecular weight: 121.16 g/mol
primary structure of proteins → primarna struktura proteina
Primary structure of proteins is a sequence of defined amino acids in some protein.
dialysis → dijaliza
Dialysis is a method by which large molecules (such as starch or protein) and small molecules (such as glucose or amino acids) may be separated in a solution by selective diffusion through a semipermeable membrane. Through this kind of membrane dissolved particles pass and colloid dimension particles fall behind. For example, if a mixed solution of starch and glucose is placed in a closed container made of a semipermeable substance (such as cellophane), which is then immersed in a beaker of water, the smaller glucose molecules will pass trough the membrane into the water, while the starch molecules remain behind.
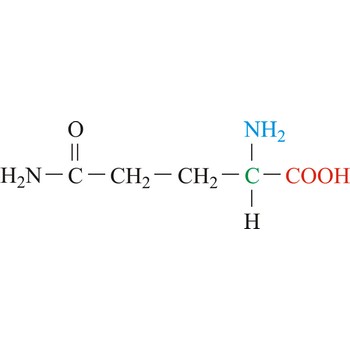
glutamic acid → glutaminska kiselina
Glutamic acid is an electrically charged amino acids. It is one of the two amino acids that contain a carboxylic acid group in its side chains. These acids play important roles as general acids in enzyme active centers, as well as in maintaining the solubility and ionic character of proteins. Glutamic acid is commonly referred to as glutamate, because its carboxylic acid side chain will be deprotonated and thus negatively charged in its anionic form at physiological pH. Glutamic acid is referred to as a non-essential amino acid because a healthy human can synthesize all the glutamic acid needed for normal body function from other amino acids.
- Abbreviations: Glu, E
- IUPAC name: 2-aminopentanedioic acid
- Molecular formula: C5H9NO4
- Molecular weight: 147.13 g/mol
glutamine → glutamin
Glutamine is neutral amino acids with polar side chains. It serves as an important carrier of ammonia and contributes it to the formation of urea and purines. Glutamine is not recognized as an essential amino acid but may become conditionally essential in certain situations, including intensive athletic training or certain gastrointestinal disorders. It is synthesized by the enzyme glutamine synthetase from glutamate and ammonia.
- Abbreviations: Gln, Q
- IUPAC name: 2,5-diamino-5-oxopentanoic acid
- Molecular formula: C5H10N2O3
- Molecular weight: 146.14 g/mol
protein → bjelančevina
Proteins are natural organic compounds of animal or herbal origin, essential in diet. They are natural polymers developed from a crowd of interconnecting monomers of amino acids, with relative molecular masses amounting up to a few million.
Schiff base → Schiffova baza
Schiff base is a class of compounds derived by the chemical reaction (condensation) of aldehydes or ketones with aromatic amines, for example
They were named after the German chemist Hugo Schiff (1834-1915).
glycine → glicin
Glycine is the smallest amino acid and is unique because it lacks a side chain. This gives it more conformational freedom than any other amino acid. Glycine is often found in turns and loops where other amino acids would be sterically unacceptable. Although it is formally nonpolar, it’s very small side chain makes no real contribution to hydrophobic interactions. Glycine is not essential to the human diet, as it is biosynthesized in the body from the amino acid serine.
- Abbreviations: Gly, G
- IUPAC name: 2-aminoacetic acid
- Molecular formula: C2H5NO2
- Molecular weight: 75.07 g/mol
Citing this page:
Generalic, Eni. "Amid." Croatian-English Chemistry Dictionary & Glossary. 29 June 2022. KTF-Split. {Date of access}. <https://glossary.periodni.com>.
Glossary
Periodic Table