urethane → uretan
Urethane is actually a misnomer as applied to polyurethane foam. It is a colorless, crystalline substance used primarily in medicines, pesticides, and fungicides. Urethane is not used in the production of urethane polymers or foams. The urethanes of the plastics industry are so named because the repeating units of their structures resemble the chemical urethane.
vinyl chloride → vinil klorid
Vinyl chloride, CH2=CHCl, is the monomer used in the synthesis of a polyvinylcloride.
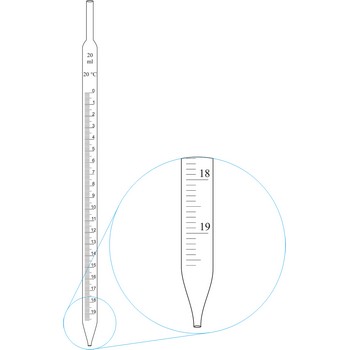
graduated pipette → graduirana pipeta
Graduated pipettes (Mohr pipette) have a scale divided into units of one and of 1/10th of a millilitre. Because of their wide necks it is less accurate than the volumetric pipette. They are used when taking volume of solutions in which accuracy does not have to be very high. By sucking in (with mouth, propipette or a water pump) the liquid is pulled in a little bit above the mark and the opening of the pipet is closed with a forefingertip. Outer wall of pipet is wiped and, with a slight forefinger loosening, the liquid is released until it reaches the mark 0. A pipette is emptied out by lifting the forefinger off and letting the liquid flow out of the pipette freely.
Graham’s law → Grahamov zakon
Graham’s law is the rates at whish gases diffuse are inversely proportional to the square roots of their densities. This principle is made use of in the diffusion method of separating isotopes. The law was formulated in 1829 by British chemist Thomas Graham (1805-1869).
graphite → grafit
Graphite is an allotrope of carbon. The atoms are arranged in layers as a series of flat, hexagonal rings. Graphite is a good conductor of heat and electricity. The layers cleave easily, making graphite useful as a solid lubricant. A process to make pure synthetic graphite was invented by the American chemist Edward Goodrich Acheson (1856–1931). The process consists of heating a mixture of clay (aluminum silicate) and powdered coke (carbon) in an iron bowl. The reaction involves the production of silicon carbide, which loses silicon at 4150 °C to leave graphite.
wavefunction → valna funkcija
Wavefunction (Ψ) is a mathematical function that gives the amplitude of a wave as a function of position (and sometimes as a function of time and/or electron spin). Wavefunctions are used in chemistry to represent the behaviour of electrons bound in atoms or molecules.
Haber process → Haberov proces
Haber process is an industrial process for producing ammonia by reaction of nitrogen with hydrogen:
The reaction is reversible and exothermic, so that a high yield of ammonia is favoured by low temperature. However, the rate of reaction would be too slow for equilibrium to be reached at normal temperatures, so an optimum temperature of about 450 °C is used, with a catalyst of iron containing potassium aluminium oxide promoters. The higher the pressure the greater the yield, although there are technical difficulties in using very high pressures. A pressure of about 250 atmospheres is commonly employed. The removal of ammonia from the batch as soon as it is formed ensures that an equilibrium favouring product formation is maintained. The nitrogen is obtained from air. Formerly, the hydrogen was from water gas and the water-gas shift reaction (the Bosch process) but now the raw material (called synthesis gas) is obtained by steam reforming natural gas.
The process is of immense importance for the fixation of nitrogen for fertilisers and explosives. It was developed in 1908 by German chemist Fritz Haber (1868-1934) and was developed for industrial use by Carl Bosch (1874-1940), hence the alternative name Haber-Bosch process.
haematite → hematit
Haematite is a mineral of iron(III) oxide Fe2O3. It is the most important ore of iron and usually occurs in two main forms: as a massive red kidney-shaped ore and as grey to black metallic crystals known as specular iron ore. Haematite is the major red colouring agent in rocks; the largest deposits are of sedimentary origin. In industry haematite is also used as a polishing agent (jeweller’s rouge) and in paints.
hafnium → hafnij
Hafnium was discovered by Dirk Coster (Denmark) and Georg Karl von Hevesy (Hungary) in 1923. The origin of the name comes from the Latin name Hafnia meaning Copenhagen. It is silvery, ductile metal. Exposed surfaces form oxide film. Resists alkalis and acids (except HF). Toxic. Metal ignites and burns readily. Hafnium is obtained from mineral zircon or baddeleyite. Used in reactor control rods because of its ability to absorb neutrons.
Citing this page:
Generalic, Eni. "Zemljina kora." Croatian-English Chemistry Dictionary & Glossary. 29 June 2022. KTF-Split. {Date of access}. <https://glossary.periodni.com>.
Glossary
Periodic Table